Did you know that three Hoosiers appeared on national tickets for president or vice president in 1916? The Democrats ran Thomas R. Marshall of Columbia City for re-election in 1916 alongside President Woodrow Wilson. The Republican Party tabbed President Theodore Roosevelt‘s former vice president Charles W. Fairbanks of Indianapolis as the running mate of GOP presidential nominee Charles Evans Hughes. You may ask, who was the third Hoosier running for president or vice president in 1916? If you guessed Terre Haute-native Eugene V. Debs, you would be wrong. After being the Socialist Party presidential nominee four times from 1900-1912, Debs sat out the 1916 campaign before running again (from prison) in 1920.
The third Hoosier and national party candidate in 1916 was a man who is not well-known today, but was a former governor of Indiana, and an influential leader in the prohibition movement. As a third-party challenger, J. Frank Hanly ran as the Prohibition Party presidential nominee during the 1916 election. Founded in 1869, the Prohibition Party campaigned for laws to limit or ban the sale and manufacture of intoxicating liquors. The party nominated candidates for office, but only found real success with local elections. For Hanly, his candidacy in 1916 served as the culmination of decades of advocacy for making Indiana, and the nation, dry as a desert.

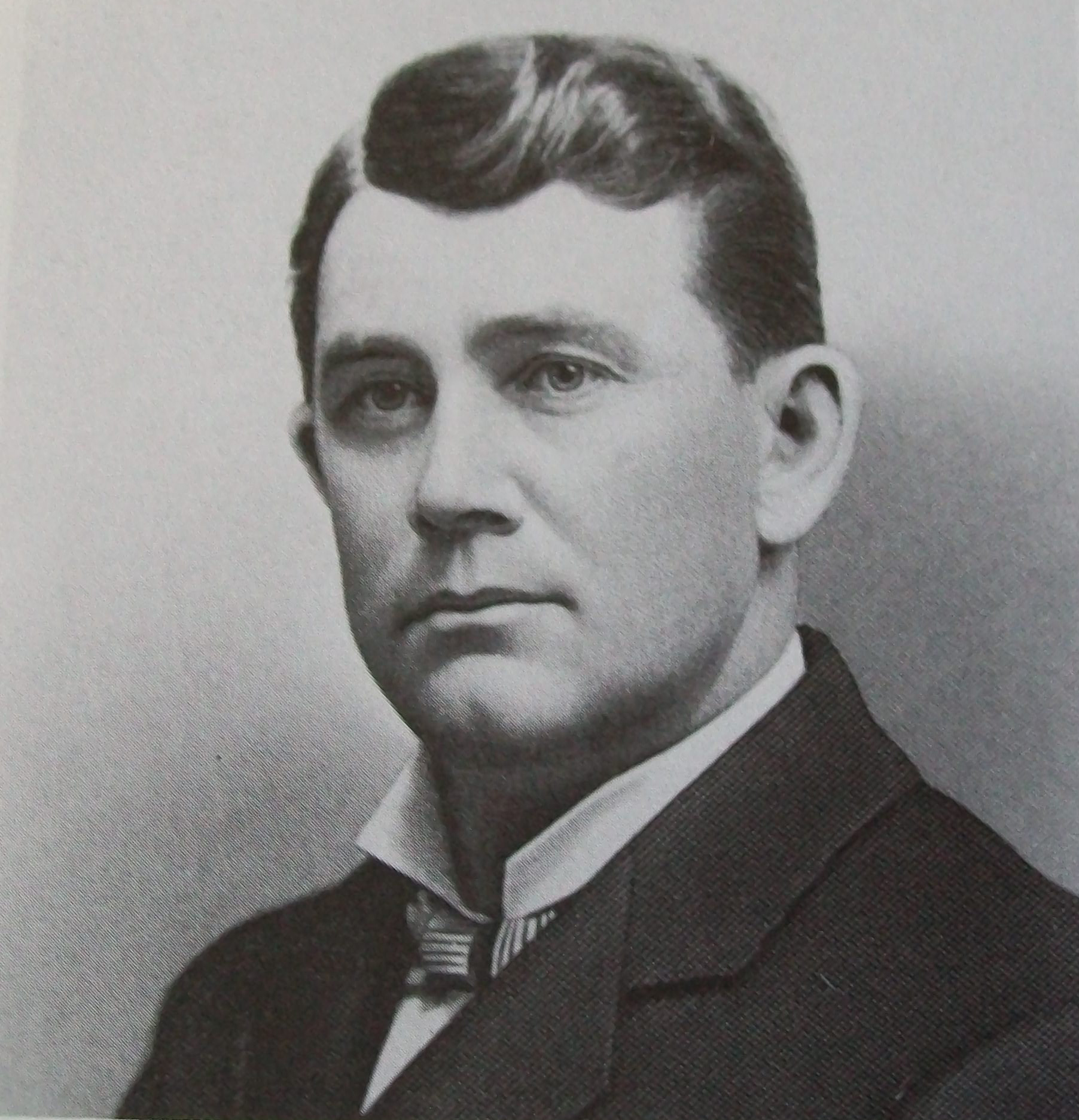
According to a 1904 profile in the Indianapolis News, James Frank Hanly was born on April 4, 1863 in Champaign County, Illinois. His early life exemplified the rough-hewn stereotype that politicians of the era both yearned to have and exploit when useful. As the News wrote, “The world had nothing to offer the cabin boy but poverty. His parents lived on a rented place and sometimes the Hanly’s wondered where the sustenance of coming days was to come from.” Hanly, described as a bookish child, reveled in debate during his schoolhouse days and had “victory perched on his banner very often.” With his mother blinded early in his life and the family thrown into even more intense poverty, Hanly was sent to live with friends of the family in Williamsport, Warren County, Indiana.
He held odd-jobs throughout his early years in Indiana, most notably ditch digging and teaching, before gaining an opportunity from a local judge named Joseph Rabb. Rabb provided Hanly with the tools to take the bar exam. After passing the exam, Hanly began work at Rabb’s office. Nearly two years later in 1890, he founded a law office with partner Ele Stansbury. Equipped with skills of law and oratory, Hanly was a natural fit for the role of public service. He was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1894 and served one term; his reelection was dashed due to redistricting. After some considerations for a seat in the U.S. Senate, Hanly decided to run for governor of Indiana in 1904 and won, defeating Democrat John W. Kern by 84,000 votes, according to the Plymouth Tribune.


Hanly served as Indiana’s Governor from 1905-1909 and his tenure was marked by a controversial fight over Hanly’s central political issue: the sale of alcohol. He committed his tenure to enacting a stronger form of public policy in regards to the liquor traffic. In an op-ed for the Jasper Weekly Courier, Hanly wrote:
Personally, I have seen so much of the evils of the liquor traffic in the last four years, so much of its economic waste, so much of the physical ruin, so much of its mental blight, so much of its tears and heartache, that I have come to regard the business as one that must be held and controlled by strong and effective laws.

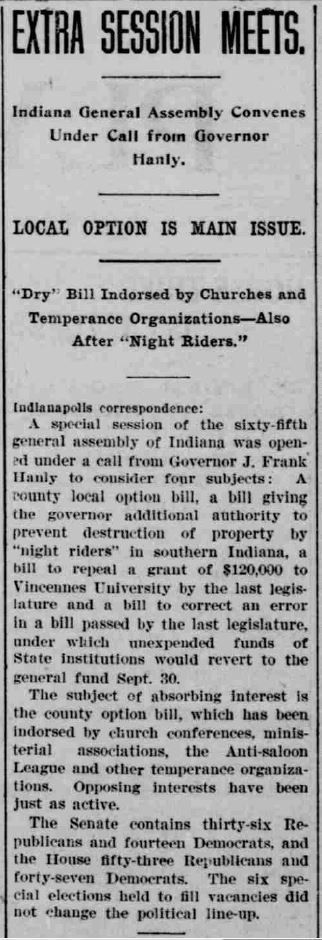
The type of “strong and effective laws” that Hanly wanted came in the form of a “county local option bill,” which Hanly foisted upon the Indiana General Assembly via a special session. This law strengthened the intent of the Nicholson Law, which required extended waiting periods for liquor licenses. Hanly saw this as the first step towards state-wide prohibition, but his opposition saw it as an opportunity. Due to his heavy-handed use of executive power during 1908, the Republican gubernatorial candidate James E. Watson was easily defeated by the Democratic challenger, Thomas Marshall.
Hanly was undeterred. He reaffirmed his position against alcohol in a rousing speech at the 1908 Republican National Convention reprinted in the Indianapolis News. Concerning the liquor traffic, Hanly declared:
I hate it as Abraham Lincoln hated slavery. And as he sometimes saw in prophetic vision the end of slavery and the coming of the time when the sun should shine and the rain should fall upon no slave in all the republic, so I sometimes seem to see the end of this unholy traffic; the coming of the time when, if it does not wholly cease to be, it shall find no safe habitation anywhere beneath Old Glory’s stainless stars.
To Hanly, the sale of alcohol equaled slavery in its immorality, and akin to his political hero, viewed his indictment of alcohol as righteous as Lincoln’s position on slavery (at least on the surface).
Over the next eight years, Hanly dedicated himself to his cause with a near-religious fervor. He wrote and published pamphlets calling for stricter laws for state liquor trafficking and for nation-wide prohibition. He also formed an organization called the Flying Squadron Foundation that routinely gave speeches throughout the country in defense of outlawing alcohol. He also founded a prohibitionist newspaper, the National Enquirer (not to be confused with the supermarket tabloid).
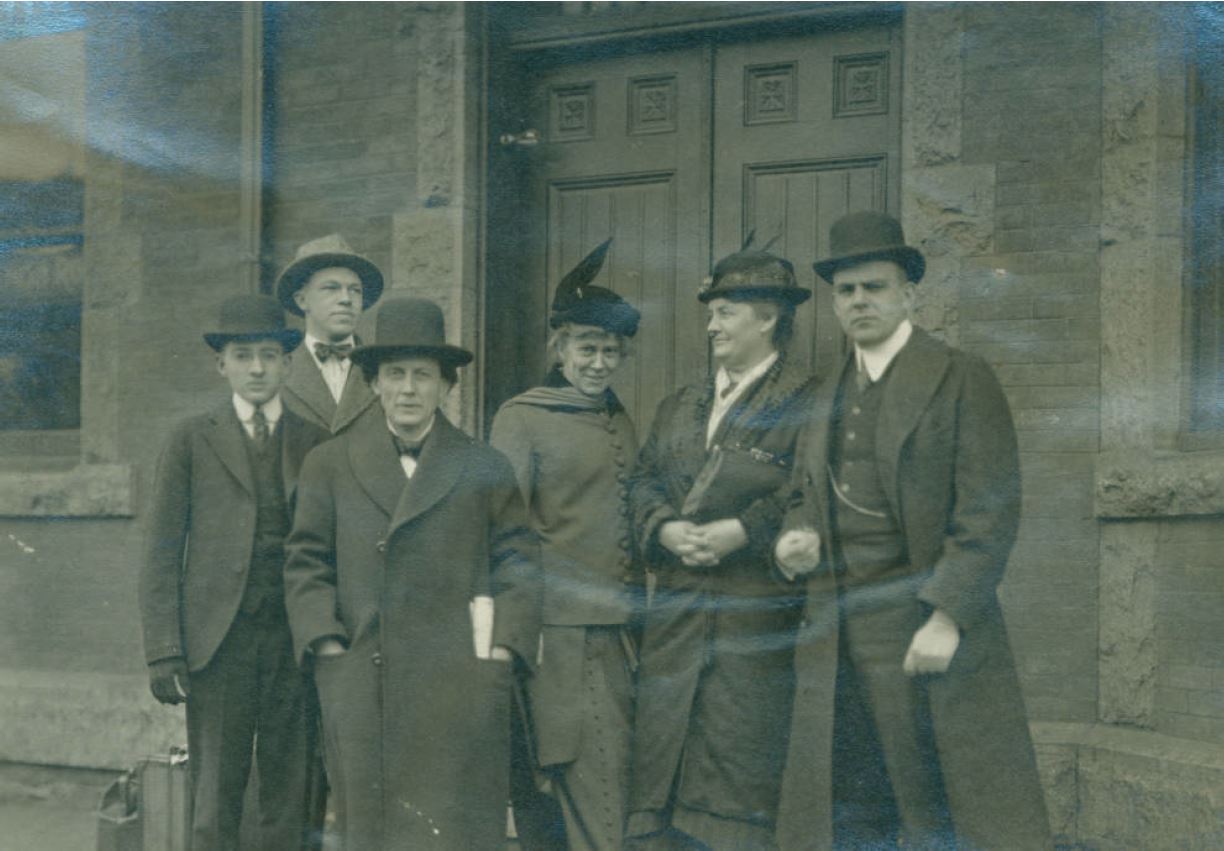

All of his activism proved valuable by the election of 1916. Originally, Hanly received the Progressive Party’s nomination for governor, after he ran unopposed in the March primary. Despite support from the party and the voters, Hanly felt ambivalent about his nomination. As the Indianapolis News reported, Hanly “spent nothing and made no promises when a candidate before the primary for the Progressive nomination as Governor.” The Progressive Party, in some respects, was a poor fit. Even though Hanly alienated himself from mainstream Republican politics due to his strict prohibitionist views, his dedication to fiscal conservatism and limited government did not align with the Progressives. While Hanly internally debated accepting the Progressives’ gubernatorial nomination, another political party began recruiting him for an even higher office.

In June 1916, Hanly abandoned the Progressive Party, and declined the nomination for governor. Later that summer, he received the Prohibition Party nomination for President of the United States. The Indianapolis News and the Indianapolis Star reported that Hanly would gladly accept this charge only after the party decided to abandon a plank in their party platform supporting “initiative, referendum, and recall” elections, which Hanly saw as anathema to his limited government views. The party acquiesced to Hanly’s demands, which later drew criticism from an editorial in the Indianapolis Star and later reprinted in the Jasper Weekly Courier. On the day of his nomination, Hanly reiterated his resolve to the cause of Prohibition and argued that “legislative enactments, administrative action, judicial decision and constitutional amendment—all shall be used for its [alcohol’s] dethronement.” In eight short years, Hanly went from Republican, to reluctant Progressive, to ardent Prohibitionist.

His disassociation with the Republican Party led to a fairly embarrassing episode reported in the August 15 issue of the Indianapolis News. The paper wrote that, “state officials are wondering how a picture of J. Frank Hanly got on the wall in [Ed] Donnell’s office [at the state printing board’s office]. Mr. Hanly, former Governor of Indiana, is now the nominee for President on the Prohibition national ticket.” A little over a week later, on August 28, the portrait disappeared. When asked how it left, Donnell “referred questioners to [J. Roy] Strickland, who disclaimed all knowledge of any theft, other than to declare that he understood the picture had been confiscated by the Democratic state committee.” The installation and later removal of the painting remains a mystery, but this story exemplified one conclusion that many political observers were making about the Prohibition Party candidate: the major parties were done with him too.

Hanly’s presidential campaign began later that August with an announcement from Hanly and his Vice-Presidential running mate, Dr. Ira Landrith, that they would conduct a “two-months’ tour of the country, will stop at approximately 600 towns.” The slogan for their campaign was “A Million Votes for Prohibition.” As part of the Prohibition Party’s push for a million votes, Hanly heavily criticized the major party candidates, Republican Charles Evans Hughes and incumbent Democratic President Woodrow Wilson. On the issue of prohibition, Hanly said that “President Wilson has not changed his mind on the liquor question, not in the last six years, at least, but we know that during these six years he has changed his mind on every other question which has come before him.” Of Hughes, Hanly remarked that the Republican nominee “stands for nothing.” By supposed contrast, Hanly and Landrith stood for women’s suffrage, an eight-hour work day, environmental protections, and military preparedness in line with the Monroe Doctrine alongside its desire to end the liquor trade.

By November 1916, the Prohibition Party appeared confident in their chances for some electoral success. The Indianapolis News covered their claims of success at a rally in Auburn, Indiana. “Ira Landrith, the vice-presidential candidate,” the News reported, “declared there now are 167 electoral votes in “dry” states; that next year there will be 200, and in 1930 there will be 300.” Their optimism was misplaced, for the election returns told a different story. Hanly and Landrith only captured 221,302 votes, or only 1.19 percent of the popular vote. They neither secured the one million votes they campaigned on, nor picked up a single electoral vote. Wilson won the election with 277 electoral votes and 49.25 percent of the popular vote. The Indianapolis News highlighted that the level of the vote for the Prohibition Party had dropped in Marion County alone by nearly 500 votes, from 1241 to 744, and throughout the State of Indiana, Hanly only garnered 16,680.

Of the returns, Hanly was delighted despite his small showing at the polls. He stated, “I believe that of all the presidential candidates at the last election, I am the happiest. The returns were no disappointment to me.” Despite the Prohibition Party’s electoral loss, the prohibition movement made great strides after the election. The News wrote“More than one-third of the people of the whole nation now live in territory where prohibition will be effective.” After the election Hanly remained an active prohibition proponent. He played a key role in lobbying for the state-wide prohibition of alcohol by 1918, two years before the 18th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution mandated prohibition across the United States. Hanly celebrated its implementation by introducing National Dry Federation President William Jennings Bryan at a meeting in Indianapolis.
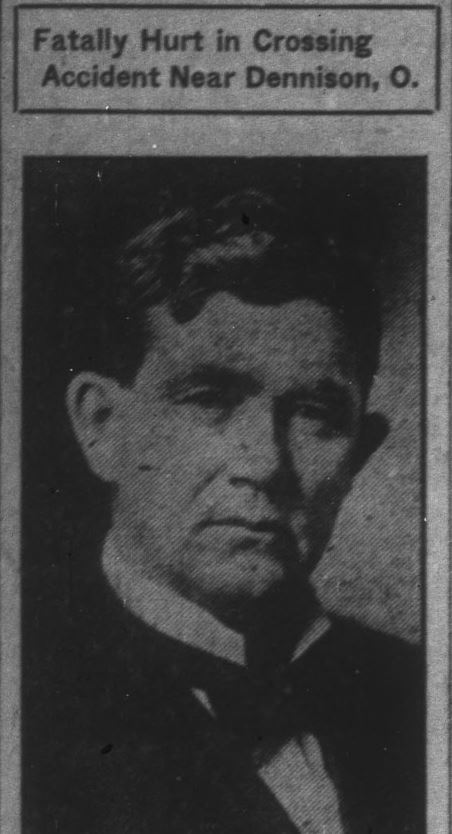

Hanly’s lifelong efforts advocating for prohibition came to an end with his untimely death on August 1, 1920, at the age of 57. He had been “fatally injured in an automobile accident near Dennison [Ohio],” reported the Indianapolis News. His funeral was held at Meridian Street Methodist Episcopal Church and he was buried in Williamsport, Indiana. In a eulogy by Indianapolis Phalanx publisher Edward Clark, Hanly was hailed as a “a national leader in the greatest moral and political reform of the century.” Clark concluded, “[Hanly] has ended life’s combat and laid down the weapons he wielded so heroically and so valiantly.”
Historian Jan Shipps argued that the choices Hanly made during his political career may have been pure opportunism, the mark of a true believer, or somewhere in the middle. The last argument seems to be the most accurate, because Hanly appeared to be a bit of both, at least in the press. He was an astute, masterful politician who used the workings of power to achieve his own prerogatives. At the same time, he was a deeply religious man whose moral judgement animated him to act as a crusader against alcohol. As Edward Clark’s eulogy intimated, Hanly knew that “to announce himself as a party prohibitionist meant unpopularity, scorn, ridicule, abuse, and political oblivion—but he hesitated not.” While he never saw the effects of Prohibition, both good and bad, in his state or in the country, Hanly’s contributions to the movement should not be neglected in our understanding of the era.





![Instep-arch support patent [marketed as Foot-Eazer], Publication date April 25, 1911, accessed Google Patents](http://blog.newspapers.library.in.gov/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/1911-Instep-Patent.png)
![Elevated Railroad Station at East Madison Boulevard and Wells Street [near Scholl's building] November 1, 1913, Chicago Daily News Photograph, Chicago History Museum, accessed Explore Chicago Collections, explore.chicagocollections.org/image/chicagohistory/71/qr4p14f/](http://blog.newspapers.library.in.gov/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/train-station-at-Wells-and-Madison-CHicaho-History-Museum-300x243.png)