As a historical researcher, I spend much of my time thinking about what the world was like one hundred years ago. Remnants of this world are seen particularly in the institutions that have survived throughout the decades. One such institution is Indiana University, which will celebrate 200 years in 2020. In my work as a researcher for the Office of the Bicentennial, I have come across many stories that add vibrant details to the seemingly-distant world of one hundred years ago.
Hoosiers in this world faced adversity, rose above challenges, and broke glass ceilings. This was the case at the School of Commerce and Finance (today’s Kelley School of Business), which was formed during IU’s centennial in 1920. The school was founded during a time of transition. World War I had just concluded, the “roaring twenties” were on the horizon, and economic catastrophe loomed on the periphery. Blanche McNeely Wean, the first woman to be admitted into the School of Commerce and Finance, witnessed this transition. She navigated through it as a widowed working mother of three during the Great Depression.

A Bloomington native, McNeely bridged “Town and Gown” by enrolling at Indiana University in 1919 to study education. She grew up in an entrepreneurial family. Her father ran a grocery store in town, where McNeely worked throughout her childhood. She would later consider this to be a core experience that sparked her interest in business. Her duties ranged from “driving the cow home and back from Dunn Meadow at 10th street for milking” to cold calling residents who might buy overstock peaches from the store. In 1919, McNeely’s father, Homer Clark McNeely, opened and operated the Yellow Cab Co. of Bloomington.
Although McNeely studied education at IU, she took nearly all of the preliminary business courses she could without being a business student. She shared with a male professor that she had ambitions to join the business world, stemming from her work experience. The professor told her that business was a “man’s world” and suggested she stick to education. Following this rejection, she turned to School of Commerce and Finance secretary Sarah Kirby, who encouraged her to ask Dean Rawles for admission into the school. In her memoir, published in 1996, Blanche Accounts, she credited her 1922 admission to the school to Kirby. She recalled “In his very formal way he [Dean Rawles] looked me over as if he had not seen me before and said, ‘Well Blanche, you have taken all the preliminary courses. I cannot see why not.’”

After that exchange, McNeely became the first woman admitted into the business school. Anna Hasler and Athleen Catterson transferred from the University of Chicago and were admitted concurrently. The three women graduated together in 1923, making them the first women to graduate from the Indiana University School of Commerce and Finance—and McNeely was the first female graduate to have completed all of the degree requirements at IU. Notable classmates included: Herman B Wells, first chancellor of Indiana University; Ernie Pyle, Pulitzer Prize-winning World War II journalist; and Hoagy Carmichael, famed singer and songwriter. McNeely wrote later in her memoir that she did not “remember that the men in our classes treated us differently. We studied together and served on committees together.” When not studying, McNeely played tennis, served on the YWCA board, and went on walks with a friend.
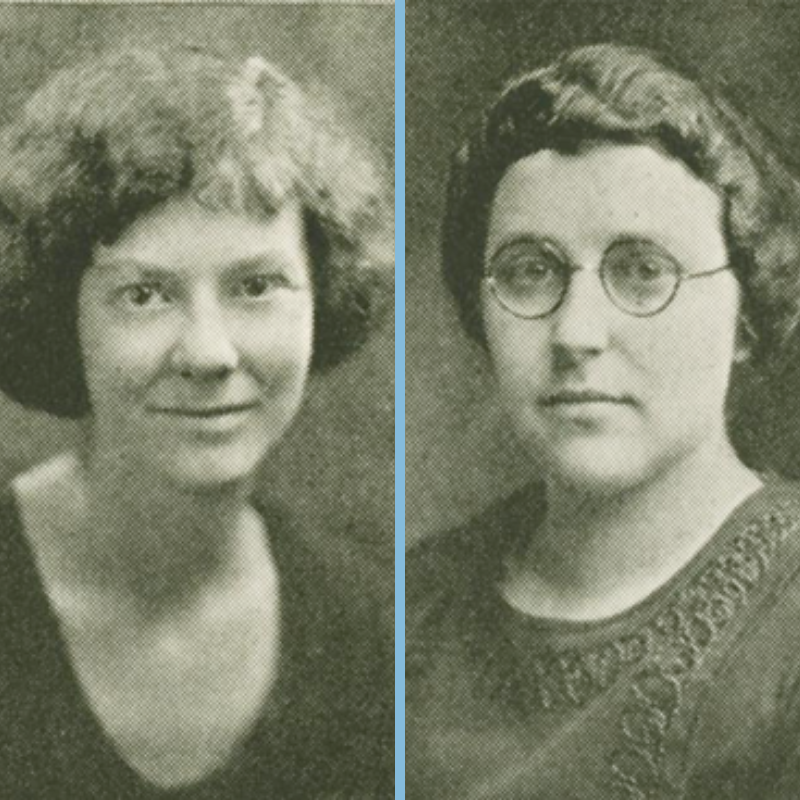

The female graduates’ success would likely not have been possible without women like Lulu Westenhaver and Sarah Kirby, who had been instrumental to the education and administrative efficiency of the school. Kirby had been a secretary when the school began and served under six different deans throughout thirty-eight years at IU. She would go onto make history in 1942 when she became the first woman to be elected an honorary member of the school’s honor society, Beta Gamma Sigma. Westenhaver came to IU in 1920 as a stenography instructor in the new business school. She served alongside Kirby as a secretary during several of those years and was a key sponsor of student groups, especially for female students. Two such groups were Omicron Delta and Chi Gamma, both of which were sponsored by Westenhaver and Kirby, as well as Professor Esther Bray.
After graduation, McNeely moved to Lafayette to begin working as a teacher, and married Francis Wean in 1926. In 1930, Francis unexpectedly passed away, widowing McNeely Wean and leaving her to raise three daughters under the age of three at the onset of the Great Depression. McNeely Wean wrote in her memoir about the time:
The shock of his death was almost more than I could bear. I found it hard to make decisions, except one, and that with emphasis. Friends without children asked whether I would consider giving one of my children to them. I was indignant and answered, ‘Why? I have my education and ability to work. I can take care of my own children.’
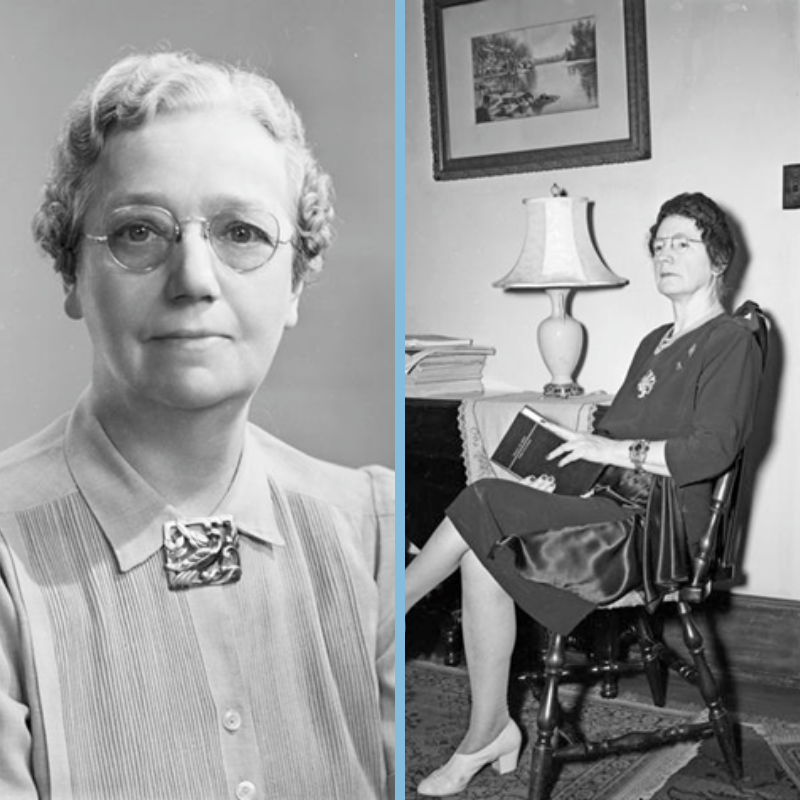

Instead, McNeely Wean moved back to Bloomington to substitute teach for Lulu Westenhaver, who was on medical leave. In Blanche Accounts, she describes that moving back to Bloomington was like a homecoming: “It was a time to renew old friendships with Herman Wells, Mr. Pritchett, Joe Batchelor, Esther Bray, and Miss Kirby.”
While teaching at IU, McNeely Wean worked on obtaining her master’s degree and was offered a trial position as the head of the business department at Central Normal College in Danville (later renamed Canterbury College). Rather than uprooting her family, she woke up every Monday morning at 2:30 a.m. to drive to Danville and teach a 6:00 a.m. class. In 1932, McNeely Wean received an official offer from Central Normal College to head the business school, serve as the dean of women for the college, and serve as the student newspaper’s advisor—with the expectation that she would first graduate with her master’s degree from Indiana University that same year. She graduated with a Master of Arts degree in May 1932, and then moved her family to Danville. She continued at Central Normal College for fifteen years while also working as an accountant for outside businesses.

In a 1982 interview with The Indianapolis News, McNeely Wean recalled how she worried and cared for Central Normal College students during the Great Depression: “We ate lots of hamburger, Spanish rice, and ‘hot dog gravy.’ I diced up the hot dogs to make it go further in milk gravy. That’s what the students called it. I had to do it because we never knew how many would show up.”
In the meantime, all three of her daughters earned their undergraduate and graduate degrees at Indiana University. In 1947, McNeely Wean left Central Normal College and started her own accounting firm out of her home. She ran the business on her own with a few employees until her grandson, Ted Andrews, joined the firm, which was rechristened Wean, Andrews, & Co. in 1980.
After McNeely Wean passed away in 1999, Andrews described his grandmother to The Indianapolis News, noting “She was a workaholic. She’d scold clients who were retiring [saying], ‘What do you mean you are retiring, you are only 75!’” McNeely Wean shattered glass ceilings for many women aspiring to careers in business, and contributed greatly to the education of business students at Central Normal College. In an interview with The Indianapolis Star in 1987, McNeely Wean expounded on the importance of ability rather than appearance, stating “I judge an individual on his or her merits. It’s not a matter of color or race, of women or men. It’s a question of ‘the job has to be done and let’s do it.’ If you can do it better than the other fellow, fine.”

Although McNeely Wean was instrumental in proving that women could succeed in the business world, even without the support of a husband, business was not yet a widely-accessible career choice for many women, especially in the world of higher education. Some women who pursued business careers turned to teaching the subject, such as business professor Esther Bray, who graduated from Indiana University in 1925. She returned to IU in 1937 to teach in the business school, where she would prove to be a force of nature and a fierce advocate for her students. Bray was the only woman on the business school faculty for many years, as instructors were not considered “faculty” throughout the university at the time. In later interviews, Bray recalled that departmental meetings were often opened with “Mrs. Bray and gentlemen, shall we come to order?” She was active in her community as a volunteer for nonprofit and political organizations. When Bray passed away in 1999, a faculty memorial resolution was approved in her honor, calling Bray a “role model for women” and “had the time been right, she would have been a congresswoman.”
Both McNeely Wean’s and Bray’s lives are testaments to the growing options for young, ambitious women who came of age during the 1920s and 1930s. Without the context of supporting figures such as Sarah Kirby and Lulu Westenhaver, the story of Blanche McNeely Wean may have been very different. Their trajectory highlights how women built communities for themselves in the male-dominated world of academia. The roots of these communities are visible today at IU through groups organized for female business students.

* While business classes had been offered at the university for years, they were dispersed throughout different departments. The creation of the School of Commerce and Finance placed business courses into the school instead of departments.
FURTHER READING
Indiana University Arbutus, 1923, 1937, 1941, and 1971.
Esther Bray, Indiana University Memorial Resolution, Bloomington Faculty Council Circular, Indiana University.
Blanche McNeely Wean, Blanche Accounts: A McNeely Family Story (Danville, IN: self-published, 1996).
Lulu Westenhaver, Indiana University Memorial Resolutions, Bloomington Faculty Council, 1959.
NEWSPAPER ARTICLES:
“Honored at IU,” The Indianapolis News, May 9, 1942.
“Instructor at IU for 28 years Dies,” The Courier-Journal (Louisville), April 23, 1959.
Mary Ann Butters, “Dinner to Focus Spotlight on Mrs. Bray,” The Indianapolis Star, March 2, 1972.
Ruth Chaney, “Congressman’s Wife has Life of Varied Interests,” The Daily Journal (Franklin, IN), October 6, 1964.
Mike Ellis, “Book to Be the Keeper of the Fate,” The Indianapolis News, September 9, 1987.
Lynn Hopper, “Awash in Fond Memories,” The Indianapolis Star, February 27, 1998.
Jean Jensen, “She’s at Home in Business,” The Indianapolis News, December 29, 1982.
Suzanne McBride, “An Education in Higher Learning: 21-Year Board Member Sees Progress,” The Indianapolis News, June 22, 1992.
Claude Parsons, “Esther Bray is Serving 16th Year on Higher Education Commission,” The Indianapolis News, April 9, 1987.
Beth Rosenberg, “Blanche Wean, 86, Still Accountable,” The Indianapolis Star, September 24, 1987.
Beth Spangle, “Blanche McNeely Wean Left a Legacy for Town and Family,” The Indianapolis News, June 9, 1999.
Lotys Benning Stewart, “They Achieve,” The Indianapolis Star, June 30, 1946.
Bill Strother, “Esther Bray Recalled as Leader, Teacher,” The Herald Times Online, December 23, 1999.
Jodi Wetuski, “Her Varied Life Adds Up,” The Indianapolis Star, July 17, 1996.
