This is Part Two of a two-part post.
In Part One we presented the text for a new marker at Sycamore Row in Carroll County, Indiana which will replace a 1963 marker that was recently damaged. This new text focuses less on unverifiable legends about sycamore trees sprouting along the Old Michigan Road told by the original marker text, in order to make room for the history of the Potawatomi that is intertwined with the creation of the road. The new marker still tells the story of the trees and their preservation—history that the local community values—but it now also hints at the complex history of the injustices the U.S. perpetuated against the Potawatomi. The marker’s limited space doesn’t allow IHB to tell the larger story, so we are expanding on that here. This story of injustice, genocide, and survivance* is often lost by historians presenting a version of Indiana history as a march towards progress. To truly understand our state’s history and the atrocities perpetuated in the name of that “progress,” we must re-center the Potawatomi and other indigenous People in that story.
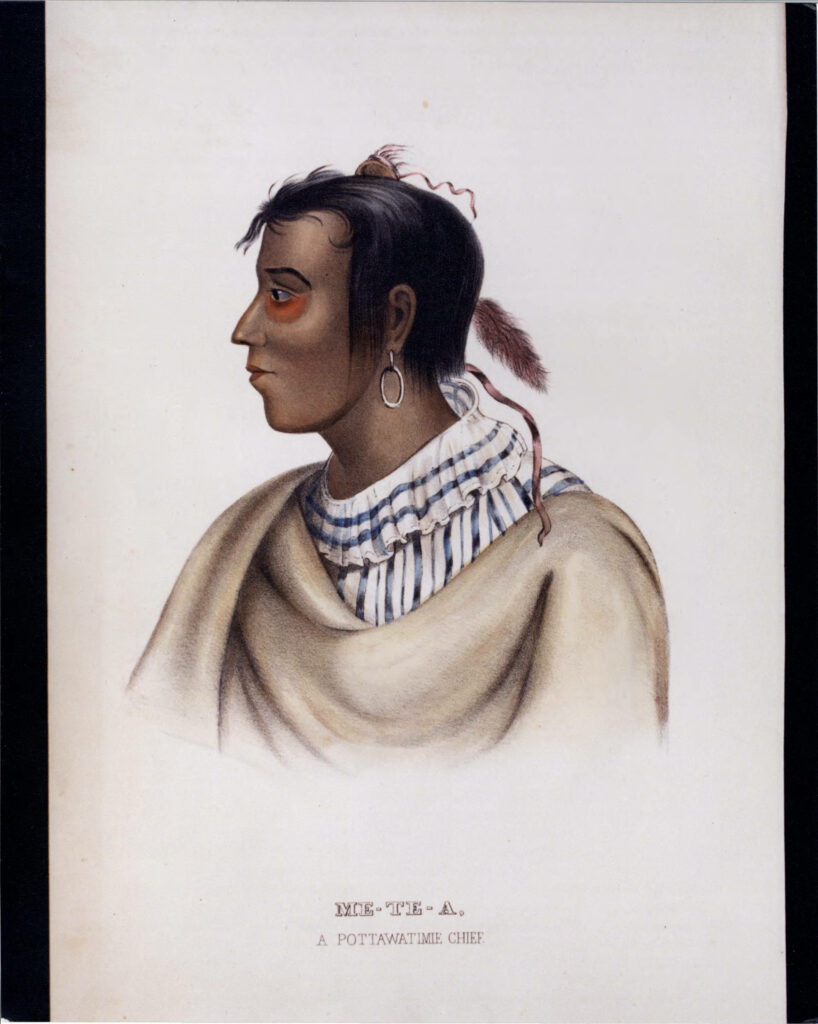

Potawatomi Removal, Genocide, Resistance, and Survivance
The Potawatomi lived in the land now called the United States for centuries before European people settled here. By the 13th century, but likely earlier, the Potawatomi (then the Bodewadmi) were living in what is now Eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. They were one of a group of Algonquin-speaking tribes united with the Odawa (Ottawa) and Ojibwe (Chippewa) into a collective called Nishnabe, which still exists to this day. (Learn more about the history of the Potawatomi through the Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center). [1]
Over the centuries, the Potawatomi migrated inland as their prophets had predicted, settling around the Great Lakes Region. Potawatomi men fished and hunted deer, elk, and beaver. Potawatomi women maintained areas of cultivated crops, which have usually been referred to as gardens, but according to historian and professor Jeffrey Ostler, these plots should be recognized as farms. Some of them were as large as 100 acres or more, surrounded by fences and producing bounties of corn, beans, pumpkins, and wheat. According to the Milwaukee Public Museum, in the winter, the Potawatomi lived in small groups coordinated with specific hunting territories. In the spring, they gathered in large villages for communal hunting and food production. Required to marry outside of one’s own community, Potawatomi people created a network of social bonds through these marriages. Trade also strengthened these relationships between communities. The Potawatomi did not have a chief that spoke for the entire tribe, but instead, village heads who met in council with the leaders of other Potawatomi communities to make decisions through intricate diplomatic negotiations. Recognizing this decentralized system of government is important in understanding the duplicitous treatymaking explained later in this post.[2]
After clashes with the Iroquois in the 17th century, the Potawatomi lived peacefully, and for a time, enjoyed a mutually beneficial partnership with French trappers in the 18th century, according to John Boursaw, a member of the Citizen Potawatomi Nation and former director of the Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center (CPCHC). However, when hundreds of Potawatomi men joined the French to fight in the Seven Year’s War starting in 1757, some returned carrying smallpox. The Great Lakes Potawatomi were devastated by the epidemic. They were also impacted by the defeat of the French by the British in 1763, with different indigenous communities supporting the French, the British, and the fledgling United States. [3]
After the American Revolutionary War, the new United States government began pushing West, surveying and selling land. The U.S. government worked towards this end through military action, economic pressure, treaty negotiations, and sanctioned genocide in order to make space for white male settlers to farm the land. White squatters and militias also murdered indigenous peoples for their land. (Learn more about 18th and early 19th-century removal and persecution of indigenous peoples in the Midwest). [4]
The Potawatomi resisted U.S. expansion in multiple ways. For example, they fought against the U.S. in the Ohio Indian Wars, they joined Tenskwatawa and Tecumseh’s resistance after 1805, and allied with the British during the War of 1812. Many of the gains the Potawatomi made were lost after the British defeat when the crown ceded its midwestern lands to the U.S. [5]

By 1825, the state and federal governments were applying severe pressure on the Potawatomi to leave Indiana. The government systematically worked to extinguish Indian-held land titles negotiated through previous treaties. And there was always the threat of violence, both from encroaching white settlers and the U.S. military. The state government viewed the Miami lands as blocking the development of the Wabash, and Erie Canal and Potawatomi lands as blocking the creation of the Michigan Road. Indiana legislators pushed for removal of both peoples. [6]
U. S. Government Strategies for Indigenous Land Theft
The U.S. government had several strategies for forcing Native Peoples to cede land. According to Blake Norton, curator of the Citizen Potawatomi Nation Cultural Heritage Center,
U.S. leaders exploited tribal autonomy by making treaties with individual villages, rather than large regional bands. This tactic helped divide communities, as gifts and annuities were leveraged against those unwilling to go. [7]
The loss of land in areas where Native Peoples were removed impacted those who remained. They could no longer self-sufficiently live off the land and they became reliant on annuities while being pushed into debt. This was intentional. As Thomas Jefferson explained to William Henry Harrison in an 1803 letter:
We shall push our trading houses, and be glad to see the good and influential individuals among [Great Lakes Indians] run in debt, because we observe that when these debts get beyond what the individuals can pay, they become willing to lop them off by a cession of lands. [8]

By 1826, the United States government tasked three commissioners, including General John Tipton, an Indian agent working out of Fort Wayne, with securing land cessions from the Potawatomi. The proposed treaty would make way for what would become the Michigan Road. John Tipton would benefit professionally and financially from this suppression and disenfranchisement of the Potawatomi—a microcosm of the larger story about the United States building its empire on the stolen lands of Indigenous People. [9]
The U.S. commissioners tasked with treatymaking presented these land cessions to the bands as a way for the Potawatomi to pay off debts claimed against them. Again, the Potawatomi only owed these debts to traders and Indian agents because they had been forced from their traditional livelihoods—an intentional part of the larger government plan to remove them. In addition to clearing accrued debt, the U.S. commissioners also promised the Potawatomi a group of eighty-six land reserves where they would hold title. [10]
According to educator and historian Juanita Hunter, other techniques used by government officials to take the Potawatomi ancestral land included: negotiating with members not authorized to speak on behalf of a tribe while referring to them in treaties as “chiefs;” making treaties with rival tribes with no claims to the land; introducing alcohol into negotiations; and encouraging encroachment of settlers onto Indian land. The threat of military intervention was also ever present. [11]
“Deceitful Lips”: The 1826 Treaty with the Potawatomi

Under these conditions, twenty-four bands of Potawatomi gathered near the Mississinewa River in Wabash County, Indiana, on October 5, 1826. Bands of Miami were also present for similar negotiations. The commissioners began the proceedings by pushing for complete removal. They painted a bright picture of life beyond the Mississippi River and promised white settlement would never touch them there. Commissioner Lewis Cass, also governor of Michigan Territory, claimed:
We are authorized to offer you a residence there, equal in extent to your land here, and to pay you an annuity, which will make you comfortable, and to provide the means of your removal . . . You will then have a country abounding in game . . . Your Great Father will never suffer any of his white children to reside there, for it is reserved for the red poeple [sic]. It will be yours, as long as the sun shines, and the rain falls. [12]
These were empty promises, and the indigenous leaders knew it. They responded that the white men had caused the problems that the indigenous bands were now facing. They explained that they could not go West because there were already people living there—other native groups with their own claims to the land. Speaking for himself and Potawatomi leader Aubanaubee, Miami leader Legro stated:
You speak to us with deceitful lips, and not from your hearts. You say the game is going away and we must follow it; who drove it away? . . . Before you came, the game was plenty . . . We own there is game there, but the Great Spirit has made and put men there, who have a right to that game, and it is not ours. [13]

The secretary documenting the details of the treaty negotiations recorded no more of the proceedings, which continued for several days. It is clear from Legro’s words that they did not want to cede more land, and yet they ultimately did. The terms of the 1826 Treaty with the Potawatomi can give us some clues to what happened. [14]
Article I provided over $30,000 in goods to the Potawatomi. With this provision, white stakeholders profited twice. The traders providing the goods received payment from the government, while the government would turn around and sell the land to settlers for profit. These annuities also furthered Potawatomi dependence on the U.S. government, which would ultimately push them further into debt. [15]
Article I also provided $9,573 in payments for debts that traders claimed the Potawatomi owed them. In a blatant conflict of interest, it was Tipton, a commissioner who regularly befitted from suppressing and removing the Potawatomi through his speculative land dealings, who decided (in his role as Indian agent) just how much debt the Potawatomi owed. [16]
The Potawatomi pushed back for larger payments and succeeded to some extent. They were able to negotiate for an annual payment of $2,000 over a period of twenty-two years with additional money provided for education and for a mill built at government expense. But Legro’s prediction was correct. The government spoke with “deceitful lips,” and the Indigenous Peoples would not receive twenty-two years of payments. Instead, the government would force them off their ancestral land within only twelve years. [17]
Article II of the treaty was even more disastrous for the Potawatomi. In this section, which included the provisions for the future Michigan Road, the treaty makers were careful not to define the route of the road. The Potawatomi thought they were ceding a mile-wide strip of land in a straight, contiguous line for the route. Even Tipton, in private correspondence, admitted that this was also his understanding of the provision. He told the land office commissioner Elijah Hayward:
I feel bound to state to you, and through you to the President, that, at the time of negotiating this treaty, these Indians did not understand that their land, not embraced within the bounds of the tract then ceded, would be required to construct this road, except where the road passed through the country retained by them . . . This was also my understanding of this treaty at the time it was made. [18]
Instead, when the State of Indiana began surveying the route, they chose a circuitous route around swamps and other undesirable land. The Potawatomi resisted this change, stopping and confronting surveyors, and delaying the road-building operation. Other councils were held between commissioners and some Potawatomi members while settlers and government officials continued to press for complete removal. In September 1831, Potawatomi members of dubious authority ceded the land for the circuitous route. Without information from the indigenous perspective it is hard to know exactly how this happened. Reports of U.S. officials claim that through an interpreter “of mixed blood,” who was educated in white schools and worked for a fur trading company, they were able to get “a few young chiefs” intoxicated and convince them to cede more land. Looking at the history of U.S. negotiation tactics, it is likely that these young men were not authorized to make such a deal. [19]
The new route for the Michigan Road cut through the remaining Potawatomi lands, further isolating and cordoning off the indigenous bands. According to Hunter, ” The commissioners, in fact, saw this fractionalization as one reason for the ratification of the treaty.” John Tipton wrote:
It was then important that the Indians be separated into bands, by the intervention of our settlements . . . We could not purchase any particular district near the centre of the Pattawatamie [sic] country; but that tribe freely consented to give us land for the road described in the treaty, and for the settlement along it. Such a road . . . will sever their possessions, and lead them at no distant day to place their dependence upon agricultural pursuits, or to abandon the country. [20]
The Potawatomi refused to sell the bulk of their lands. However, the commissioners planned the road so that it cut through the middle of indigenous lands. This purposeful intercession combined with white settlement along the road, cut Potawatomi territory into unconnected pieces, weakening their holdings. State and government officials then turned their attention to removal.
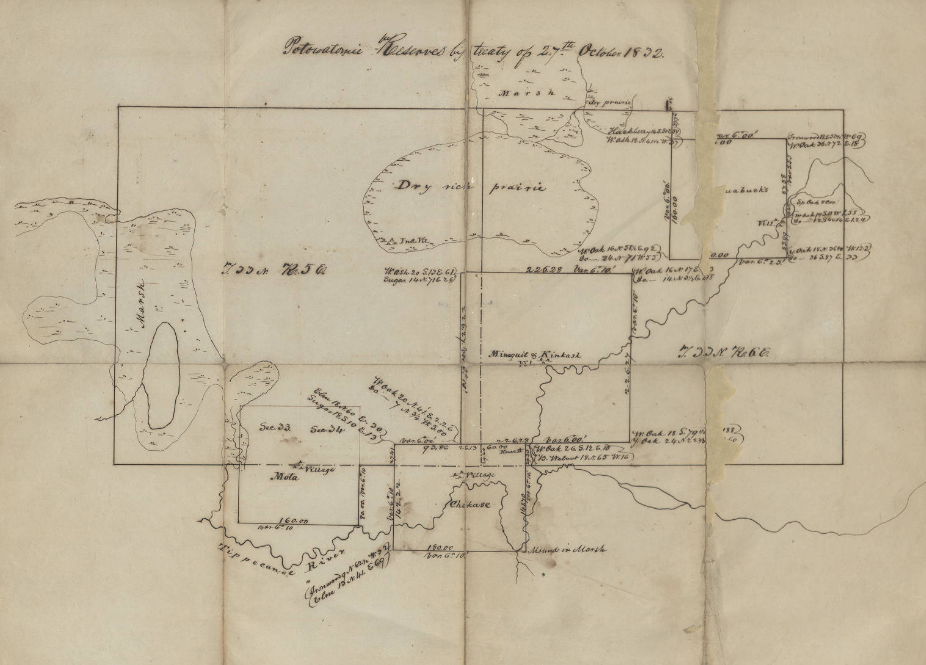
Trail of Death
In May 1830, President Andrew Jackson signed the Indian Removal Act, authorizing “an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for their removal west of the river Mississippi.” [21] The state and federal government, along with white settlers and squatters, continued to apply pressure for Potawatomi removal. In the 1832 Treaty of Tippecanoe, Potawatomi “chiefs” supposedly sold much of the remaining land. Menominee, an important Potawatomi leader, denied the validity of this treaty and resisted removal. [22] He wrote to a federal Indian agent, referring optimistically to President Van Buren:
The President does not know the truth . . . He does not know that you made my young chiefs drunk and got their consent and pretended to get mine. He would not drive me from my home and the graves of my tribe, and my children, who have gone to the Great Spirit, nor allow you to tell me that your braves will take me, tied like a dog. [23]
Menominee stood his ground and gathered followers. In response, Indiana Governor David Wallace had him arrested and ordered the forced removal at gunpoint of most of the remaining Potawatomi. The CPCHC explained:
On the morning of September 4, 1838, a band of 859 Potawatomi, with their leaders shackled and restrained in the back of a wagon, set out on a forced march from their homeland in northern Indiana for a small reserve in present-day Kansas. To minimize the temptation for the Potawatomi to try to escape and return home, militia members burned both fields and houses as the dejected members of the wagon train departed. [24]

A white witness described the scene:
The whitemen were gathering thick around them, which was but a sad necessity for their departure. Still they clung to their homes. But the flames of the torch were applied—their villages and wigwams were annihilated. [25]
It was John Tipton who led the militia group that forced the Potawatomi on this Trail of Death. In a horrific twist of irony, the route they took followed part of the Michigan Road. According to the CPCHC:
The journey was a 660-mile trek for which the Potawatomi were not prepared and through terrain to which they were not accustomed. The heat was oppressive and water was often scarce. They had only a few hundred horses to carry people and supplies, and promised additional wagons did not arrive before their departure; so, even the weak and elderly were forced to walk. The pace and conditions of the march debilitated the health of travelers. A day rarely passed that a member of the party did not die, usually a child, forcing their bereft and exhausted families to leave the bodies behind in hastily dug graves. In the end, more than forty people died during what the Potawatomi came to call the Trail of Death. [26]
This tragedy was not some unintended consequence of settlement. Removal was the plan from the beginning. The U.S. government, state governments, and white settlers chose the systematic genocide of Indigenous Peoples in order to take their native lands for their own use. Methods for the perpetuation of this crime included the tactics seen here: making treaties with people not authorized to speak on behalf of indigenous bands, pushing Indigenous Peoples into debt and dependence through encroachment and over hunting, flagrantly violating treaties, and finally, violence and murder. White people benefited directly from this genocide, taking the fertile land and prospering while continuing the persecution of Native Peoples. [27]
For example, Tipton, who helped negotiate the 1826 Treaty and led the forced removal of the Potawatomi, bought several sections of land along the Michigan Road. He later benefited financially from the sales of these lands as businesses and residences sprung up along the road. In 1831, John Tipton purchased the land surrounding the section of the Old Michigan Road called Sycamore Row, where IHB and local partners will install a new historical marker. We can only hope that the phrases on that marker about the 1826 Treaty and the pressure put on the Potawatomi will spur interest in learning more about this enduring people. [28]

Survivance
And they did endure. Even in the face of persecution and genocide, the Potawatomi continue today as sovereign nations, including the Prairie Band Potawatomi Nation located in Kansas and the Pokégnek Bodéwadmik, or Pokagon Band of Potawatomi, located in Michigan and Indiana. These tribal governments maintain their own educational and health systems, infrastructure, housing developments, law enforcement, and more. The Potawatomi people also continue to teach future generations traditional culture, arts, history, and language. In 1994, the U.S. government finally recognized the sovereignty of the Pokagon Band through an act of Congress signed by President Bill Clinton. [29]
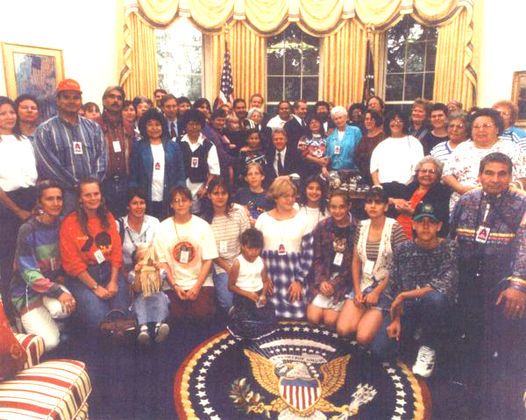

According to the Pokagon Band:
The Pokagon people have endured thanks in part to their values of Wisdom, Love, Respect, Truth, Honesty, Humility, and Bravery. Adapting these deeply-rooted ideals to contemporary circumstances has made the Band an engine for economic development and a model for sustainable living in the region. [30]
Learn more about the Potawatomi culture through the Pokagon Band Potawatomi website and the Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center.

* “Survivance” is a term coined by White Earth Ojibwe scholar Gerald Vizenor to explain that Indigenous People survived and resisted white colonization and genocide and continue as a people to this day. Theirs is not a history of decline. Their work preserving and forwarding their culture, traditions, language, religions, and struggle for rights and land continues.
Sources:
[1] Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center, “History,” https://www.potawatomiheritage.com/history/; Jon Boursaw, “The Flint Hills: A Major Chapter in Potawatomi Migration,” Symphony in the Flint Hills Field Journal (2011): 28-37, Kansas State University Library, newprairiepress.org/sfh/2011/flinthills/3/.
[2] Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center, “History,” https://www.potawatomiheritage.com/history/; “Potawatomi,” Milwaukee Public Museum, http://www.mpm.edu/content/wirp/ICW-56.
[3] Boursaw, 29-30; Jeffrey Ostler, Surviving Genocide: Native Nations and the United States from the American Revolution to Bleeding Kansas (New Haven and London: Yale University Press, 2019), 34-35.
[4] Jill Weiss Simins, “Democracy for Some: Defining the Indiana Landscape through the Rectangular Survey System,” Untold Indiana, December 2017, https://blog.history.in.gov/democracy-for-some-defining-the-indiana-landscape-through-the-rectangular-survey-system/. For a more thorough study of the genocidal policies and actions of the United States government, area militias, and squatter-settlers, see Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz, An Indigenous Peoples’ History of the United States (Boston: Beacon Press, 2014).
[5]”Potawatomi,” Milwaukee Public Museum.
[6] Juanita Hunter, “Indians and the Michigan Road,” Indiana Magazine of History 83, No. 3 (September 1987): 244-266.
[7] “The United States’ Handling of the ‘Indian Problem’,” Citizen Potawatomi Nation, September 7, 2018, https://www.potawatomi.org/the-united-states-handling-of-the-indian-problem/.
[8] Thomas Jefferson to William Henry Harrison, February 27, 1803, Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Jefferson/01-39-02-0500.
[9] John Tipton, Land Deed, State Volume Patent, Indiana, Issued January 3, 1831, Document Number: 11836, Accession Number: IN1110_.054, U.S. Department of Land Management, U.S. Department of the Interior, accessed glorecords.blm.gov/; John Tipton, Land Deed, State Volume Patent, Indiana, Issued January 3, 1831, Document Number: 11837, Accession Number: IN1110_.055, U.S. Department of Land Management, U.S. Department of the Interior, accessed glorecords.blm.gov/; Nellie Armstrong Robertson and Dorothy Riker, eds., John Tipton Papers, Volume I: 1809-1827 (Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau, 1942), accessed Indiana State Library Digital Collections; “Trail of Death,” Citizen Potawatomi Nation Cultural Heritage Center, https://www.potawatomiheritage.com/encyclopedia/trail-of-death/.
[10] Armstrong Robertson and Riker, Tipton Papers: Vol. I, 537; Ratified Indian Treaty 146: Potawatomi – Near Mouth of Mississinewa Upon the Wabash, October 16, 1826, National Archives Catalogue No. 121651643, Record Group 11, National Archives, https://catalog.archives.gov/id/121651643; Hunter 244-45.
[11] Hunter, 246.
[12] Armstrong Robertson and Riker, Tipton Papers: Vol. I, 578-80; Hunter, 252.
[13] Ibid.
[14] Ibid.; Ratified Indian Treaty 146: Potawatomi.
[15] Ibid.; Hunter, 254; Tipton Land Deed 11836; Tipton Land Deed 11837.
[16] Ibid.
[17] Ratified Indian Treaty 146: Potawatomi; Hunter 254-56.
[18] Armstrong Robertson and Riker, Tipton Papers: Vol. II, 419; Hunter, 256.
[19] Hunter, 256-57.
[20] Armstrong Robertson and Riker, Tipton Papers: Vol. I, 602; Hunter, 266.
[21] “An Act to Provide for an Exchange of Lands with the Indians Residing in Any of the States or Territories, and for Their Removal West of the River Mississippi,” May 28, 1830, Twenty-First Congress, Session I, Chapter 148, 411, A Century of Lawmaking for a New Nation: U.S. Congressional Documents and Debates, American Memory, Library of Congress.
[22] “Articles of a Treaty Made and Concluded on Tippecanoe River, in the State of Indiana, between Jonathan Jennings, John W. Davis and Marks Crume, Commissioners on the Part of the United States, and the Chiefs, Headmen and Warriors, of the Pottawatimie Indians” (Treaty with the Potawatomi, 1832), The Avalon Project: Documents in Law, History and Diplomacy, Yale Law School, Lillian Goldman Law Library, https://avalon.law.yale.edu/19th_century/pot1832.asp.
[23] “Potawatomi Trail of Death,” Kansapedia, 2012, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/kansapedia/potawatomi-trail-of-death/17944.
[24] “Trail of Death,” Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center, https://www.potawatomiheritage.com/encyclopedia/trail-of-death/.
[25] “Potawatomi Trail of Death,” Kansas Historical Society.
[26] “Trail of Death,” Citizen Potawatomi Cultural Heritage Center.
[27] See footnote 4.
[28] Tipton Land Deed 11836; Tipton Land Deed 11837. See also footnote 9.
[29] Prairie Band Potawatomi Nation, The Official Website of the Prairie Band Potawatomi Nation, https://www.pbpindiantribe.com/; Pokégnek Bodéwadmik, Pokagon Band of Potawatomi, https://www.pokagonband-nsn.gov/; “Pokagon Band of Potawatomi Commemorate 25th Anniversary of Reaffirmation of Sovereignty,” (Winnipeg, Canada) Indian Life, November 4, 2019, https://www.newspaper.indianlife.org/.
[30]“Our Culture,” Pokégnek Bodéwadmik, Pokagon Band of Potawatomi, https://www.pokagonband-nsn.gov/our-culture.










