In the fall of 1902, a crime syndicate was uncovered in the city of Indianapolis – not a syndicate of gambling, booze, or other illicit activities. No, this was a gang of “ghouls,” or men who robbed graves and sold bodies to medical schools on the black market.
Practitioners of this trade have been called many things – grave robbers, body snatchers, resurrection men, ghouls. Regardless of what they go by, they have a long and dark history tied inextricably to the advancement of medical science. In the 14th century, a professor at the University of Bologna began teaching anatomy using dissection as a tool of instruction. Soon after, four students at the university committed the first documented case of body snatching. The need for corpses had outpaced the legal means of obtaining them, driving students to procure cadavers by unlawful means. The rest, as they say, is history.
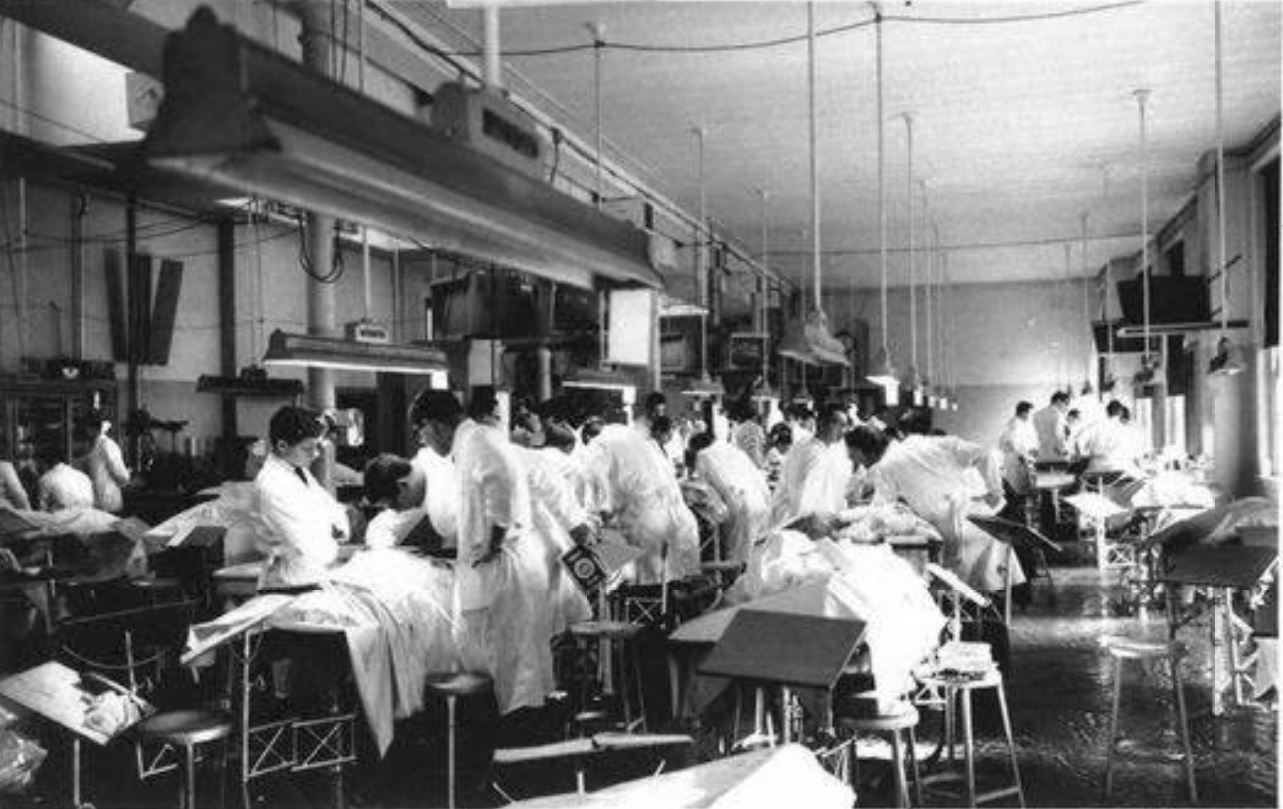

As medical education advanced, the need for human specimens rose at a dramatic pace. For centuries, however, the supply was met mostly by legal means – largely, the remains of criminals condemned to death. However, in the 17th and 18th centuries a confluence of two factors – a reduction of executions and the proliferation of medical schools – created a massive shortage. One which would be filled by a barely underground network of so-called “Resurrection Men.”
While illegal, the practice of stealing corpses to sell to medical schools often went unprosecuted as it was perceived as being “for the greater good.” The dissection of cadavers – weather obtained legally or otherwise – has been used to train new physicians in anatomy, lending them an unprecedented level of understanding of the human body. This, along with the fact that most of the victims were poor or people of color also helped law enforcement turn a blind eye. However, as the practice continued and more prominent families were victimized by the traumatizing act, states began expanding the legal channels through which medical schools could procure specimens. These acts are referred to as anatomy laws.
Indiana’s first anatomy law was enacted in 1879, perhaps not-so-coincidentally a year after the grave of John Scott Harrison, son of former President William Henry Harrison and father of future President Benjamin Harrison, was robbed and his body discovered at the Ohio Medical College. The 1879 law provided that:
the body of any person who shall die in any state, city or county prison, or jail, or county asylum or infirmary, or public hospital, within this State, shall remain unclaimed. . .for twenty-four hours after death. . .may be used as a subject for anatomical dissection and scientific examination.
While the law was meant to provide a morally sound avenue for medical schools to obtain bodies for dissection, that avenue still took advantage of the poor and mentally ill as it was highly unlikely that any of the deceased were ever given the opportunity to consent to their remains being used in this way.

But even with this law in place, there were still sometimes shortages. The early 20th century was one of those times. In 1902, at least five institutions in Indianapolis needed a steady supply of corpses. As the winter semester of the 1902-03 school year approached, these institutions vied for the inadequate lawful supply and eventually turned to the black market to fill their needs.
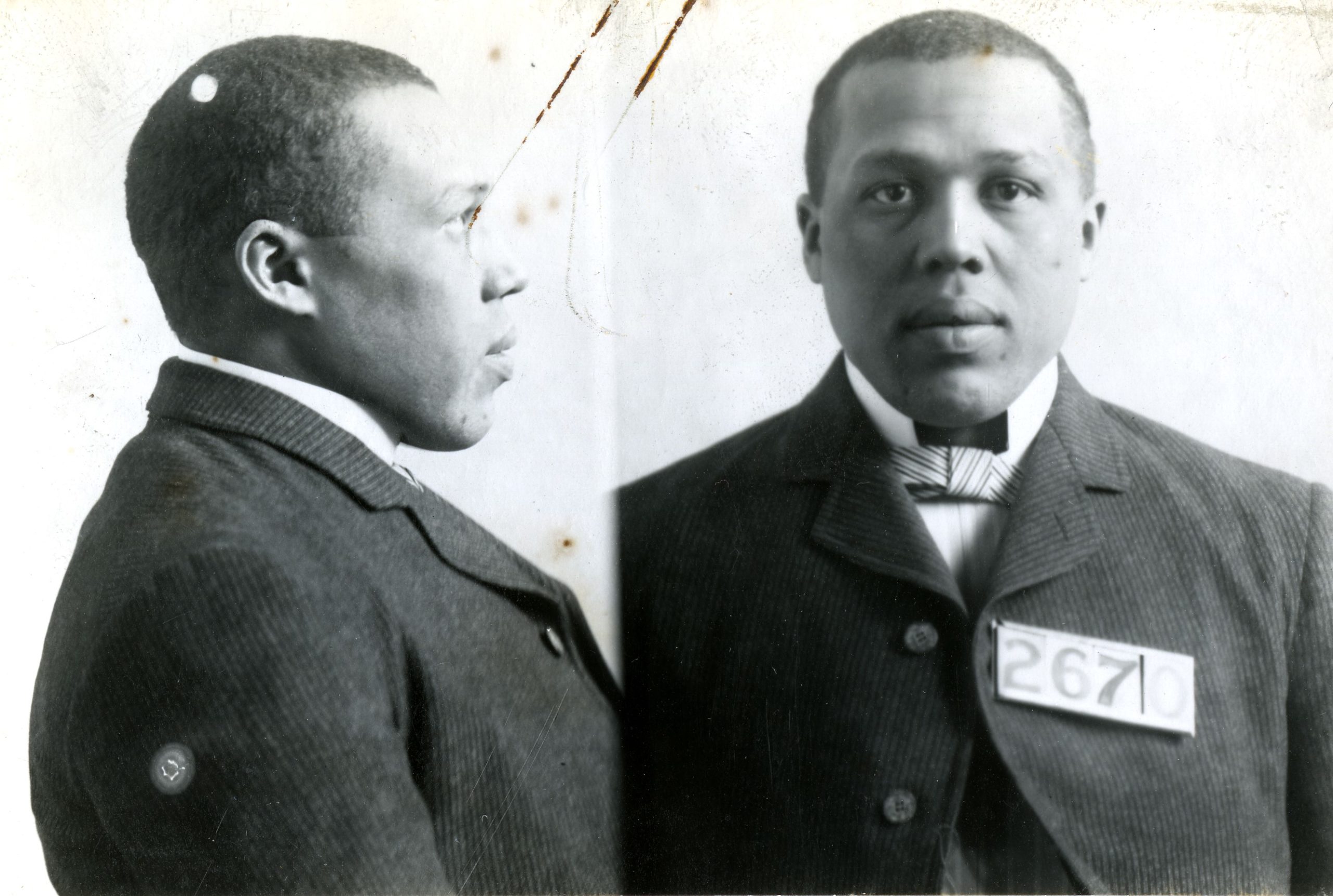

Dominating the black market was Rufus Cantrell. Having been a driver, porter, clerk, and even an undertaker, in 1902, he added a new title: The King of Ghouls. He, along with approximately seven other men, ran one of the most successful body-snatching syndicates in the city. According to the September 30, 1902 issue of the Indianapolis Journal:
He did not use hooks in pulling out corpses, as was done years ago. He only used hooks when a corpse was fastened in a coffin. Instead of digging down at the head of the grave, as was the former custom, he adopted the plan of digging in the center. The covering of the box was then sawed through and the small lid on the coffin shoved back. No lights are used by the ghouls . . . except an occasional match, which is lighted down in the grave.
It was hard, grim, and dirty work, but it paid off. Cantrell reported that between July and September of 1902, he and each of his men had earned $420 from their nighttime exploits, nearly as much as the average American made in a whole year. But their profits wouldn’t last long.
At least three different Indianapolis residents received anonymous tips that the graves of their recently buried loved ones may be found empty. Upon further investigation, the families discovered that this was indeed the case, and, more horrifying still, they discovered the missing remains in the basement of the Central College of Physicians and Surgeons. Panic gripped the city as newspapers published these stories. Families began guarding the graves of their recently interred relatives. Citizens called for investigations. Detectives staked out cemeteries and medical schools, waiting for the Ghouls to show themselves.

However, a break came from an unexpected source. A pawnbroker by the name of Emil Mantel grew suspicious of a customer after loaning him $28 in return for four shotguns. Mantel contacted his attorney, Taylor Gronniger for advice on the situation. When Mantel gave the name of the suspicious customer as Rufus Cantrell, Gronniger connected the dots. He had heard rumors about Cantrell’s unsavory practices, and here Cantrell was, pawning off more shotguns than any one person would need – shotguns that could be used to scare off any unwanted observers intruding on illegal happenings – and just when the grave robbing business was too hot to continue. So, Gronniger relayed his hunch to Detectives Asch and Manning of the Indianapolis Police Department. By the end of the next day, the detectives had arrested Rufus Cantrell and six of his associates and extracted full, corroborating confessions from each man.
Cantrell, the leader of the “gang of ghouls,” gave his confession in excruciating detail, seemingly proud of his escapades. He and his assistants had plied their gruesome trade at Crown Hill Cemetery, the German Catholic graveyard, Mount Jackson Cemetery, Traders Point Cemetery, and the Old Anderson graveyard, as well as the cemetery at the Central Indiana hospital for the Insane, where, Cantrell confessed, he and his posse had emptied over 100 graves.
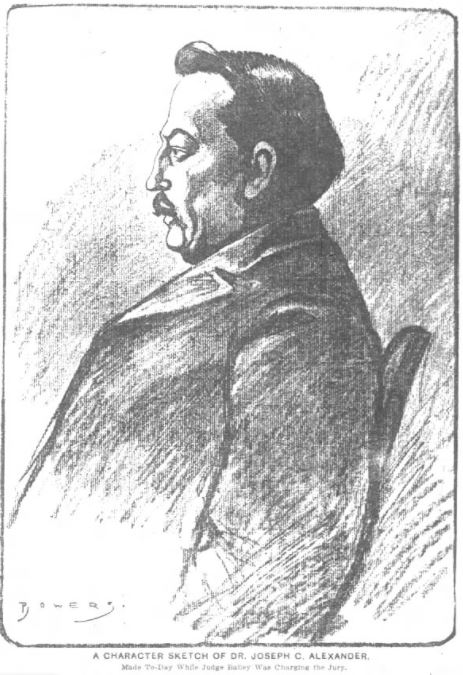

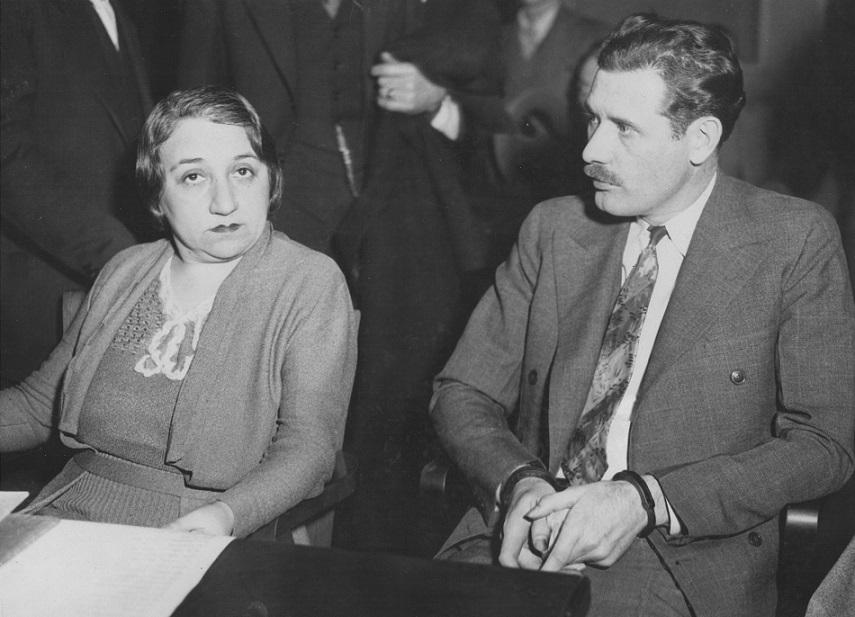
He went on to implicate Dr. Joseph Alexander of the Central College of Physicians and Surgeons as his principal buyer. However, while most medical men simply feigned ignorance of the source for the bodies they were buying, Cantrell described Alexander as playing a much more hands-on role in the operation. Not only did Alexander knowingly buy stolen bodies, he identified potential targets, accompanied Cantrell on scouting missions, and even joined the gang in their nightly expeditions. Alexander was arrested, but quickly posted bail.
As Cantrell’s confessions continued, more empty graves were unearthed. The various medical schools around the city were searched thoroughly, but the bodies were nowhere to be found. Detectives Asch and Manning received a tip that Dr. Alexander had commissioned twenty pine boxes from a local box-builder to be delivered to the Central College of Physicians and Surgeons just days after the arrests had been made. This seemed like just the break they were looking for – surely the boxes had to be connected to the missing bodies. However, upon further investigation, it was discovered that Central College was in the process of moving locations and the boxes had been commissioned for the mundane purpose of packing away delicate medical instruments.

In mid-October, just as a grand jury was called to make indictments in the case, the mystery of the missing bodies was solved, at least in part. On October 14, 1902, the Indianapolis Journal reported:
Amos Smith . . . on his way to work, yesterday morning about 6 o’clock, partially cleared up the mystery of the bodies recently spirited away from the medical colleges. He found two bodies tied in sacks in a dry goods box at the side of Hibben, Holloweg & Co.’s store . . . The same young man, in walking farther south noticed two more bodies at the rear door of the Central Medical College.
After being positively identified by family members, there was speculation that a competing medical college in the city had disposed of the bodies near the Central Medical College in an attempt to throw all suspicion on that institution while dissuading further investigation. While these grizzly details were being spread in newspapers throughout the city, the grand jury received its instructions and began hearing testimony in the case. By the end of the grand jury’s investigation, twenty-five indictments were handed down and allegations had been made against seventy-five different people who were all part of three additional body-snatching syndicates in the city. Among the indicted were Cantrell and his associates, Dr. Alexander, four physicians from other schools, cemetery workers who facilitated the robberies, and various low-ranking employees of medical schools who had played some small part in the operation.

After several delays, the first Ghoul Gang trial, that of Dr. Joseph Alexander, began in early February. Alexander’s defense attorney’s strategy seemed to be to cast as much doubt on the character of the star witness, Rufus Cantrell, as possible. First, they attempted to link him to the unsolved murder of a Chinese immigrant who had been killed a year earlier. When that didn’t stick, the defense brought into question the sanity of the King of the Ghouls by introducing evidence that Cantrell had been diagnosed with epilepsy, at that time a broad diagnosis encompassing several mental illnesses.
Multiple physicians were brought to testify on Cantrell’s mental health. Each in turn pronounced Cantrell “insane.” Cantrell and the state begged to differ. Upon cross examination, each doctor admitted to having ties, past or present, to the Central College of Physicians and Surgeons, the same college which employed Dr. Joseph Alexander. Coincidence? Perhaps.
Coincidence or not, the evidence presented by the defense seems to have been enough to sway at least some of the jurors. The February 16, 1903 issue of the Indianapolis Journal reported:
Dr. Joseph C. Alexander’s status in the community is unchanged. He is neither the convicted felon of the heinous crime of complicity with ghouls and neither is he wholly absolved from the accusations made against him by the state’s attorney. . . Yesterday morning at 10 o’clock, after deliberating since the same hour Friday morning, the jury reported through its foreman . . . that it had not arrived at a verdict and undoubtedly would be unable to do so, and it was discharged from further service.
The result of one of the most anticipated trials of the year resulted in a hung jury. While the state’s attorney promised a retrial, it never came to fruition. Cantrell, who had all along hoped that his cooperation would result in a lighter sentence, saw the writing on the wall and refused to testify in the retrial. With their star witness gone, the state had little evidence against the doctor – or any of the other four physicians originally indicted, who had maintained their innocence throughout and whose only accuser was the now silent Cantrell. The next big trial was that of the King Ghoul himself.
Taking a page from Dr. Alexander, Cantrell’s defense team entered a plea of insanity at the onset of the trial. The state, of course, used the testimony of Cantrell himself given in interviews with police as well as during the grand jury investigation. The question of the trial was not if Cantrell had robbed graves, but why? Was he a greedy criminal just trying to make a buck, or was he criminally insane?
To make the case for the latter, Cantrell’s own mother was put on the stand. Through her testimony, the defense told the jury:
that they proposed to show Cantrell to be insane . . . that while Cantrell lived in Gallatin, Tenn., from the age of one to fifteen years, he suffered from epilepsy; that when twelve years old he was thrown from a horse and his head was injured; that when he was ten or twelve years old he had a delusion that he was called by God to preach, and told his friends that he talked with God face to face; that while at work in the field he would kneel at the plow and pray and preach from a Biblical text; that he still suffers from delusions and in the jail has preached to prisoners; that when taunted by his friends in Tennessee over his inability to preach he would become profane and once assaulted a minister with his tongue when he refused to ordain him; that he has a violent temper and has attempted the lives of himself and others; that he delighted to call himself the “King of the Bryan campaign,” and had cards printed with the words, ‘Rufus Cantrell – the Democratic hero;’ that he suffered a sunstroke in Indianapolis, which incapacitated him for work in hot places, and that he succumbed to heat while employed in the Malleable iron works. All these things, Cantrell’s attorneys would prove.
It should be noted that traumatic brain injuries can affect the mental health of those who experience them – they can cause mood swings, agitation, combativeness, and other cognitive symptoms. And both epilepsy and sunstroke were used in the 19th century to describe various mental illnesses. That being said, it’s difficult to tell from newspaper reports alone how much the testimony given was exaggerated in an attempt to keep Cantrell out of jail. After all, he did deny having any mental illness during the trial of Dr. Alexander.
Yet another topic that may have played a part in the trial, and certainly played a part in the sensationalized coverage of the case, is race. Rufus Cantrell and his associates were all Black men. Alexander and the other physicians, all of whom would eventually walk free, were white. It’s important to note that people of color, facing systematic discrimination, were often driven to find income in alternative ways. These alternative ways were, in some cases, illegal. This could have influenced Cantrell’s decision to enter the profession of grave robbing. However, there were gangs of white ghouls in the city working right alongside Cantrell’s gang – grave robbing was a lucrative business if you could get past your moral qualms.
So, the influence of race on Cantrell choosing this line of work isn’t clear. What is clear, however, is that his associates, and not the white physicians, were prosecuted for their crimes. It’s also clear that newspapers took every chance they could to point out the race of the accused. In the end, race can’t not have played a role in the trial, but it’s difficult to tell through reports – all written for white newspapers – how extensive that role was.

On April 26, 1903, Rufus Cantrell, the King of the Ghouls, was found guilty of two charges and sentenced to three to ten years in the Jeffersonville State Reformatory. In the end, Cantrell and four of his associates were convicted and sentenced to between one and ten years each. The twenty other men indicted by the Grand Jury were cleared of all charges due to lack of evidence.
Convictions weren’t the only thing to emerge from this tale, though. The system of public institutions delivering the unclaimed bodies of the deceased directly to medical schools was clearly not working as desired. As a result of this and other similar trials, the Indiana General Assembly passed the Anatomical Education Act in 1903, establishing the State Anatomical Board, which would oversee the distribution of bodies to medical schools. The State Anatomical Board is still in existence today, continuing to oversee the distribution of donated bodies to medical schools. According to anatomist Sanjib Kumar Ghosh, body donation constitutes the sole source of cadavers used in teaching anatomy in the vast majority of the world, including in the United States. Learn more about the history of dissection here.
Find all sources for this blog post here.