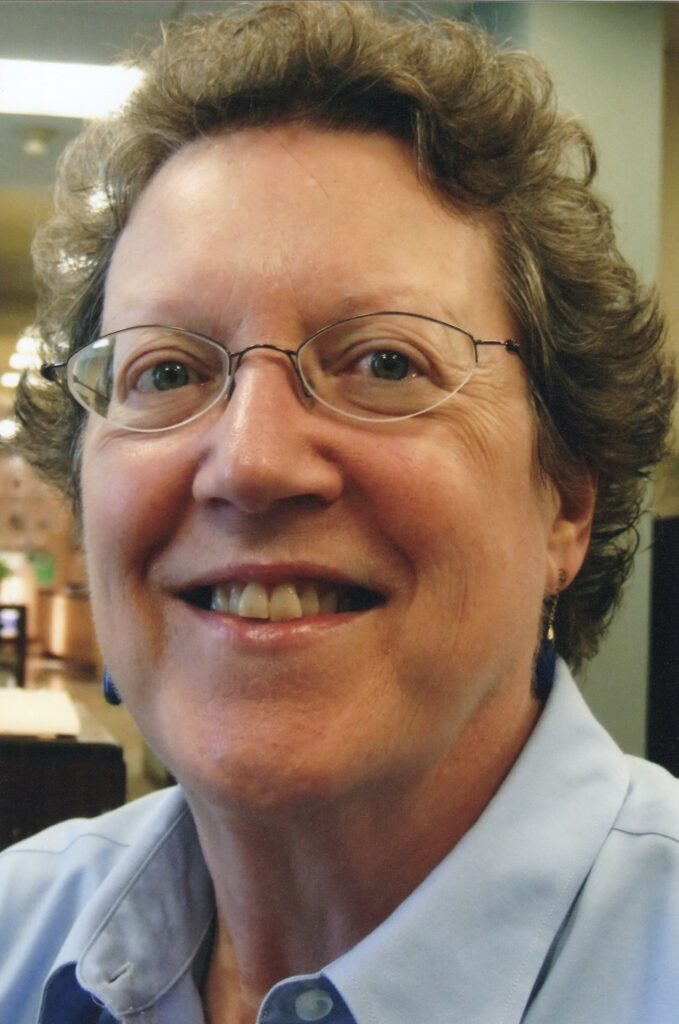
The Indiana Historical Bureau would not be what it is today without the vision and leadership of Director Pamela J. Bennett. Known to us simply as Pam, she passed away earlier this year, prompting us to remember the profound impact she had on the field of history. Colleagues and friends lauded Pam as a take-charge person, who was a strong collaborator and an excellent writer and editor. During her decades at IHB, she prioritized accessibility and transparency, high quality research, and telling the story of all Hoosiers. She modeled what a public servant truly should be. She also broke the glass ceiling for female leaders in the field and was a devoted mentor to a generation of scholars, ourselves included. In our work at the Bureau, we do our best to carry on Pam’s legacy by meeting Hoosiers where they are and communicating the relevance of history.
Although synonymous with Indiana history, Pam was born in Baltimore on July 3, 1943. She graduated from Gettysburg College in 1965 with an A.B. in Chemistry. After falling in love with British novels, Pam attended Indiana University–Bloomington and completed an A.M. in English Literature. At IU, she served as Assistant Editor of the Indiana Magazine of History and several other history journals and projects.
Pam’s first role at the Indiana Historical Bureau was that of editor when she joined the agency in July 1973. She began her long tenure as director just three years later, when IHB separated from the Indiana Historical Society. As director, she actively worked to safeguard Indiana’s historical records. Her strong belief in the power of knowing history as the basis for thoughtful citizenship led her to provide students and adults with access to Indiana’s history and culture through a variety of educational materials and programs. These included workshops for historical groups and educators on such topics as public relations, the role of the local historical society, and classroom resources.

One of Pam’s first major initiatives as IHB director was the restoration and exhibition of the governors’ portrait collection. Many portraits had fallen into disrepair and required significant funding to restore. In typical Pam fashion, she thought outside of the box to get the job done. According to a 1979 Evansville Courier article, Pam believed that “‘historical mementos ought to fund something historic.'”[1] So, she made sets of commemorative medallions that had been collecting dust in the Bureau available for purchase. They had been minted in 1916—in celebration of the state’s centennial—and 1966, the date of the state’s 150th anniversary. This strategy proved successful, and IHB began the process of restoring the paintings with an eye toward extending the collection as a cultural, historical, and educational tool.

Before the connectivity of the internet, Pam worked to disseminate history to all corners of the state through various programs. In 1981, she reestablished the Indiana County Historian program, in conjunction with the Indiana Historical Society, to “improve the historical communication network in the state.”[2] Each appointed historian served as a clearinghouse of sorts, becoming experts in their county’s historical resources in order to field residents’ in-depth questions.
Jeannette Rooney, Assistant Director of Local History Services for IHS, recalled that Pam:
played a crucial role in evolving it into the productive and thriving program that today supports local history across the state. When I began working in IHS Local History Services, I had the pleasure of working with Pam through the County Historian Program, and she was a wonderful mentor as I learned all the aspects of coordinating this fantastic group of volunteer historians. Over the seven years we worked together, I knew I could always count on her to know what was going on around Indiana. She was so supportive of local history efforts and the work of county historians – she truly loved the work of history, and she has left quite a legacy! She will be missed.
The program continues to fulfill Pam’s mission to “move local historical information to every Hoosier’s fingertips.”[3]
Pam was a driving force behind another statewide program: National History Day. She coordinated NHD since 1980, when the Indiana program was still in its fledgling state. Under her direction, Indiana became one of the model state programs in the network. National History Day awards outstanding history projects among 6th-12th graders through its annual competition. In describing the value of History Day, Pam wrote in 1989 that it is a “strong reminder to those of us concerned with both the past and the future that we have a responsibility to provide these students with the skills, content and context necessary to make studied and thoughtful decisions in the twenty-first century.”[4] Describing the annual awards ceremony, Pam proclaimed “It is a delightful experience to hear 1200 Hoosiers cheering about something other than basketball.” In addition to overseeing Indiana’s program for over twenty years, she served on the board of U.S. National History Day.
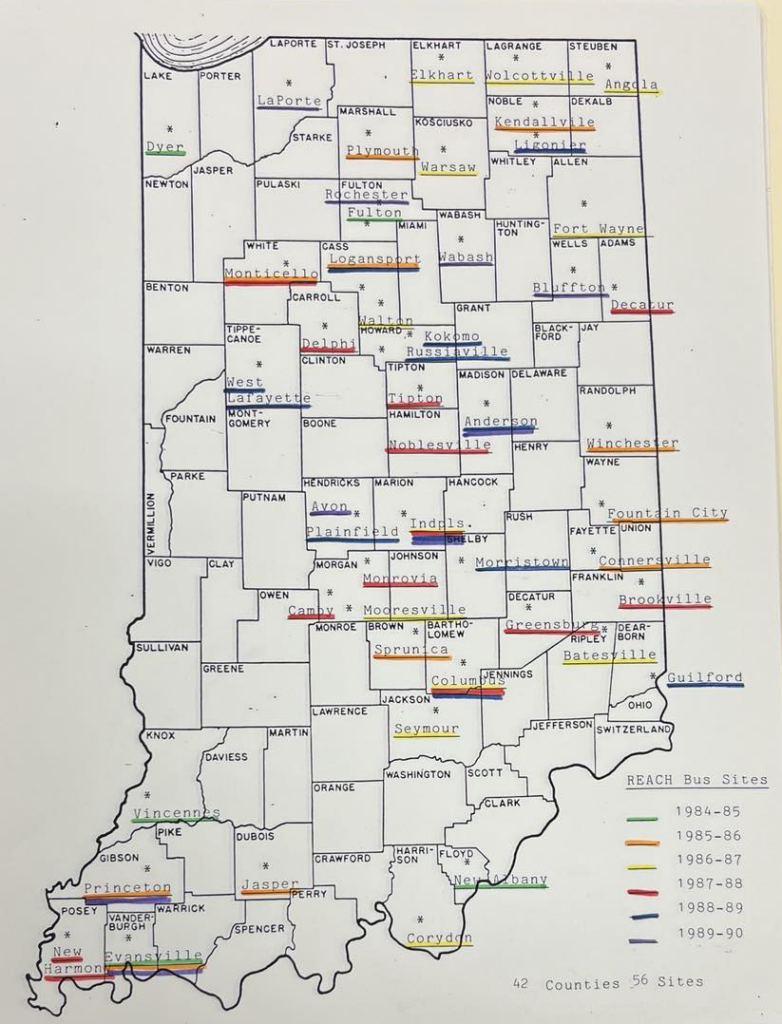
In her work to make history accessible to Hoosiers around the state, Pam and the Bureau—in collaboration with the Indiana Arts Commission and Indiana State Museum—spearheaded the innovated REACH bus program. The bus operated as a mobile museum, visiting remote school corporations in the 1980s. Children hopped on the rainbow colored bus, where they learned about natural history by examining stalagmites and viewed original oil paintings by Hoosier artists such as T.C. Steele. REACH encouraged teachers to incorporate the arts and inter-disciplinary learning into curricula.[5]
The popularity of the program is reflected in letters, including that sent by Monrovia PTO President Mary Ann Henderson who stated, “Since we are a small country school our teaching resources are limited, but when we are able to obtain a program such as yours it not only enhances the education of our students it benefits our teachers, parents and community!”[6] Similarly, State Senator Steven R. John wrote, after viewing the bus at the State House and General Assembly, “I saw how it provides the citizens of Indiana, adult and student alike, with an experience in the arts and history that cannot be duplicated.”[7] The program was recognized by the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts and the National Alliance for Arts in Washington, D.C. Arts Dialogue-Australia also invited organizers to its conference.[8]
Alongside these outreach projects, Pam oversaw internal programming. Among the most important was the State Historical Marker Program. Markers serve as tangible reminders of the state’s rich and diverse history and help return stories to the landscape. While the program has historically been a public-driven initiative, Pam fostered a sense of collaboration and community ownership over markers. Because of the network she helped forge, the Bureau has been able to install over 750 markers across the state, commemorating topics ranging from STEM to sports.
Pam’s legacy lives on not only in cast aluminum, but in the pages of over a dozen publications that she helped edit and publish, including Bury Me in a Free Land: the Abolitionist Movement in Indiana 1816-1865, with Gwen Crenshaw; The Centennial History of the Indiana General Assembly, 1816-1978, with Justin Walsh; and Indiana 1816-1850: The Pioneer Era, with Donald F. Carmony. Such publications have been foundational to the work of many Indiana and Midwest historians.
Pam’s expertise was highly sought after and she earned a seat at many important tables. She served on the boards of several organizations, including the American Association for State and Local History (AASLH), serving as Vice President from 1988-1989 and President from 1990-1992. Through AASLH, she worked to provide professional development and recognition to state and local historical agencies throughout the country. Pam also advised on state and national historical celebrations, including the U.S. Constitution Bicentennial, Lincoln Bicentennial, Indiana Quarter design, and the American Revolution Bicentennial.

Pam received numerous professional accolades for her prolific work. In 1989, she was the recipient of the Indiana Council for Social Studies’ Citizens Award for outstanding contributions to social studies. In 2010, the Marion County Historical Society presented Pam with the Fadely History Award for “outstanding effort” to promote history in Indianapolis and Marion County. The Indiana Historical Society presented Pam with the 2011 Eli Lilly Lifetime Achievement Award for “extraordinary contributions over an extended period of time to the field of Indiana History.” The Bureau has honored her legacy by naming the Bennett-Tinsley Award for Undergraduate History Research and Writing after her and plans to dedicate our new marker center in her honor.
There are not enough awards to signify Pam’s impact. Perhaps the words of colleagues will help. President of Indiana Landmarks Marsh Davis remembers her as “a stalwart presence who commanded respect as one of the bastions of Indiana history.” Jeannie Regan-Dinius, who worked closely with Pam over the course of 20+ years in her role at the Division of Historic Preservation and Archaeology, told us:
She made me a better historian, challenging me to improve my skills and writing. Her guidance was always fair, honest, and caring. Her work at the statewide level was an inspiration for women working in the history field to see that we could be in charge, provide quality work, and be supportive of other historians.

Colleagues had a chance to tell Pam how much she meant to them in person at her 2015 retirement party. Commemorating Indiana’s bicentennial the following year without her leadership was strange. However, it gave us an opportunity to practice history in a way that reflected her stalwart, collaborative nature.
Pam would probably want to be remembered as a facilitator. Former IHB historian Jill Weiss Simins reflected “I think Pam especially got joy out of connecting people with opportunities. She encouraged us to do more than just what the job required and built a team of young historians dedicated to trying to meet challenges.” In her decades at the Bureau, Pam helped forge a nexus between K-12 schools, citizen historians, universities, humanities organizations, and residents across the state. She cultivated a reputation that has made the Bureau a respected partner, valued resource, and the “go-to” agency for questions about Indiana history from partners, educators, and the public.
From our little corner of the Indiana State Library, we continue to think broadly, ambitiously about how to connect with Hoosiers and to ask big questions, like “how does history inform identity?” While we grieve our fearless leader, we will, as Pam was fond of saying, “Carry on!” as devoted public servants and stewards of Indiana’s stories.
Sources:
[1] “Memento Sale to Buy Back ‘A Bit of this History,'” Evansville Courier, May 14, 1979, 2, accessed Newspapers.com.
[2] “County Historians,” Indiana Historical Society, accessed https://indianahistory.org/across-indiana/hometown-resources/county-historians/.
[3] “History Aides Sought on County Basis,” South Bend Tribune, December 16, 1980, 11, accessed Newspapers.com.
[4] Letter, Pamela J. Bennett, Indiana Historical Bureau, to Roy Shoemaker, Indiana Historical Society, December 5, 1989, courtesy of Indiana Historical Bureau Collection, Policy Files-Appointing Authorities, Deputies, and Division Directors, 1908, Indiana Archives and Records Administration.
[5] Elizabeth Jacobson, “Bus Brings Art, Past to Noblesville School,” Noblesville Ledger, September 30, 1987, 1, accessed Newspapers.com.
[6] Letter, Mary Ann Henderson, President of Monrovia PTO, to Celia Yohman, Coordinator, Reach Bus Program, June 13, 1987, courtesy of Indiana Historical Bureau Collection, Policy Files-Appointing Authorities, Deputies, and Division Directors, 1908, Indiana Archives and Records Administration.
[7] Letter, Steven R. Johnson, State Senator, to Mary L. Snyder, Chairperson, Reach Bus Committee, August 1988, courtesy of Indiana Historical Bureau Collection, Policy Files-Appointing Authorities, Deputies, and Division Directors, 1908, Indiana Archives and Records Administration.
[8] “Long Range Plans: REACH: Resources Educating in the Arts, Culture, and History,” p. 1, courtesy of Indiana Historical Bureau Collection, Policy Files-Appointing Authorities, Deputies, and Division Directors, 1908, Indiana Archives and Records Administration.