* See Part I to learn about the origins of Federated Metals’ Indiana plant and community protest to its pollutants.
Carl Weigand, acting chief of air pollution control, reported in 1969 that Federated Metals’s Hammond-Whiting smelting plant “has a hell of [a] stink problem” (Munster Times). He worked untiringly to combat air pollution generated by “The Region‘s” industries. Weigand’s description of his professional obstacles mirrored the conflicting financial and environmental interests enmeshed in the plant: “Sometimes all a company has to do is call up a councilman or city hall to mention, ‘we could move this operation'” and pollution policies would go unenforced. “But,” Weigand countered, “‘I’m a stubborn German.'”
That year, the Munster Times noted that the Calumet Region was 11th in air pollution in the U.S. When including the Chicago area, it was the second or third highest. Nationally, Americans turned their attention to the impact of industry on the environment, especially following the Santa Barbara oil spill. In 1970, Senator Gaylord Nelson created the first Earth Day, and throughout Indiana Hoosiers acted to raise awareness about the imminent pollution crisis. In addition to general clean up campaigns, panel discussions, and seminars, students built monuments made of trash and participated in marches. The constituent support for Earth Day encouraged Congress to enact a swell of landmark environmental legislation, including the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency in December 1970, the Clean Air Act amendments of 1970, and the Clean Water Act in 1972.

In this framework, Federated Metals found itself on the periphery of a heated public debate about the fate of Lake George in the late 1970s. The Times reported in 1979 that silt containing toxic metals, like arsenic and mercury, was found at the bottom of the “‘decaying lake,'” potentially making fish dangerous to eat. This complicated Calumet College‘s proposal to deepen the lake, and resulted in a “turbulent hearing involving debates over private vs. public rights, hazardous waste and legislative intent.” The college owned the title to the lake, except for the section belonging to Federated Metals. College president Rev. James F. McCabe petitioned to drain the lake and remove sand, which would then be sold, generating approximately $1.5 million for the struggling school.
Rev. McCabe contended “If you force us to preserve a decaying lake, it will be an infringement on the rights of private ownership.” But the U.S. Corps of Engineers advised against dredging because it could stir up pollutants. The Indiana Department of Natural Resources, however, thought the petition should be approved, with conditions, because “The proposed project would increase the recreational potential and desirability of the lake, and would preserve the existing wildlife habitat.”
In 1981, “emotional tension” arose when senators debated a bill allowing Calumet College to sandmine Lake George, despite the city having an ordinance against sand-mining. The Times reported on a skirmish on the Senate floor between bill sponsor Senator Ralph Potesta (R) and opponent Senator Frank Mrvan (D). The legislators argued over ownership of the lake, control of which would be taken from the DNR with passage of the bill. Senator Mrvan opposed this, as well as the potential for property damage caused by sand-mining. He was accompanied by women from the Robertsdale neighborhood, who protested “the most lobbyed [sic] bill to be considered this session” in the Senate chambers. State policemen manned the chambers after one woman reportedly threatened to shoot Senator Potesta if the bill passed. When it did, the Times noted “tiny pieces of a printed copy of the bill flurried to the floor of the Senate from where the women were seated. One began to cry.” The project was expected to generate $38 million ($2-$3 million allocated to the college) and some of the sand would be used to fill the Cline Avenue extension. The debate about dredging the lake was for naught. Calumet College scrapped the idea in 1989, stating “Calumet College has no interest—long-term—in being in the lake business, the park business, the sand business, the real estate business or any related business” (Times).
Senator Mrvan had earlier opposed Federated Metal’s 1977 expansion, which involved building a “sludge treatment plant designed to extract nickel compounds used for nickel-plating steel.” He exclaimed, in response to the City Council’s approval of municipal-rate bonding for the plant, “‘I don’t believe this. Here are nine councilmen just coming in and we’re expected to pass this thing in one night when we’ve never seen it before.'” Mrvan also took issue with the unannounced caucuses that took place prior to the vote and influenced councilmen.
Although it had closed its Indiana plant in 1983, Federated Metals found itself in hot water in 1985, when it had to pay civil penalties to the Indiana Environmental Management Special Fund for permit violations. The Times stated that the company “failed to provide groundwater monitoring equipment on its property where hazardous waste was treated and stored.” In December of that year, HBR Partners, Inc. purchased the former plant.
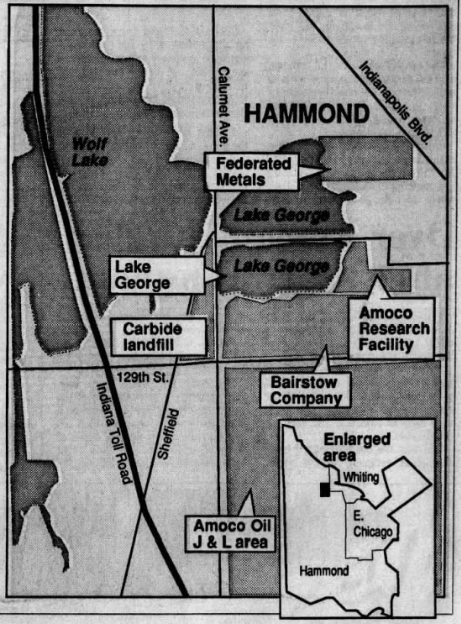
Federated’s troubles deepened in 1986, when Councilman Gerald Bobos requested an investigation into possible contamination of Lake George by dump sites owned by Federated and the former Amoco facility. Preliminary studies conducted in 1984 indicated that “‘at one time there were 50,000 cubic yards of persistent toxic substances—picking liquors, degreasers and fine heavy metal powders—on the site that could be filtered into the lake'” (Times, March 1986). The study also noted that a child sustained third-degree burns while playing at the dump in 1978.
“Innuendos” and “allegations” is how Councilman Edward Repay described Bobos’s presentation of the surveys, which he used to convince the council of the need for an official investigation. Repay, who sponsored the lake dredging, contended that “we’ve got studies from last year from the Robertsdale Foundation that show the sand is clean. I’ll go along with those studies.” Ultimately, Repay voted to investigate the dump sites, but not before accusing opponents of the dredging as guilty of “‘rotten, no-good, uncitizenlike behavior'” for presenting the studies.
Feeling the need to explain himself, Repay wrote to the Munster Times that his anger towards a Hammond councilman, presumably Bobos, was deserved. Repay leveled that his ire was not because the councilman and United Citizens Association (UCA) brought up the alleged toxic state of the Federated site, but “that they waited to use it as a ‘trump card’ against possible improvements to George Lake.” (Bobos had earlier mentioned that he requested the 1984 studies months prior, but the state board’s delay meant he was unable to use them in the decision to issue a dredging permit). Repay maintained “This is ‘one-upsmanship,’ not statesmanship or an act of a responsible civic organization.” Repay agreed that action should have been taken when the child was exposed in 1978, but the “inaction of a councilman and the leaders of the UCA is reprehensible and deserving of angry criticism.”

Ultimately, the EPA planned to investigate, which site inspection official Harry Atkinson considered crucial because there were over 800 alleged dump sites in the state, but Lake County has “‘tons’ of such alleged sites.” The Times reported that federal inspectors tried to examine the former site of Federated Metals in 1985, but the property owners denied access.
In 1990, the U.S. Justice Department sued Federated Metals, Inland Steel, and Bethlehem Steel, jewels in The Region’s industrial crown. According to the Logansport Pharos-Tribune, the Justice Department sued for violation of pollution laws, which threatened Lake Michigan by “‘creating fish too contaminated to eat, forcing frequent beach closings, harming wildlife living along the shore, and depositing toxins in lake bottom sediment.'” The Northwest Indiana Times reported that at the time Indiana was one of seven U.S. states without air pollution control laws and relied on federal regulations that only limited small amount of emissions. Increased enforcement of pollution laws through heavy fines, a Justice Department official contended, “would teach industrial polluters that befouling the air and waterways can cost more than spending to control hazardous wastes.” The director of the Grand Cal Task Force, a citizens environmental group, approved of the “aggressive plan,” stating “In the past, smoke has meant jobs. . . . People were afraid to put pressure on the companies. Now there aren’t as many jobs and pollution is just as bad.”

The following year, Federated Metals and the Indiana Department of Environmental Management (IDEM) came to an agreement to make the site safer. The Munster Times reported that within a year the smelting company would place a “sophisticated clay cap” over nineteen acres of contaminated slag in Lake George and install monitoring wells. Federated’s residual heavy metals had been linked with “mental retardation in children and high blood pressure in adults.” Preventing these health effects, an IDEM official said, “has been a thorn in our side for quite a long period of time.”
The Times credited citizens living in the Robertsdale neighborhood for the remediation. The paper stated that the group had worked for years to “get the site cleaned up and fenced off from unsuspecting children who enjoyed riding their bikes on the lead, zinc and copper dust piles because they were soft to land in.” Kids also scavenged for metal to sell at the former site. By 1991, Federated Metals, a subsidiary of Asarco Inc., installed a security guard and fence to prevent this from reoccurring.

But hazards posed by the former Federated Metals site endured into 21st century. The Times reported in 2003 that the “hazardous waste dump” had “never been closed or capped, allowing the release of toxins into the air and the contamination of water that runs into the lake [George].” That year, environmental consulting and remediation company ENACT began a “long-awaited cleanup” of the former Federated site.
To David Dabertin, a now retired EPA official and Hammond resident, history repeated itself in 2017. IDEM renewed Whiting Metals’s permit (which operates at the former Federated site), despite the EPA investigating off-site soil contamination in residential areas. This area included the St. Adalbert Catholic Church, which complained in 1939 that Federated’s noxious fumes kept students home. According to the Northwest Indiana Times, IDEM renewed the permit without a public hearing or meeting. Dabertin, one of the local children that had ridden his bike through the piles of metal dust, railed that issuing the permit in
an area where lead may be an issue without obtaining the test results is foolish and bordering on the negligent . . . The refusal to hold a public hearing is plain cowardice. And IDEM’s attempt to address my concerns about the prior ownership of the facility by relying on the unintelligible correspondence of its prior director is so nonresponsive it is insulting.
In April 2018, Dabertin introduced himself to Governor Eric Holcomb near the former Federated site and calmly informed him, “You are telling these people there is lead in their backyard, but [the state environmental agency] just permitted that facility to produce lead . . . That’s a disconnect.” Former U.S. EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt quietly accompanied Governor Holcomb on his visit to the EPA Superfund site and the following day authorized $1.7 million to remove contaminated soil. According to the Northwest Indiana Times, soil sampling detected the presence of lead above the EPA’s designated level. Removal of contaminated soil was slated to start the following week, beginning with properties inhabited by “sensitive populations,” such as pregnant women and children under the age of seven. But remediation costs at $50,000 per property, and the bankruptcy of Federated Metals, left no “responsible party” to replace the homeowner’s soil. It remains to be seen who will bear the financial burden of restoring the yards.
Will these efforts satisfy the community’s concerns about Federated Metal’s impact on their health? Or will they fall short, like Federated’s attempt to quell citizen protest in 1939 by replacing a problematic smokestack? That history is yet to be written.




