Historians tend to write about the leaders of movements – the “big picture” people espousing new ideologies or courses of action. This focus makes sense. These larger-than-life historical figures had an outsized impact on our past and they lend themselves to more dramatic stories. But what about the lesser-known folks who make change at a local level? Can we make space to honor these quieter voices and their work putting big ideas into action? In this post we’ll look at the late-in-life work of Jane L. (Brooks) Hine to save Indiana’s native bird species. While not one of the major voices of the burgeoning conservation movement, Hine’s ornithological work helped convince Hoosiers that birds were worth protecting as part of delicate ecosystems, from forests to farms.


Jane Levisa Brooks was born in Ohio in 1831 and studied literature at Oberlin College, graduating in the 1850s. She married her sister’s widower, Horatio Hine, adopting children from that union and having three more of her own. The family moved to a farm in Sedan, DeKalb County, Indiana in December 1861. Jane Hine focused on raising her children and helping with the farm work over the following decades. (The family also returned to Ohio for a time before circling back to the Sedan farm permanently). [1] It was not until the mid to late 1880s, when Hine was in her late fifties, that she began to study ornithology (the branch of zoology focused on birds). [2]

Women around the world were engaged in scientific work long before they were allowed to study at universities and gain accreditation. Hine joined an informal coterie of women doing physics equations, tinkering with inventions, and categorizing plant species at the kitchen table instead of the university laboratory. Without an avenue open for formal study, Hine simply followed her passion for birds. She became an ornithologist by doing ornithology. That is, she began keeping careful, scientific observations of the birds that populated the farmland and forests around her home in a journal. She also began attending the same meetings and reading the scientific journals of professionally-accredited ornithologists. For example, in 1890, Hine attended a meeting of ornithologists, mainly professors, which was part of a larger meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Indianapolis. [3]

Soon, other scientists came to respect and seek out her data. Amos Butler, a prominent ornithologist and a founder of the Indiana Academy of Science, sought Hine’s data for his Birds of Indiana report for the Indiana Horticultural Society. Amos extensively cited Hine’s observations on bird species around her Sedan home and called her “a faithful observer of nature and a careful recorder of her observations.” [4] Butler’s report was widely circulated by various organizations and the Horticultural Society made Hine a member. [5] After the publication of this report, Hine rocketed to prominence in naturalist circles.
By 1891, Hine was speaking regularly at Farmers’ Institutes, first in the nearby town of Waterloo, and then around the state. [6] Through these talks, she made a significant impact on bird conservation. At this time, many farmers saw birds as pests, nothing more than thieves of seeds and fruits, and shot them on sight. Hine knew she wouldn’t be able to convince everyone to love birds for their own sake as she did, so she found a more practical approach. She painted a larger picture of the ecosystem around farms, with birds as an essential component. Most significantly, Hine told farmers, birds ate the insects that ruined crops. This got their attention. After presenting at the Waterloo Farmers’ Institute in February 1891, the local newspaper reported:
Mrs. Hine is well known not only in this State, but throughout the U.S. among ornithologists, as one [of] the best among them in everything that pertains to the life and habits of the different birds that inhabit the forests and fields on our farms. Her description of different species of birds that were valuable to farmers as insect destroyers was listened to with marked attention by the many farmers present. [7]

In addition to her talents as a reliable collector of scientific data and a convincing speaker for bird preservation, Hine was a colorful and engaging writer. While she continued contributing ornithological data for scientific reports, she also began writing articles for scientific and general audiences. For example, she wrote “Tyrant Flycatchers” for the Waterloo Press in 1891 and contributed an article on thrushes, bluebirds, and robins to the Indiana Board of Agriculture report in 1893. [8] Most popular were the articles she penned for the Farmer’s Guide, which was published in Huntington, Indiana, but had statewide circulation and a large readership. She wrote “Birds That Befriend Our Trees” and “Farmers, Take Care of Your Birds,” both arguing for conservation of bird species. [9] In 1896, she contributed a series of articles under the title “Farm Birds in Northern Indiana,” carefully and colorfully describing bird species. [10] Readers, especially the young ones, couldn’t get enough of these articles from “Aunt Jane” and they clamored for more in their letters to the editor. [11]


By the turn of the twentieth century, Hine’s influence continued to grow. Butler again cited her data in a widely-circulated report for the Indiana Academy of Science. [12] She continued to present to Farmers’ Institutes but also to more general audiences, such as literary clubs, around the state. [13] Reporting on the 1899 meeting of the Indiana Audubon Society, the Waterloo Press called for several actions to protect birds. One of these was to have Hine speak widely to the public and especially school children to “awaken an interest in the dear birds by telling of their habits and her own experience watching them.” [14] The article highlights both her expertise and the regard to which her knowledge was held in her community, hinting at how contagious her enthusiasm must have been.
Hine also successfully advocated for the “Indiana Bird Law,” which protected insect-eating birds essential to the ecosystem and especially certain species of trees used in orchards and for timber. She told the Waterloo Press in 1904:
The people of DeKalb county have reason to be proud of our Indiana Bird Law. Only two counties of the state sent petitions, through their Farmer’s Institutes, to the State Legislature for its passage, without which no action could have been taken. Our county, DeKalb, was one of the two counties. The law provides for the protection of our insectivorous birds . . . Our timber and orchards have need of them. Sometimes, both before and since the passage of this law, there has been much slaughter among our woodpeckers . . . but that is in the past; and now boys let us loyally stand by our Indiana Bird Law. [15]

The farmers who attended the institutes where Hine regularly spoke had evolved from shooting the birds on their property to petitioning the Indiana General Assembly for their protection. Hine could have stopped there. She had influenced bird conservation and been accepted by the scientific community as an expert in her field. In fact, in 1906, she presented at the prestigious Twenty-Fourth Annual Congress of the American Ornithologists’ Union. [16] The Indianapolis Daily Sun referred to her as “one of the foremost authorities on native birds in the state.” [17] Fortunately for Hoosier bird lovers, she still had more to contribute.
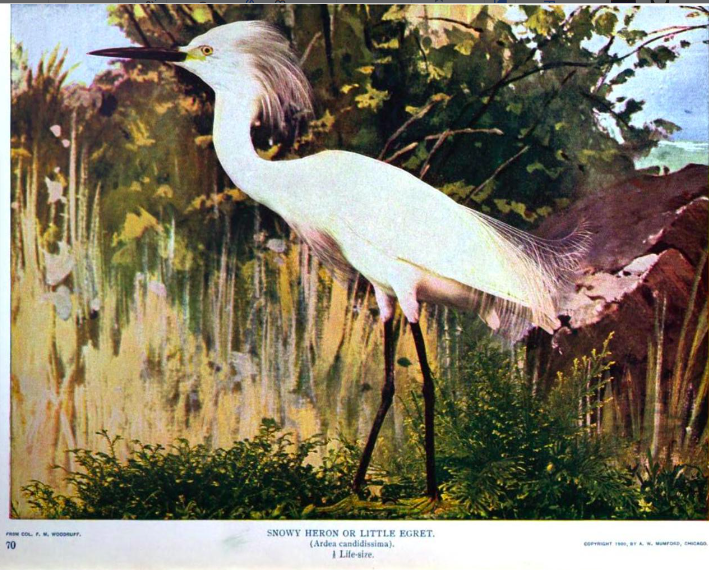
In 1911, at the age of eighty, Hine made perhaps her most notable contribution to Indiana ornithology in the form of “Game and Land Birds of an Indiana Farm,” published in the Biennial Report of the Indiana Commissioner of Fisheries and Game. [18] In this collection of articles on twenty-nine families of birds, Hine wrote vividly on her personal experiences with the various species and their characteristics and habitats. Her serene and poetic writing painted an idyllic picture of her farm and its feathered residents. She wrote:
I have seen, on a misty morning, an Egret that seemed, as it rose white and beautiful in the mist, more like a spirit than a bird. [19]

Each featured bird was accompanied by a full color photogravure (a type of photographic engraved print) taken by Hines. She also included a poem, “My Birds,” in which she made a passionate argument against the killing of birds for fashion or agriculture. [20] Instead she advocated for their protection, based in part on a religious argument and partly through descriptions of their unique beauty, characteristics, and contributions to the natural environment. The poem begins:
No bird that the Lord has created
Shall come to misfortune through me;
Not one of my jolly old Robins,
Though they take the fruit from my trees [21]
After several more stanzas describing all of “her” birds, she concluded:
Not one of my beautiful Wax-wings,
Though they take my cherries I know;
Not one of the birds God has given me;
Not even my jaunty old Crow.Shall have from me aught but kind treatment,
When He who created them all,
Would feel both compassion and sorrow
If even a Sparrow should fall. [22]
Newspapers and magazines raved about the collection of articles, reprinted large sections, and included her poem as well. She became known far and wide as “the bird woman of Indiana.” [23] For the next few years she continued speaking to local clubs, but her major work was complete. Jane L. Hine died in Sedan on February 11, 1916. [24] The Waterloo Press praised her as “an authority” on ornithology and the natural sciences. [25] Other newspapers, scientific journals, and the Indiana Audubon Society also paid tribute to her contributions. [26]


It would be difficult to quantify Hine’s impact on the conservation movement or summarize her exact place in the history of women in science. But maybe each spring when we hear the birds chatter outside our windows we can just take a minute to thank Hine for protecting our native species at a time when they had few voices to speak for them.
Learn more about bird conservation in Indiana through the Indiana Audubon Society.
Notes
[1] 1850 United States Federal Census, Berlin Township, Erie County, Ohio, August 29, 1850, National Archives, Record Group 29, Series Number: M432, Page 460A, Line 10, AncestryLibrary.com; 1860 United States Federal Census, Berlin Township, Erie County, Ohio, June 14, 1860, National Archives, Record Group 19, Series Number: M653, Page 172, Line 38AncestryLibrary.com; 1870 United States Federal Census, Lawrence / Richland Township, DeKalb County, Indiana, Roll: M593_309, Page 364B, National Archives and Records Administration, Ancestry.com; Seventy-Fifth Anniversary General Catalogue of Oberlin College, 1833—1908, (Cleveland, OH: O. S. Hubbell Printing Co., 1909), 121, HathiTrust; Marriage Record, Lake County Ohio Courthouse Records, p. 160, Various Ohio County Courthouses, 1853-1875, Film Number 000974916, AncestryLibrary.com; History of DeKalb County, Indiana (Indianapolis: B. F. Bowen & Company, 1914), 991-92, GoogleBooks; “Mrs. Jane L. Hine Died Early Saturday Morning,” Waterloo Press, February 16, 1916, 1, 8, Newspapers.com; “Jane L. Hine,” photograph of grave, Waterloo Cemetery, DeKalb County, Indiana, Find A Grave Index, AncestryLibrary.com.
[2] “Noblesville,” Waterloo Press, June 14, 1888, 8, Newspapers.com; Jane L. Hine, “Water Birds and Waders of Our Indiana Farm,” [Hine’s journal], circa 1880s, transcribed in Terri L. Gorney, Jane Brooks Hine: An Indiana Bird Woman (self-published, 2014), Indiana State Library.
[3] “The Men of Science,” Indianapolis News, August 21, 1890, 1, Hoosier State Chronicles.
[4] Amos W. Butler, Birds of Indiana with Illustrations of Many Species, pamphlet (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Burford, State Printer, First Published 1890), 5, 59, 63, 83-84, 92, 100, 102, 104-105, 117, GoogleBooks; Amos W. Butler, “A Catalogue of the Birds of Indiana” in Transactions of the Indiana Horticultural Society for the Year 1890 (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Burford, State Printer, 1891), Appendix C, GoogleBooks.
[5] Transactions of the Indiana Horticultural Society for the Year 1890 (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Burford, State Printer, 1891), 12, GoogleBooks.
[6] “Farmers’ Institute,” Waterloo Press, March 5, 1891, 1, Newspapers.com; “Sedan,” Waterloo Press, January 28, 1892, Newspapers.com.
[7] “Farmers’ Institute,” 1.
[8] Jane L. Hine, “Tyrant Flycatchers,” Waterloo Press, March 19, 1891, 5, Newspapers.com; Jane L. Hine, “ A Family of Feathered Friends,” in Forty-Second Annual Report of the Indiana State Board of Agriculture, 1892-1893 (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Buford, Contractor for State Printing and Binding, 1893), 555-56, GoogleBooks.
[9] Jane L. Hine, “ A Family of Feathered Friends,” in Forty-Second Annual Report of the Indiana State Board of Agriculture, 1892-1893 (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Buford, Contractor for State Printing and Binding, 1893), 555-56, GoogleBooks; W. S. Blatchley, ed., Indiana Department of Geology and Natural Resources Twenty-Second Annual Report (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Buford, Contractor for State Printing and Binding, 1897), 544, GoogleBooks.
[10] W. S. Blatchley, ed., Indiana Department of Geology and Natural Resources Twenty-Second Annual Report (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Buford, Contractor for State Printing and Binding, 1897), 544, GoogleBooks.
[11] Farmer’s Guide, July 3, 1897, 11, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, July 17, 1897, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, August 28, 1897, 11, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, September 4, 1897, 11, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, September 11, 1897, 11, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, November 13, 1897, 11, GoogleBooks; Farmer’s Guide, February 22, 1902, 123, GoogleBooks.
[12] A. W. Butler, “Additional Notes on Indiana Birds,” in Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science, 1894 (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Burford, State Printer, 1898), 162-166, HathiTrust.
[13] No Title, Waterloo Press, January 20, 1898, 1, NewspaperArchive.com; “Institute Proceedings,” Albion Noble Democrat, February 10, 1898, 1, NewspaperArchive.com; “Sedan Bulleted,” Waterloo Press, October 13, 1904, 8, Newspapers.com; “Sedan,” Waterloo Press, October 12, 1905, 8, NewspaperArchive.com.
[14] “Our Native Birds,” Waterloo Press, March 9, 1899, 5, Newspapers.com.
[15] “Our Indiana Bird Law,” Waterloo Press, November 24, 1903, 1, Newspapers.com.
[16]“The Twenty-Fourth Annual Congress of the American Ornithologists’ Union: Program,” in Bird Lore, edited by Frank M. Chapman (Harrisburg, PA and New York City: D. Appleton & Co., 1906), 212, GoogleBooks.
[17] “Local and General,” Indianapolis Daily Sun reprinted in the Waterloo Press, August 3, 1911, 4, Newspapers.com.
[18] Jane L. Hine, “Game and Land Birds of an Indiana Farm,” in Biennial Report of the Commissioner of Fisheries and Game for Indiana (Indianapolis: Wm. B. Burford, State Printer, 1911), 294-470, GoogleBooks.
[19-22] Ibid.
[23] “Game and Land Birds of an Indiana Farm, Fort Wayne Journal-Gazette, August 6, 1911, 1, NewspaperArchive.com; “Talked on Birds,” Waterloo Press, May 16, 1912, 1, Newspapers.com.
[24] “Personal Mention,” Waterloo Press, April 25, 1912, 5, Newspapers.com; “Local and General,” Waterloo Press, January 28, 1915, 8, NewspaperArchive.com; “All Around Pick Up,” Waterloo Press, May 27, 1915, 4, Newspapers.com; Indiana State Board of Health, “Jane Hine, Certificate of Death, February 11, 1916, Richland Township, DeKalb County, Indiana, p. 127, Indiana State Board of Health Death Certificates, 1900-2017, microfilm, Indiana Archives and Records Administration Roll Number 04, AncestryLibrary.com; “Mrs. Jane L. Hine Died Early Saturday Morning,” Waterloo Press, February 16, 1916, 1, 8, Newspapers.com.
[25] “Mrs. Jane L. Hine Died Early Saturday Morning,” 1.
[26] “Reports of Affiliated State Societies and Bird Clubs: Indiana Audubon Society” in Bird Lore, edited by Frank M. Chapman (Harrisburg, PA and New York City: D. Appleton & Co., 1917), 447, GoogleBooks; John Hall Sage, “Thirty-Fourth Stated Meeting of the American Ornithologists’ Union,” in The Auk: A Quarterly Journal of Ornithology 42, (1917), 76-77, GoogleBooks.