Two or three black men brought segregation of Indianapolis’s YMCA into sharp focus in 1888, when they attempted to join the organization. Although the YMCA lacked an official policy mandating segregation, they denied the black mens’ applications. Two years later, a group of African American men formed a Young Men’s Prayer Band in Indianapolis. By 1902, this band merged into a “colored Y.M.C.A.”
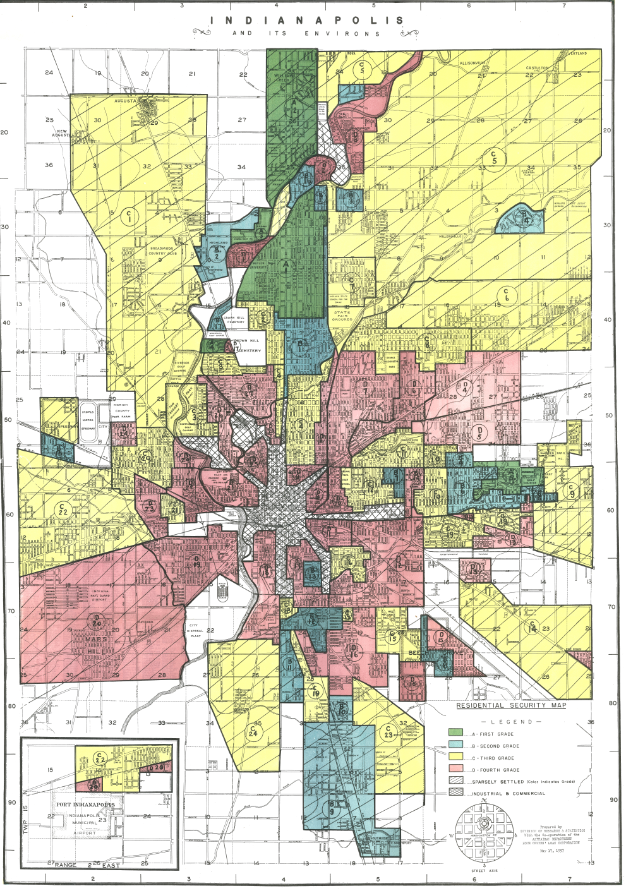
The Y opened at the tail end of a major influx of African Americans to the city following the Civil War and Reconstruction. In the forty years between 1860 and 1900, the African American population of Indianapolis grew 3,000 percent. Many white residents did not welcome these newcomers. Oftentimes, African Americans were relegated to segregated areas of the city due to housing discrimination and exclusion from facilities. Indiana Avenue was at the center of the largest African American community in the city, with 30,000 black residents living within a ten mile radius of the Avenue by the 1950s.
The establishment of this YMCA provided facilities for those men who had been excluded from the central organization. In an Indiana Magazine of History article, Dr. Stanley Warren points out that:
the necessity of finding a way to survive within a limiting system driven by segregationist tendencies has been the base from which many great African-American traditions and organizations have begun.
In the capital city, the organization then called “The Indianapolis Colored YMCA” served as an example of these great African-American traditions. Emerging out of the discriminatory practices of Indianapolis, this branch of the “Y” grew into one of the largest and most influential black YMCAs in the country.
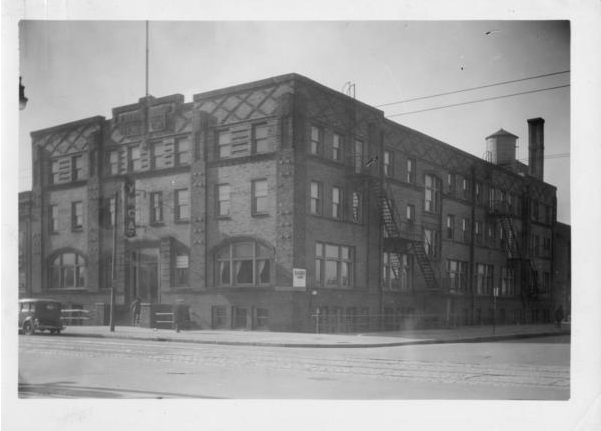

Before that could happen though, they needed a building able to accommodate their rapidly growing membership. By 1911, just nine years after its formation, the YMCA outgrew its building located at California and North Streets in the city. To remedy this, they proposed the construction of a new building. The building cost an estimated $100,000, a figure that seemed unobtainable to many in the community, where even the working professionals barely got by due to the limited job opportunities available to them.
Fortunately, just as the YMCA members began to plan their fundraising strategy, they gained a rather unlikely ally in a white, Jewish, Chicago businessman. Julius Rosenwald, part-owner of Sears, Roebuck, and Company, announced that he would give $25,000 to any community able to rise $75,000 towards the construction of a Colored Young Men’s Christian Association. With this support, members of the Indianapolis Colored YMCA joined forces with the white members of the Central YMCA for an incredible fundraising push. Two teams formed, one for the white members and one for the black members, and they set out on their mission. In just ten days, they surpassed their $75,000 goal. African American entrepreneur Madam C.J. Walker was one of the largest contributors to the YMCA’s Building Campaign Fund.
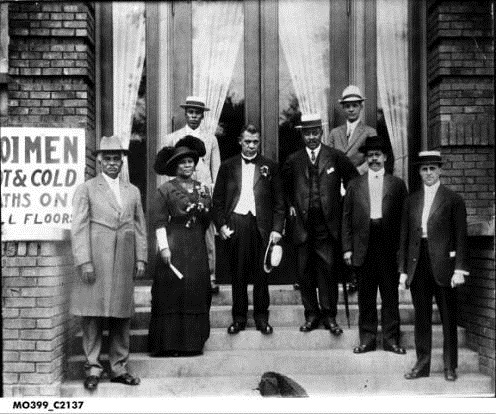

On July 28, 1912, with a crowd of over 5,000 people in attendance YMCA committee men broke ground on the site of the new building. Three months later another celebration with thousands of spectators was held for the laying of the cornerstone. Workers completed construction on the building, located at the corner of Michigan Street and Senate Avenue in downtown Indianapolis, in July 1913.
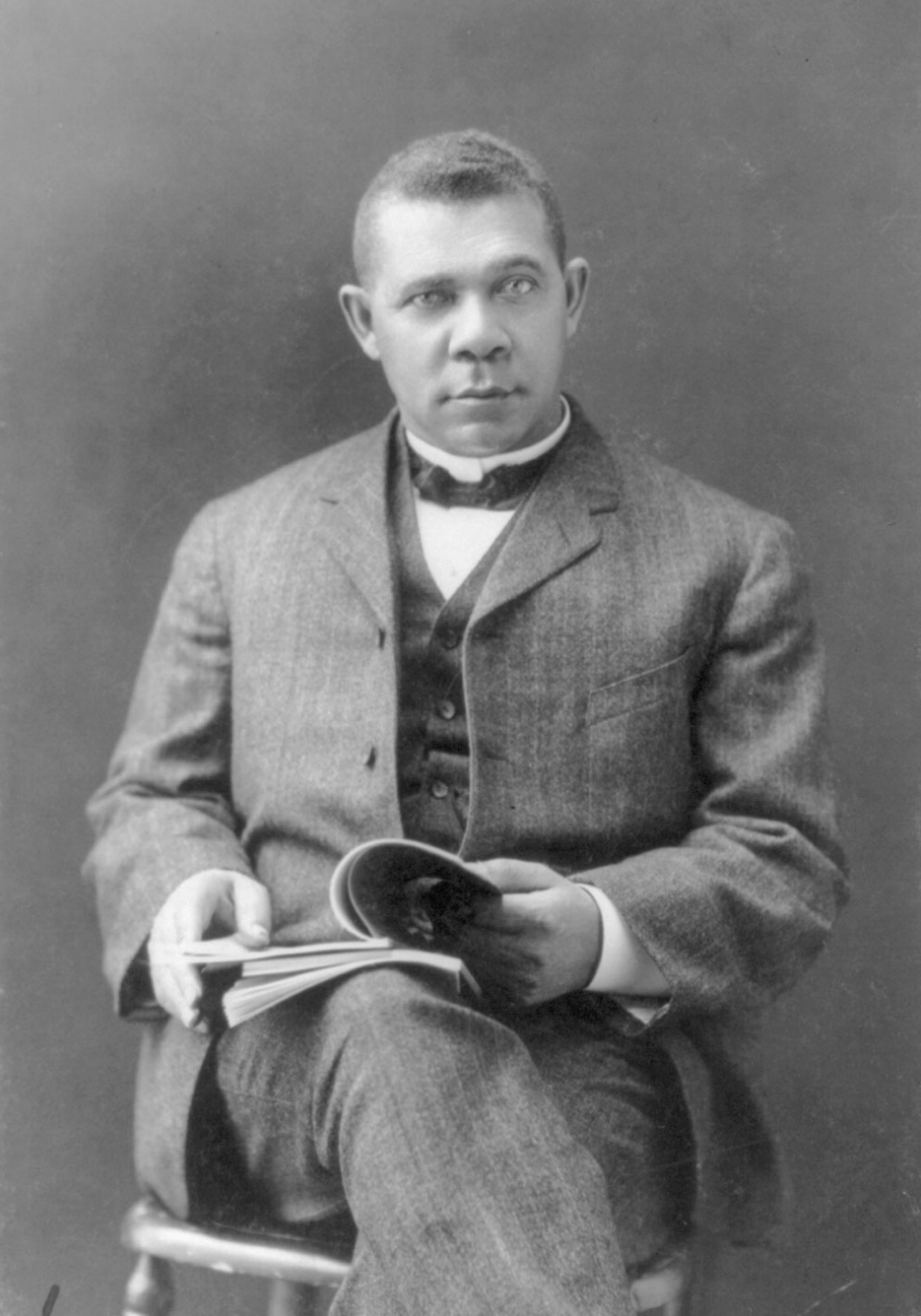

YMCA members held a week of festivities and ceremonies in celebration of the opening of the new Senate Avenue Y, as it was called. Celebrations-attended by both black and white residents-included a ladies night, fraternal night, and athletic night. The highlight of the week, though, was Tuesday July 8 – the official dedication, which featured an address by Booker T. Washington, civil rights activist and founder of Tuskegee institute.In his address, Washington commended the citizens of the city, black and white, for banding together to make the Senate Avenue Y a reality. Then, he said:
I am proud of being a member of the Negro race and never
more so than tonight. I spurn the men who sympathize with me because I am a member of the Negro race. We have work to do and difficulties to overcome . . . Let the white people know about the good deeds in our race. In too many cases white people hear only of crime. They do not hear about the hard-working, industrious, sober colored men, and Indianapolis has many of the latter class.
In many cases, African American churches were the heart of the black community. The Indianapolis Colored YMCA, itself a Christian organization, became another center of the African American community in Indianapolis. Majority black neighborhoods such as this did not have access to the same social, recreational, and charitable organizations as the white communities. Because of these segregationist policies, black communities had long provided these facilities for themselves, often led by their churches. This is where the Senate Avenue Y stepped in, building on and expanding the work of African American churches. The Senate Avenue Y was located in the heart of the Indiana Avenue African American community and offered adult education classes, held bible studies, provided meeting space for a variety of organizations, and even established an amateur basketball team.

According to historians, these Senate Avenue programs:
fostered self-respect and self-reliance and tried to provide young men with proper role models and male companionship . . . [they] served as sanctuaries which preserved African American Masculinity and prepared black men and boys for their leadership role in the struggle for equality that lay ahead.
In order to reach more and more young men and boys, the Y held annual membership drives. These campaigns borrowed military organizational structures, dividing members into divisions of “enlisted men.” These men worked hard to recruit as many new members as possible. Those groups that enlisted the most new members were inducted into the Society of High Producers and The Royal Order of the Spizzerinktum, meaning “the will to succeed.” These tactics worked fabulously; membership jumped from just fifty-two in 1903 to over 5,000 by 1930.

These wildly successful membership drives turned the Senate Avenue Y into one of the largest African American YMCA branches in the country. But being large does not necessarily make an organization important or influential. To understand the influence of the Y, we need to go right back to the very beginning of the branch, to the establishment of Monster Meetings.
The roots of the Senate Avenue YMCA Monster Meetings can be traced to the very early years of the Indianapolis Colored YMCA, and executive secretary Thomas Taylor. He instituted public forums where men, and later women, could gather on Sunday afternoons between November and March to listen to lectures on a wide variety of topics. Originally, Taylor wanted to call the forums “Big Meetings” but the proposal was rejected by the Central YMCA board because their annual meeting was already being called the Big Meeting. So, Taylor one-upped them and labeled his forum series the “Monster Meetings.” Taylor could not have known how fitting that name would become.
In the Taylor years, the meetings featured local religious leaders speaking almost exclusively on religious matters, but in 1916 a new executive secretary took the meetings to a new level. That executive secretary was Faburn Defrantz. (In 1947, he successfully spearheaded the effort to convince IU to allow African American basketball player Bill Garrett to play for the school’s varsity team. A “gentleman’s agreement” had barred African Americans from playing in the Big Ten).

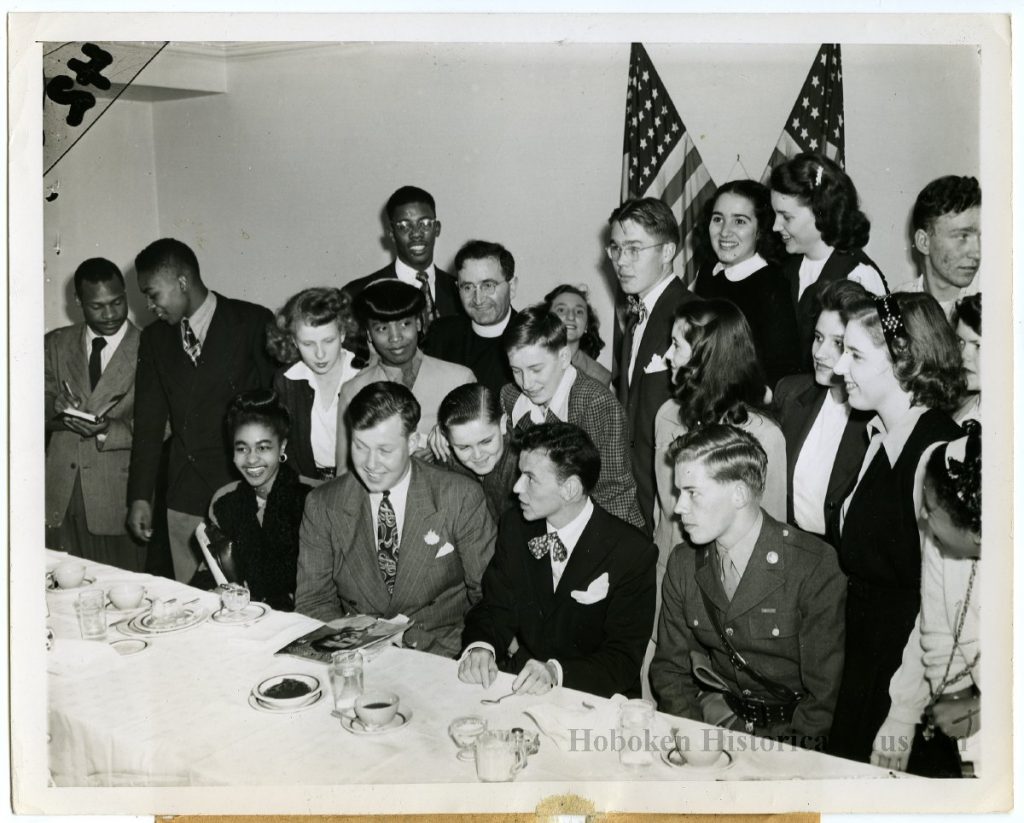
During DeFrantz’s tenure, Monster Meetings continued to feature local ministers delivering religious messages. But they soon expanded to include some of the most well-known African American leaders in the nation, speaking on a variety of hot-button issues. In his seminal article “The Monster Meetings at the Negro YMCA in Indianapolis,” Dr. Stanley Warren provided a list that sampled some of the hundreds of speakers and topics featured at Monster Meetings during the DeFrantz years. These included authors, NAACP leaders like Walter White, professors, university presidents, politicians like Governor Paul V. McNutt, newspapermen, famous athletes such as Olympic gold medalist track star Jesse Owens, religious leaders, and former First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt. Unfortunately, I have not located a collection or archive containing the speeches given at these Monster Meetings. Luckily, some snippets of some of the lectures are preserved in the pages of newspapers like the Indianapolis Recorder.
The lectures bespoke major events and concerns of the period. In 1930, months after the 1929 stock market crash, Freeman B. Ransom, attorney for the Madam C. J. Walker Company, discussed “Unemployment and How to Solve It.” In 1931, during the Prohibition Era, Reverend Charles H. Winders and Boyd Gurley debated the question “Prohibition: Shall Indiana Stay Dry?” Dr. George Washington Carver, Director of agricultural research and professor of chemistry at Tuskegee University, asked in 1932 “Great Creator, What Is a Peanut, Why Did You Make It?”
In 1940, as World War II raged in Europe, Dr. Max Yergan spoke on “Democracy: A Goal to Defend.” After U.S. entry into World War II, Dr. Lorenzo Greene spoke on “The Negro in National Defense,” Phillip Randolph lectured about “The Negro in War and Peace,” and William Hastie discussed “The Fight Against Discrimination in the Armed Forces.”
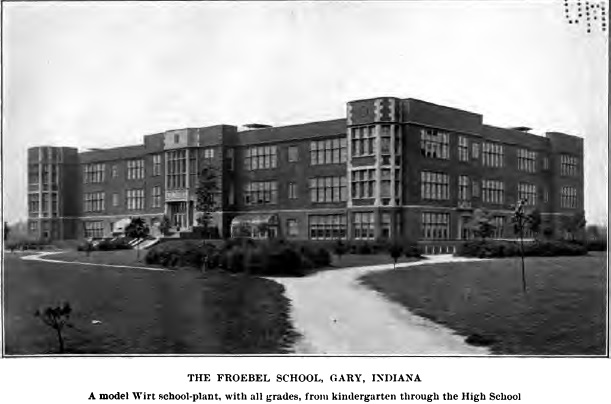
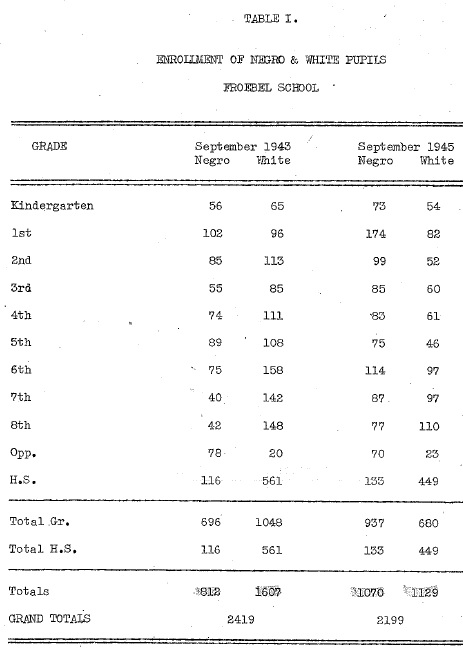
In 1947, one year after the Froebel School Board in Gary, Indiana voted for desegregation after hundreds of white students staged a walk out in protest of integration, Joseph Chapman spoke on “Democracy in Gary Schools.” In the early Cold War era, Former Crispus Attucks teacher and the first African American woman to study at the University of Oxford spoke about “Education and International Good Will” in 1952. Former First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt spoke to a desegregated audience at the Murat Temple about “International Human Rights” in 1953.
And finally, leading up to and during the Civil Rights Movement, speeches such as “Integrated Society or a Segregated Society,” “The Civil Rights Crisis and American Democracy,” and “The Civil Rights Resolution in America” demonstrated that the black citizens of Indianapolis’s discussed and debated the same issues as those around the nation. The following details some of the most prolific speakers at the Monster Meetings:
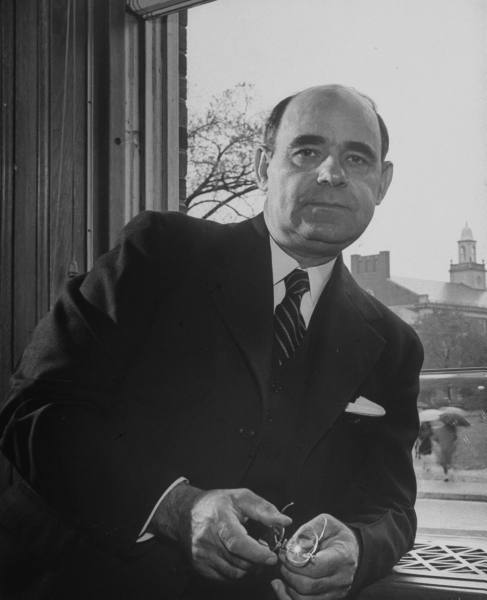

Dr. Mordecai Johnson was a fixture of the Monster Meeting schedule, opening the meeting season for over forty consecutive years. He got involved with the YMCA in 1916, when he served as a student secretary and became a life-long supporter of the association. In 1926, Dr. Johnson became the first African American president of Howard University, one of the nation’s historically black universities. He served in that capacity until 1960. During his decades speaking at Monster Meetings, he covered a wide range of topics, including:
- “Anti-Semitism and the Negro Ministry”
- “Civilization’s Civil War”
- “Implications of the Atomic Bomb”
- “Ghandi and the Liberation of India”
- “Segregation is Suicide”
Described as a man who “made people listen even when they did not believe,” Johnson was a powerful speaker and he lent his skill to important topics. As Cold War tensions mounted, he spoke of the dangers American segregation posed to the nation. He said:
“Through our nation’s moral weakness caused by segregation, we are committing scientific and technical suicide. We are five years behind militarily due to this moral weakness. Oh my brothers, let us pray it is not too late – only Almighty God knows whether it is not too late already…”
He went on to address the recent affirmation of Brown Vs. Board of Education, which declared segregated schools unconstitutional.
“It is my judgement that the death knell of segregation has been sounded. I see no disposition on the part of the Supreme Court to yield to the opponents of integration. The Court is informed by a sense of world duty which is inexorable.”
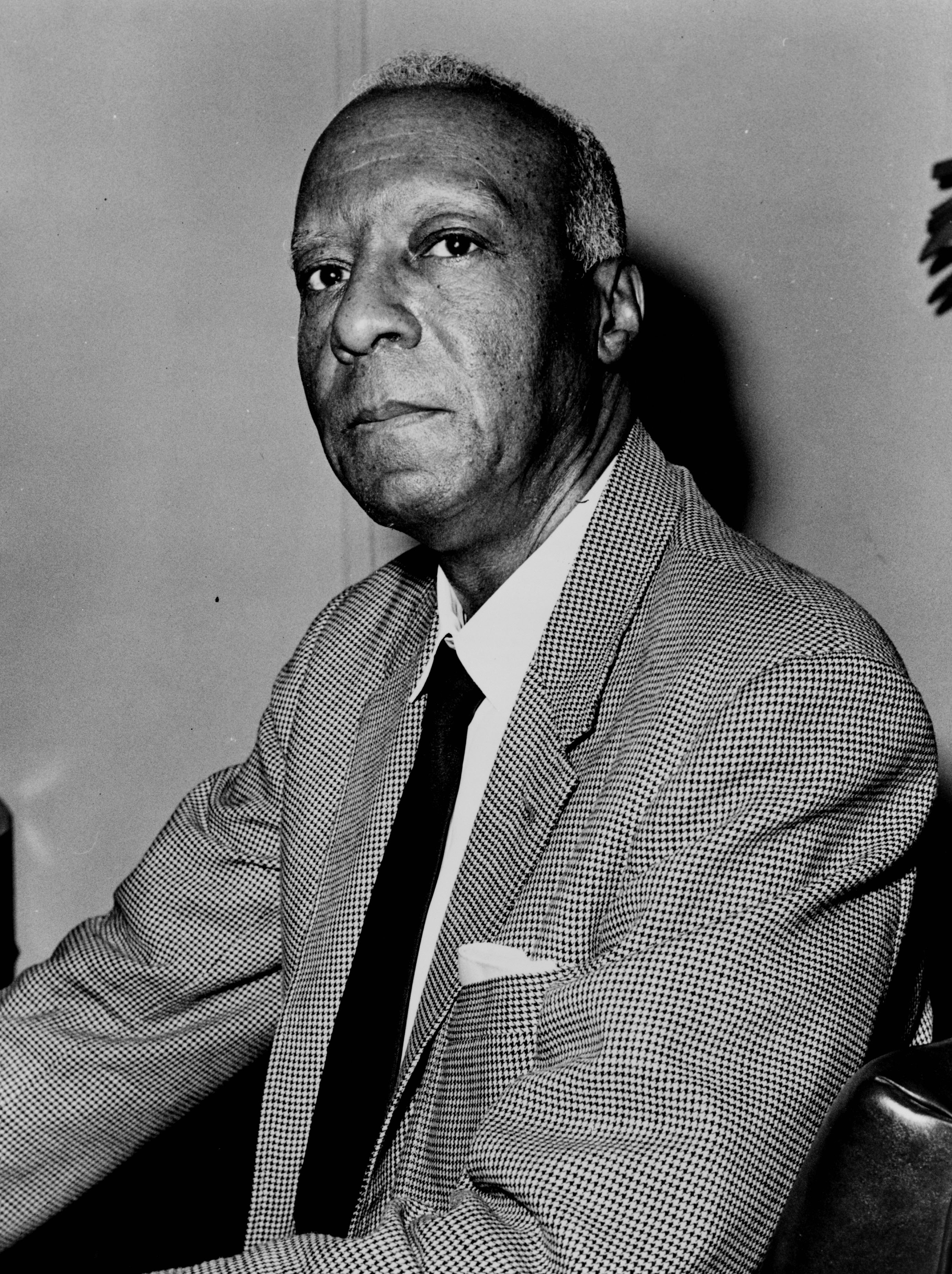

Another name that appears more than once in the list of prominent figures featured at Monster Meetings is that of A. Philip Randolph. In 1925, Randolph organized the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, the first labor union comprised principally of African American workers. A major civil rights activist, he played a large part in pressuring President Franklin Roosevelt to issue an Executive Order that banned discrimination in World War II defense industries. He also pressured President Harry Truman to issue an Executive Order that ended segregation in the armed forces. (The 1945 Freeman Field uprising in Seymour, Indiana, where Tuskegee Airmen protested illegally-segregated officers’ clubs by forcibly entering the white officers’ club, also played a large part in Truman’s Executive Order). Randolph was not satisfied with those successes, though. In 1955, he stood in the Senate Avenue YMCA and declared:
“Negroes are yet second class citizens. Civil revolution was never completed, free public schools were never established, Negroes cannot buy property where they wish, nor can they enter certain businesses. They cannot join all the various unions. The Negroes cannot vote in some parts of this county; therefore they are not yet free.”
Later, in 1963, Randolph organized the March on Washington, where Reverend Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his “I Have A Dream” speech, which highlighted the injustice of many of the same racist, segregationist policies Randolph underscored in his Monster Meeting lecture.

In 1958, Martin Luther King Jr. himself, made an appearance on the YMCA Monster Meeting roster with a speech entitled “Remaining Awake through a Revolution.” Due to intense interest in King’s lecture, organizers moved the event to Cadle Tabernacle, which could accommodate a larger audience. In one of his first public appearances since he suffered a brutal attack at a book signing that year, the Baptist minister maintained his message of nonviolence, urging the use of love in the face of violence. He proclaimed:
“A new age of justice is challenging us to love our oppressors . . . We must not assume this new freedom with attitudes of bitterness and recrimination, for, if we do, the new age will be nothing but a duplicate of the old one . . . A new world is being born, and the old world will die. We must be prepared for the new world to come. Segregation is nothing but slavery covered up with certain niceties and complexities. If our democracy is to live, segregation must die . . . Use love. Love is a sure winner. Remember that as Christians we are working with god. If we do it the way God wants us to do it, we will be able to sing with pride, ‘My Country ‘tis of thee’ for Freedom must ring from every mountainside.”
The Senate Avenue YMCA Monster Meetings played a central role in not only educating members about topics of local, national, and international importance, but also in galvanizing the community into action. According to Dr. Warren, “As the popularity and importance of these mass education meetings grew, both the public and YMCA members exhibited a higher level of community activism.” For those who regularly attended Monster Meetings, the YMCA became a foundation for the changes that they worked towards in the coming decades. The meetings were a place where, in the words of Dr. Mordecai Johnson, “The redcap and the lawyer, the laborer and the doctor, seek together to find answers to social and political questions.”
*Interested in the Civil Rights Movement in Indiana? Check out this post about the 1972 National Political Black Convention, which drew over 10,000 black Americans to Gary. Influential leaders, such as Black Panther co-founder Bobby Seale, Revered Jesse Jackson, and Coretta Scott King, lent their support in creating a cohesive political strategy for black Americans.