A Purdue forestry student wrote in the forestry department’s satirical yearbook, The Log, in 1934,
If you can read, sometime and somewhere you have read of great discoverers that have made what we call History. Some of these famed discoverers and explorers were men such as Columbus, Balboa, and Magellan, but they are the past. Now, what I want to tell you about is the explorers of today, and the vast areas that have yet to be trodden by mankind.
These contemporary explorers were the freshman class of the Purdue forestry school, who braved the “Wilds of Southern Indiana,” every summer to practice forestry at the Purdue Forestry Summer Camp at the Clark State Forest, near Henryville, Indiana from 1929-1958. The summer camp, still in operation today in Michigan, provided a place for forestry students to apply the theories they learned in the classroom, bond with fellow classmates, and facilitate sustainable forestry management in Indiana and the greater Midwest.
Purdue first offered forestry classes during the 1905-1906 school year, and by 1926, Purdue had its own forestry department within the School of Agriculture. Though Purdue forestry students had been taking week-long trips to the Clark State Forest to study and practice forestry for years, the new department head, Burr Prentice, decided that a longer, more formal period of study was needed to prepare Purdue forestry students for the job market. Prentice established the first forestry camp in the summer of 1929. For eight weeks, the entire forestry student body roughed it in the Clark State Forest, and completed surveys, conducted research, and learned how to properly manage timber to ensure a sustained timber yield. It was so successful that students returned to the forest to work every year until 1958.

Clark State Forest, Indiana’s first state forest, served as an ideal place for the students to practice forestry. Indiana established the forest in 1903 to lead the way in the state’s reforestation. Originally, half the land that currently comprises the United States was covered in forests; Indiana alone contained 20 million acres. However, like many forests nationwide, European-American settlers cleared much of Indiana’s forests for farming, fuel, and lumber by the mid-19th century. The widespread clearing of forests helped foster a new conservation ethic in the nation and Indiana in the late 19th century that advocated a different perception of natural resources. Instead of viewing natural resources, including forests, as inexhaustible, conservationists advocated using science and technology to rationally plan efficient development and use of natural resources to ensure enough would be available for future generations.
Foresters, including Indiana’s first state forester, the noted botanist Charles C. Deam, started practicing scientific forestry to help conserve enough trees for future use. They made sure annual cutting did not exceed annual growth of trees, employed methods to reduce disease and fire damage of trees, and conducted experiments to discover which trees were best suited to their specific location. By the time the Purdue forestry students arrived in 1929, the forest had grown from an original 2,000 to 5,000 acres. It also featured a large reserve of hardwood timber and evergreens, as well as over 100 experimental tracts Deam had created and monitored for years to help determine the trees that grew best in Indiana’s soil and climate.
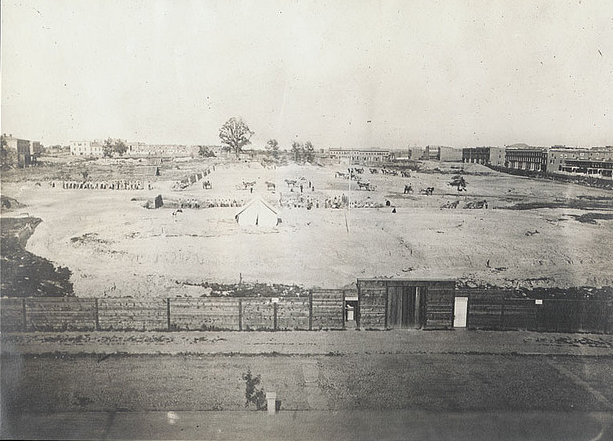
The first camp site at the forest was far from glamorous. The only building for the students was an old red barn, which served as a kitchen, dining room, and study hall.

Students lived in tents pitched over wooden platforms, which were only big enough for two bunks and a small walkway. There was no running water or electricity. Students had to take turns carting water from the Forest Supervisor’s home for drinking, cooking, and bathing, so it was used sparingly. The rustic accommodations, and hot and dirty surroundings, inspired the students to christen their camp “Camp Butt.” Students nicknamed Stinky, Shiny, and Rosey even lovingly built a sign bearing the name for their camp in 1932 that the director of the camp, Professor Geltz, allowed them to keep for “the admiration and reverence of the coming generations.”
In 1933, the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) began work in the Clark State Forest. Part of their duties involved building a mess hall, study hall, modern bathroom, an instrument shed, and student and staff tent frames for the forestry camp. Students in The Log expressed uncertainty about their new campsite, saddened that their original campgrounds would “no longer flourish in all its simple grandeur.” One student wrote
Electricity and running water can’t always be a companion of the ambitious forester. Those facilities, in my opinion, are for foresters that can’t take it.
However, the thirty nine students who arrived at the new camp in 1935 found it unfinished. Thankfully, there was still no electricity, running water, or showers.

But, there was a big mess hall and study hall complete with two fire places. Even when the entire modern camp was finished in 1936, Professor Geltz created a side camp to keep the tradition of rough living conditions alive that would show the students what field work in forestry was like. The students began spending a week of their experience living in the side camp, sleeping under the stars in tents, cooking for themselves, and writing field notes by lantern light in the evenings.

Since the students spent so much of their time working, they seemed to have spent little time in their new, luxurious accommodations anyway. The work day was from 8AM to 5PM, Monday through Friday, and from 8AM to 4PM on Saturday. The students spent most days in the field, practicing dendrology (study of trees), silvics (growing and cultivation and trees), mensuration (measuring the growth and yield of timber), entomology (study of insects), and surveying, building roads or trails, maintaining the state forests’ buildings, or working in the nursery. In addition to forestry work, each student also had a special assignment to help cook meals, clean, chop wood for fuel, hall water, and other chores. After supper, students studied together in the study hall.

When the camp was shut down during World War II, Purdue forestry professors decided students could handle even more work and revised the curriculum. The department increased the camp from eight to ten weeks long and required the students to complete three courses (forest surveying, applied silviculture, and forest measurements) while attending. Instead of attending after their freshman year, students now arrived ready to work at Henryville after their sophomore year.
However, true to form as young college students, the campers still found ways to have fun in their off time. They played hockey, swam, and hiked. During the 1930s,

the students played baseball games against the CCC men also working in the state forest, who had their own athletic field. On Wednesday and Saturday nights, the students were allowed to leave the camp. Many of them went to nearby Henryville to play pool or date the local girls. Most years also included a special trip to Louisville to tour Churchill Downs, the Slugger baseball bat factory, and a saw mill.
The students also dabbled in sketching and writing poems, essays, and jokes to express themselves in their free time. Existing copies of The Log contain humorous recollections of daily activities in the camp, cartoons, and poems about forestry work. Clement Bryan, a forestry student from 1933-1937 who edited the summer camp yearbook in 1934 wrote the following simple poem after a hard days’ work as a forester at camp:
Tired and weary,
Sweaty,
Dirty,
Lagging step and listless hands;
His work done
–the forester.

Unfortunately, in 1954 rumors started that the US Highway 65 (now Interstate 65), which roped around the forest, would be rerouted through the campsite. The students spread through the forest to investigate and found a State Highway Commission crew surveying the area for the new highway that would pass within a few feet of the camp. In 1958, the Purdue Forestry department acquired 17 buildings for a new campsite along the shores of Lost Lake in the Nicolet National Forest, near Tipton, Wisconsin. The last camp held at the Clark State Forest ended in August 1958.
Forestry students included an article in their 1959 Log year book dedicated to the closing of the camp at Clark State Forest to show how embedded the camp was in Purdue forestry tradition.
Since the summer of 1929 nearly 800 students and staff have studied, and taught, and cried, and laughed, and sweat[ed], and learned, and lived, at the Forestry Camp, Henryville, Indiana. But on August 1, 1958…the camp was abandoned. But memories of the camp will never die, and for years to come Purdue foresters will talk about ‘when the camp was at Henryville.’
Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources is one of a few universities that still offers a residential camp for students. Increasing expenses led many universities to eliminate their camps. Purdue’s camp survived because of the generosity of John S. Wright, who endowed the program to keep it affordable for students. The camp now also includes students in other disciplines, such as fisheries, aquatic sciences, and wildlife. Participants focus on land measurement, surveying, inventory of natural resources, and resource management. The 2016 summer camp was held in Iron River, Michigan. To enjoy more of the school’s history, explore their FNR Past and Present webpage, which contains histories and photos of the summer camp, copies of The Log year book, and class photos from 1938.