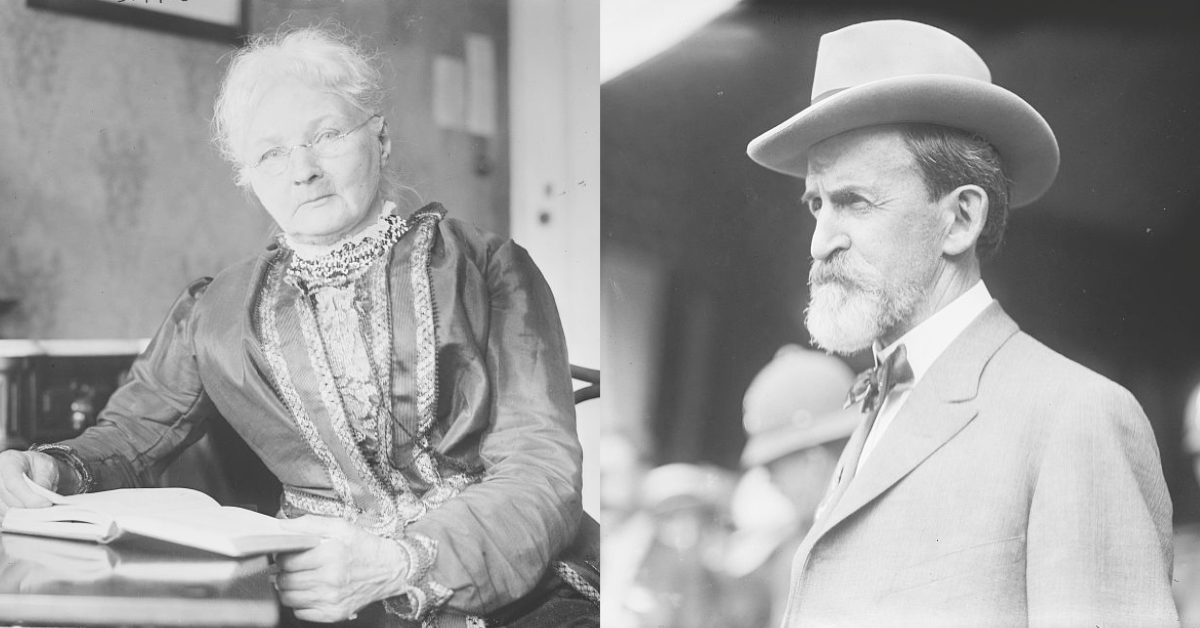
During the peak of labor struggles in the early 20th century, almost no figure was as recognized and loved by workers than Mary “Mother” Jones. An Irish immigrant who dedicated her life to cause of labor, Jones was described by the Evansville Courier as “probably the most widely known woman labor leader in the United States.” During her decades in the struggle, Mother Jones traveled all around the country organizing coal miners for the United Mine Workers of America (UMWA), catching the ire of mine owners and the political leaders that supported them. However, one member of the political establishment that Jones not only liked but even campaigned for was Democratic Indiana Senator John W. Kern. A dedicated defender of organized labor himself, Kern used his power in the U.S. Senate to advocate for Jones’s release in the summer of 1913 while she was imprisoned for organizing coal miners. Years later, she campaigned on his behalf, reminding labor that Kern stood up for her when very few public leaders would. Their political partnership stands out as one of the most unique pairings during America’s Progressive Age.
Contrasting Journeys, Converging Missions
While Mary Harris “Mother” Jones claimed to be born on May 1, 1830, she was likely born in 1837 in Cork, Ireland to Richard and Ellen Harris. Details about Mother Jones’s birth and childhood are scant. “My people were poor,” Mother Jones wrote in her autobiography, “For generations they had fought for Ireland ‘s freedom. Many of my folks have died in that struggle.” When she was a teenager, Jones and her family emigrated to Canada. “His [Richard Harris’s] work as a laborer with railway construction crews took him to Toronto, Canada,” Jones wrote years later, noting “Here I was brought up but always as the child of an American citizen. Of that citizenship I have ever been proud.” The exact date of their departure to America is unclear, but as biographer Elliot J. Gorn writes, “by the early 1850s, they had saved enough for Ellen and the children to set sail for North America. The family was soon established in Toronto, with Richard Harris, approaching fifty, working on the rapidly growing Canadian railroads.”
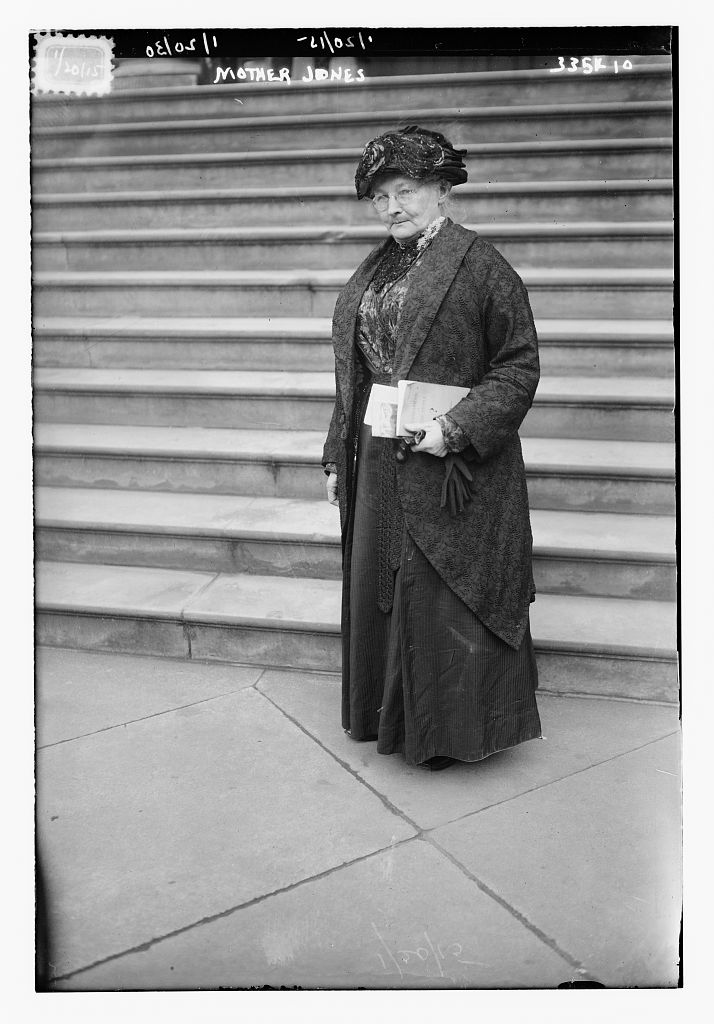

Her early education equipped her with skills she would use for decades as a labor organizer. “After finishing the common schools,” she recalled later, “I attended the [Toronto] Normal school with the intention of becoming a teacher. Dress-making too, I learned proficiently. My first position was teaching in a convent in Monroe, Michigan. Later, I came to Chicago and opened a dressmaking establishment. I preferred sewing to bossing little children.” Biographer Elliott J. Gorn corroborates most of this, writing, “Mary learned the skills of dressmaking, but she was intent on another career. Late in 1857, at age twenty, she obtained a certificate from the priest at St. Michael’s Cathedral attesting to her good moral character. With this credential, she took the examinations for admission to the Toronto Normal School, passed, and enrolled in November 1857. She never graduated, but she attended classes through the spring of 1858, getting more than enough training to secure a teaching position.”
She eventually made her way to Memphis, Tennessee, resuming her career as a teacher. It was here that she met and married her husband, George Jones, in 1861. Unfortunately, their lives together were cut short, with tragedy forever reshaping her life and work. In 1867, her husband and four children died in a yellow fever epidemic. She shared her perspective on this in an August 24, 1925 article for the Evansville Press, which was subsequently published in her autobiography:
In 1867, a yellow fever epidemic swept Memphis. Its victims were mainly among the poor and the workers. . . . One by one, my four little children sickened and died. I washed their little bodies and got them ready for burial. My husband caught the fever and died. I sat alone through nights of grief. No one came to me. No one could. Other homes were as stricken as was mine. All day long, all night long, I heard the grating of the wheels of the death cart.
After their deaths, she returned to Chicago and set up a clothing business, which was lost in the Great Fire of 1871. “The fire made thousands homeless,” Jones wrote in the Press, “We stayed all night and the next day without food on the lake front, often going into the lake to keep cool. Old St. Mary’s church at Wabash Avenue and Peck Court was thrown open to the refugees and there I camped until I could find a place to go.”

These tragedies caused her to abscond traditionally-female jobs, likely in the search for meaning, and instead she espoused the cause of labor—a consequential role she would play for the rest of her life. “From the time of the Chicago fire,” she declared in the Evansville Press, “I became more and more engrossed in the labor struggle [,] and I decided to take an active part in the efforts of the working people to better the conditions under which they worked and lived.” She spent the next fifty years of her life dedicated to improving the lives of workers all over the United States.
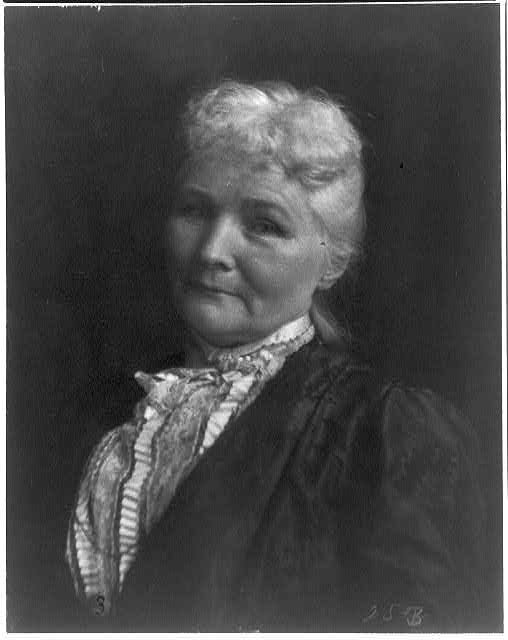
John W. Kern’s life was very different from that of Mother Jones. Born on December 20, 1849 in Howard County, Indiana, Kern belonged to a solidly middle-class family. His father was a doctor who moved the family to Iowa for a time before moving back to a permanent residence in Howard County. It was in these early years, according to biographer Peter J. Sehlinger, that Kern developed a “strong predilection for politics and education,” likely as a result of his father, who was an “outspoken Democrat and an avid reader who subscribed to magazines and constantly enlarged his varied library collection.” At the age of fifteen, Kern earned his teaching license in Howard County and served as a schoolmaster to save up money for his education in law.

Kern graduated from the University of Michigan in 1869 and settled in Kokomo to establish his law practice and start a family. A year later, he ran for public office for the first time, as a Democratic candidate for the Indiana General Assembly, a race he lost. Despite his defeat, it gave Kern clout with the local political establishment and led to his first public office, that of Kokomo’s municipal attorney, a position he held from 1871-1884. He won his first election in 1884, becoming the reporter for the Indiana Supreme Court, serving in this capacity for four years until he lost reelection in 1888. The move to Indianapolis during his years as court reporter continued to grow his stature, and in 1892, Kern was finally elected to the Indiana General Assembly as a state senator. During his time in the Indiana State Senate he became known for his advocacy of organized labor. He worked tirelessly to pass a slew of bills that championed workers, from a right-to-organize law, a worker’s compensation law, and a child labor law. While not a socialist in the Debsian mold, Kern was a progressive who believed that democratic institutions should curb the excesses of capitalism. As he was quoted saying by biographer Peter Sehlinger, “For years and years and years organized capital was fostered and fed by favorable legislation, until it grew defiant and insolent . . . . As a result labor organized that it might live.”

Despite his growing political profile, Kern lost several statewide and national races. He unsuccessfully ran for Governor of Indiana in 1900 and 1904 and was Willian Jennings Bryan’s running mate in the 1908 presidential election, losing to William Howard Taft and the Republicans. This all changed when the Democrats gained control of the Indiana General Assembly in 1910 and swiftly chose him as the next U.S. Senator from Indiana. (This was before the direct election of senators by voters was added to the U.S. Constitution.) During his years in the Senate, Kern governed as a solid Wilsonian progressive who continued to earn the respect of organized labor as one of their staunchest advocates. He continued to fight against child labor, pressing for the passage of state and federal child labor laws. In 1913, he was elected by the Senate as majority leader; in this role he left his most enduring legacy. He brought the role of Senate majority leader into the modern era, working closely with President Woodrow Wilson to pass a wide range of laws, including the Clayton Antitrust Act, the Federal Reserve Act, the Federal Trade Commission Act, and the Federal Employee’s Compensation Act, to name a few. Not until Lyndon B. Johnson (also a Democrat) held the role in the 1950s did a majority leader occupy such an outsized role in the Senate.
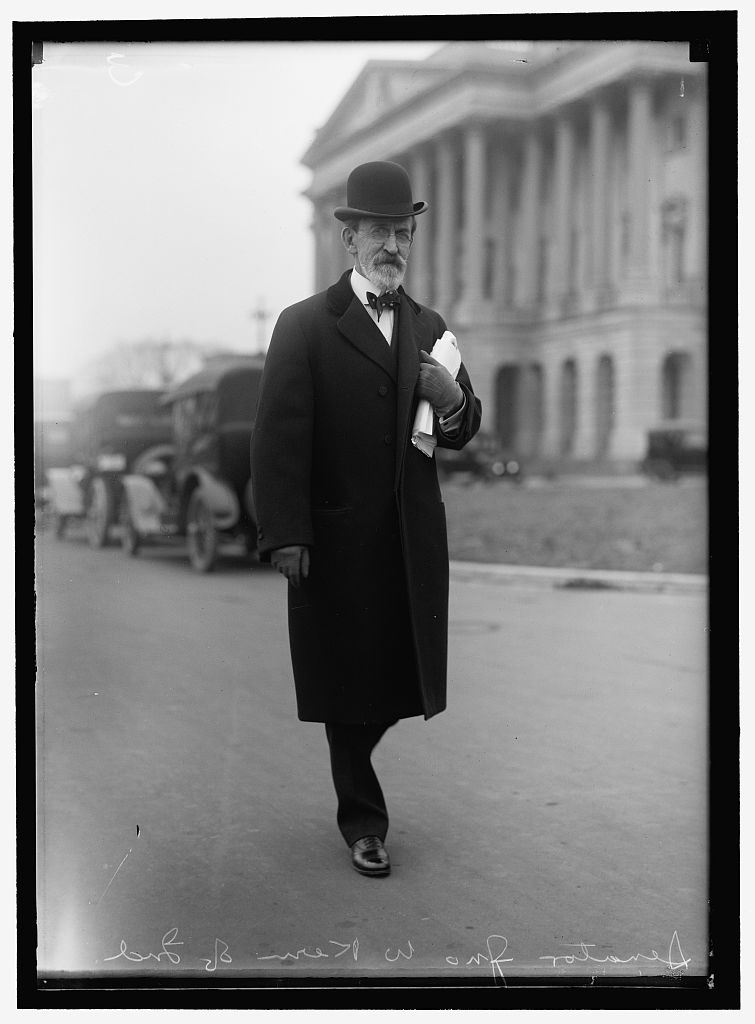

Jones, Kern, and Life in the Mines
Life as a worker in the coal mines was treacherous. Injuries and deaths of miners in Evansville, to name only one city, were chronicled in the papers of its local newspapers for decades. Frank Hudson, a 19-year-old miner who worked at the Diamond Coal Company’s mines in Evansville, was “crushed to death” by “a heavy piece of soapstone” near a worksite entrance in 1888, as reported by the Evansville Courier. In 1897, a miner named William Delgeman was nearly killed at the Diamond coal mine by a premature blast explosion, leaving him with a broken arm and severe burns, the local newspapers Courier and Journal noted. The Courier reported a massive explosion in 1898 that “hurled backward” worker Daniel Breidenbach and “burned both arms from the elbows to the tips of his fingers and also burned his face and the back of his neck.” In 1902, the Journal reported that when Mother Jones was attending the annual UMWA convention in Indianapolis, one coal worker, William Cox, died of injuries sustained when slate fell on him. Three other workers were injured in similar circumstances. Over 20 years later, on November 9, 1921, miner Ben Harper died in the hospital after severe burns from an explosion, as noted by the Richmond Palladium and Sun-Telegram.

Due to the horrific circumstances in Indiana and elsewhere, workers began to organize, and the United Mine Workers of America (UMWA) was founded in 1890. Mother Jones described this organizing work in her autobiography: “The United Mine Workers decided to organize these fields and work for human conditions for human beings. Organizers were put to work. Whenever the spirit of the men in the mines grew strong enough a strike was called.” She worked for the UMWA off and on for over 30 years, speaking at their annual conventions in Indianapolis, organizing workers nationwide, and helping to resolve internal disputes.
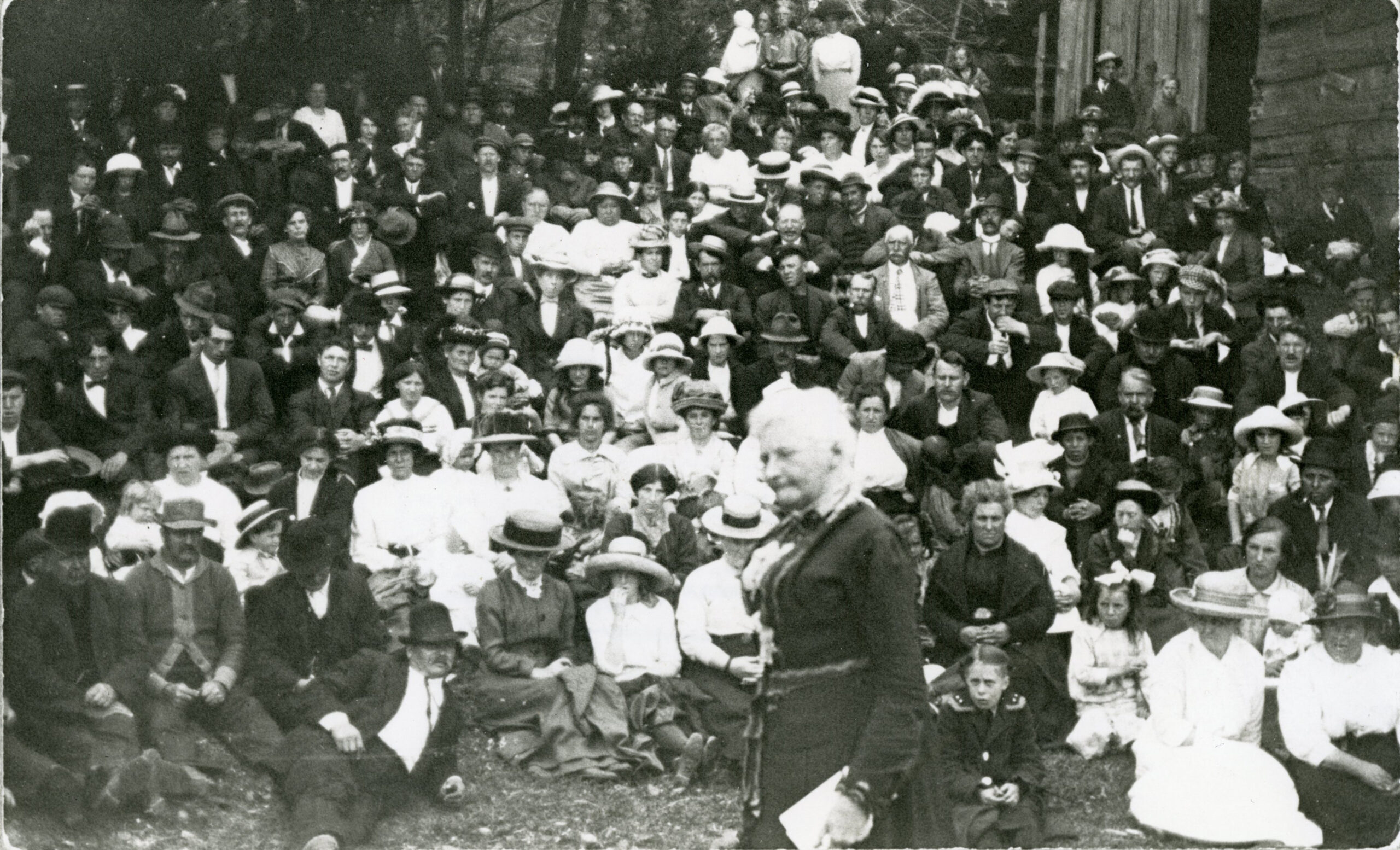

In addition to Indiana, Mother Jones spent a lot of her time organizing in West Virginia, where she was imprisoned during a strike action in 1912. She was left in horrific conditions for months, cramped in a small cell with very little sunlight or adequate food. As the Indiana Socialist reported on May 24, 1913, “the climax of this new form of government [what the Indiana Socialist called, as they it saw it, corporate control of government] came the dastardly arrest of ‘Mother’ Jones on the charge of murder. [Jones, along with 48 labor organizers, were charged with “conspiracy to murder” for the death of Fred Bobbett, who died during a labor uprising.] for The mockery of it was sickening. She has fought the good fight against the murder of little children in the mines of enlightened States.” She appealed to public officials about her imprisonment and the conditions the miners faced.

The national leader who defended her more than nearly anyone else was Senator John W. Kern. Upon learning of the conditions that she and others imprisoned experienced, Senator Kern opened an inquiry into the mines of West Virginia and read a telegram from Mother Jones on the Senate floor. Jones recounted this telegram in her autobiography:
From out the military prison walls of Pratt, West Virginia, where I have walked over my eighty-fourth milestone in history, I send you the groans and tears and heartaches of men, women and children as I have heard them in this state. From out these prison walls, I plead with you for the honor of the nation, to push that investigation, and the children yet unborn will rise and call you blessed.
He received swift backlash for his actions by his West Virginian colleagues in the Senate, who tried to block Kern’s resolution that called for investigations into the mines and their owners. As the Indianapolis Star wrote, “Senators Goff and Chilton of West Virginia bitterly resisted the adoption of the Kern resolution today and a verbal duel took place in the Senate chamber which was little short of sensational.” The men from West Virginia were no match for the Senate Majority Leader, however, and on May 27, 1913, the Senate adopted Kern’s resolution and a “broad investigation” was opened in the Senate on the conditions of the coal mines in West Virginia, the Indianapolis News reported. Three days earlier, on May 24, Mother Jones was released from jail, according to the Appeal to Reason.

Three years after the events in West Virginia, in her speech at the UMWA convention on January 20, 1916, she applauded Kern for his efforts to help her get out of jail. “I presume I would still be in jail in West Virginia if Senator Kern had not taken the matter up,” she declared to the delegates, adding “I want to say to you that every working man in the nation owes a debt to Senator Kern.” She then campaigned vigorously for Kern’s reelection to the Senate and Wilson’s reelection to the presidency. in 1916, stumping in front of 10,000 people in Evansville at the annual Labor Day picnic. As historian Elliott J. Gorn wrote of her Evansville speech, “she declared her socialist beliefs but endorsed Woodrow Wilson for reelection, saying, ‘Socialism is a long way off; I want something right now!’” She also called for a six-hour workday, declaring, “With modern machinery all the work of the world could be done in six hours a day. . . . The worker would have time to improve his mind and body.” Regarding Kern and his efforts to get her out of jail in 1913, Jones said “the miners owe Senator Kern a debt which they can never repay.” Even though Jones campaigned for Kern hard, he lost reelection in 1916 and retired from politics due to ill-health.

Impacts
On November 30, 1930, Mary “Mother” Jones died at the age of 92 or 93 (despite her claim that she was 100) at her home in Silver Springs, Maryland. Indiana newspapers published Numerous obituaries and tributes. William Green, the head of the American Federation of Labor, said in the Indianapolis Times, “in the death of Mother Jones a unique and picturesque figure has been removed from the ranks of labor . . . . The loss sustained cannot be measured and the services rendered will never be surpassed or excelled.” As Bruce Catton wrote for the Evansville Press, “the workingman these days get a far better break than he did when Mother Jones first entered the arena; and a part of this improvement, at least, is due to Mother Jones herself.” As she requested in 1928, Jones was buried at the United Miners Cemetery in Mt. Olive, Illinois, next to miners who gave their lives to the cause of labor. The Indianapolis Times described her funeral train’s procession into Mt. Olive: “A crowd of almost five thousand persons, many of them miners, stood silently Thursday night as the body of Mother Jones was taken from a train which had brought it from Washington. . . . All along the route from the east homage was paid at every stop to the memory of Mother Jones. Miners in many towns placed wreaths upon her coffin.”

John W. Kern died of tuberculosis on August 17, 1917 at a sanitarium in North Carolina. As biographer Peter J. Sehlinger wrote, Kern “died while working on a Labor Day speech he was preparing for delivery in Indianapolis.” Even to the very end, he organized for labor causes. Tributes to the fallen senator poured in from friends and colleagues. Claude Bowers, his personal secretary and future U.S. Ambassador to Chile, said to the Indianapolis News, “Senator Kern sacrificed his life in the service of his country, and when the history of the first of President Wilson’s administration is written and the inner facts are disclosed the greatness of the man will be established.” Indiana Governor James P. Goodrich also said to the News, “As a statesman he was close to the people and ever sought to represent the best interests of his constituents as he saw them. His death is a loss to the entire state and nation.” William Jennings Bryan, who selected Kern as his running mate for the presidency in 1908, said of the senator, “I never knew a man who had my confidence more completely nor my affection more fully than did this, my departed friend.” He was laid to rest at the family homestead in Hollins, Virginia.

The political partnership between Mother Jones and John W. Kern represented two sides of the democratic coin, with Jones the rabble-rousing labor organizer who worked from the bottom up and Kern the Senate majority leader pushing for reform from the top down. Each had a vital role to play in the Progressive Era, a time of massive social, political, and economic change, and their pairing represented a real shift in attitudes regarding organized labor and labor organizers. Mother Jones understood and reflected on this years later in her autobiography, saying of Kern (whom she mistakenly refers to as “Kearns”):
The working men had much to thank Senator Kearns [sic] for. He was a great man, standing for justice and the square deal. Yet, to the shame of the workers of Indiana, when he came up for re-election they elected a man named Watson, a deadly foe of progress. [The man who defeated Kern was Republican Harry New, not a man named Watson.] I felt his defeat keenly, felt the ingratitude of the workers. It was through his influence that prison doors had opened, that unspeakable conditions were brought to light. I have felt that the disappointment of his defeat brought on his illness and ended the brave, heroic life of one of labor’s few friends.
Kern’s friendship with labor represented his long-held view of democracy, which stemmed from a Jeffersonian antipathy towards wealth, position, and privilege. He deeply believed that Americans were better off, and capitalism was better off, when the balance between capital and labor was more equal. In his alliance with Mother Jones and organized labor, John W. Kern embodied his own commitment to a freer and more equitable society.