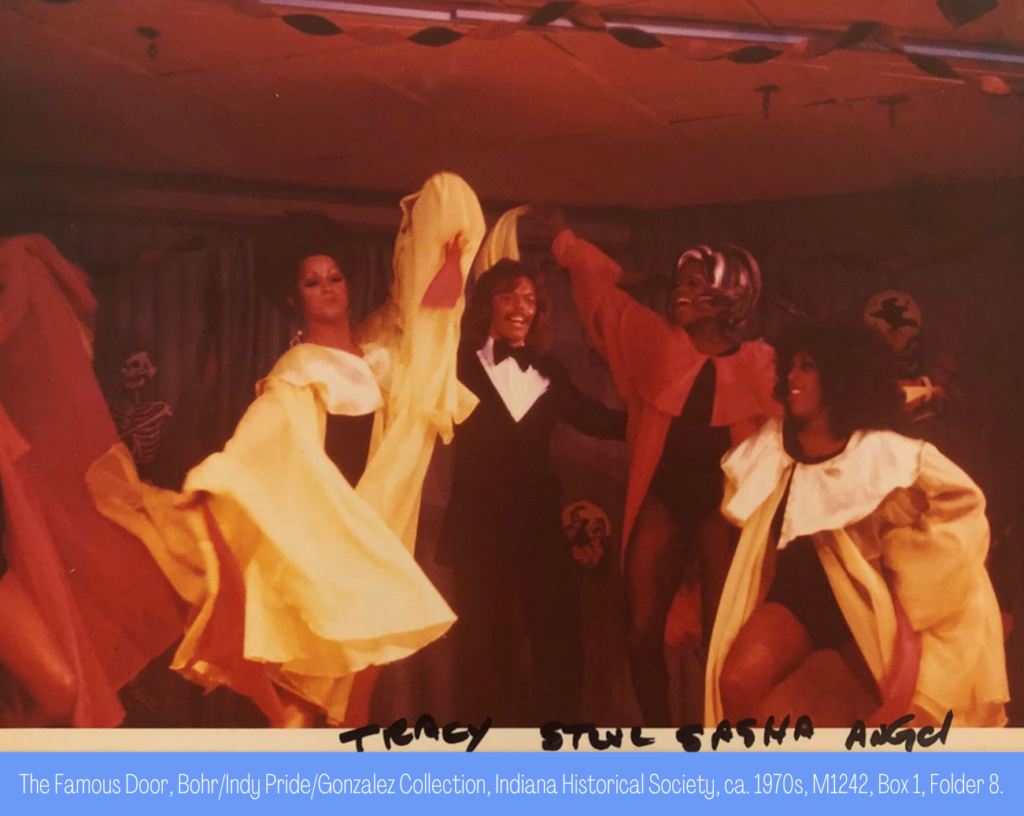
A note on terminology: This post examines gender non-conforming or gender-questioning individuals. This includes those who identified as “cross-dressers [CDs],” male/female “impersonators,” “transvestites [TVs],” “transsexuals [TSs],” and, in modern terminology, “transgender.” When unsure about how individuals identified or what pronouns they preferred, they will be referred to as the name that appears in relevant publications.
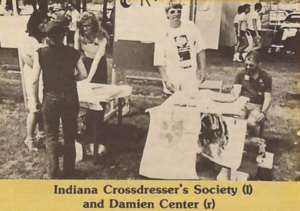
For gender non-conforming Hoosiers, the pursuit of kinship and shared identity was often fruitless, if not outright dangerous. Before the connectivity of the internet and the advocacy of organizations like Indiana Youth Group and GenderNexus, many were bereft of social opportunities and emotional support. Beginning in 1987, the Indiana Crossdresser Society (IXE) served these Hoosiers by providing social forums and offering resources to individuals struggling with gender identity. The group also challenged instances of discrimination within and outside of the LGBTQ community.
The Works newsletter provides a bit of insight into early Hoosier female impersonators (at least in predominantly-white areas of Indianapolis), who performed at bars along Virginia Avenue from the early 1900s until World War II. Articles in 1982 remarked on the resurgence in popularity of impersonators, noting that the Alley Cat Lounge and Disco had begun hosting weekly shows. By the mid-1980s, however, The Works reported that the queer community had been gatekeeping gender non-conforming or gender-questioning individuals, approximately 20,000 of whom lived in Indianapolis. In a 1984 Works article, Jim Chaffin—a gay, cisgender man—chastised the “drag queen” mentality among Indiana’s LGBTQ community. He implied that because society considered gay individuals too effeminate “more ‘normal’ acting gays” needed to come out. Couching his criticism in masculine rhetoric, Chaffin alleged of those who kept their identities private: “you guys don’t have the b*lls to just go ahead and say what you are.”
In the following issue, Roy Pershing, also known as LaNora Takie, fired back at Chaffin’s narrow view of queerness and Chaffin’s insistence that masculine gay men live publicly. The author noted that while Chaffin likely had good intentions, it is the “individuals’ business and no one else’s,” that:
‘We are told that we are wrong everyday by straights and others; so is it necessary for this kind of behavior to go on within the community?’ Furthermore, ‘Could you please tell me what your idea of a normal acting gay person is? Is it an overweight, big mouth who runs a male wh*re house or is it someone who dresses in leather from head to toe? . . . To me, a normal acting gay person is a person who is himself and doesn’t run around forcing him or her lifestyle’ on others.’
The author also felt that Chaffin’s use of “drag queen” was derogatory, and that Pershing/Takie considered themself to be an “entertainer” and “impersonator.”
Facing alienation in the Indianapolis area, some Hoosiers like Betty and Lori attended meetings in Cincinnati hosted by Cross-Port, a group that provided support and social opportunities for gender non-conforming people. According to Cross-Port’s newsletter InnerView, Lori was one of the first Hoosiers to attend these meetings, where she “stood close to seven foot in those spike heels, and spent much time ducking the beams in Heather’s basement.” By early 1987, Betty and Lori helped form a similar group in Indianapolis, called Iota Chi Sigma, better known as the Indiana Crossdresser Society (IXE). About thirteen people attended this first meeting, presided over by Chairperson Laura, who “received special recognition for wearing a dress.” In a Q&A published in InnerView, IXE described itself as a “gender group interested in helping gender conflicted persons in the context of a social meeting.” This included a broad range of individuals, who could “be anybody from the transvestite who just wants to wear womans [sic] panties to the transexual person who believes themselves to be of the opposite sex.” Cross-Talk, the “gender community’s news and information monthly,” remarked that IXE members, feeling that the “gender community was always too hard on itself,” sought to “show a ‘happier’ side.”

After their first gathering, IXE met the first Thursday of every month at the 21 Club, and within a year, attendance outgrew that of Cross-Port. InnerView noted that Cross-Port members sometimes traveled from Cincinnati to Indianapolis to attend IXE meetings and Christmas parties. While in town, visitors shopped at Glendale Mall and Stuart’s Shoes, and participated in fashion shows at the downtown Hyatt Regency. One self-conscious visitor reported that they were treated courteously at these shops.
By 1989, IXE had over 100 members residing in the tri-state area—which included Kentucky—helping forge a social network of support for the marginalized community. According to an Indianapolis Star piece entitled “Cross-dressers Seek Society’s Acceptance,” most members were heterosexual men experiencing “gender conflict,” and came from a variety of professions, including carpentry, business, and law enforcement. The paper noted that once a month, about thirty members socialized at a Westside apartment clubhouse, many bringing their spouses. At one meeting, cosmologists gave members make up tips. At another, police officers advised them on how to avoid a “scene” in public.
The Star piece profiled IXE member Sharon Allan, who spent about 30% of his life dressing as a woman, undergoing “painful electrolysis” to achieve smooth skin, perming his hair, and piercing his ears. Sharon married his high school sweetheart, Ann, who knew about his cross-dressing from the beginning of their relationship. On their first date, she removed the choker from her neck and placed it around his. Ultimately, the couple divorced because Ann felt that although Sharon “is a wonderful person . . . his cross-dressing left no room for me as a woman in the marriage.'” Despite this blow, Sharon chose to be transparent about his identity with his young son in order to facilitate trust, stating, “‘I came to decide there was nothing wrong with what I was doing. There was nothing wrong with feeling feminine, inside or out.'”
Adam, a middle-aged health care professional, did not share Sharon’s perspective. According to the Star article, he began wearing women’s clothes as a teenager, but reported, “It’s not something I want to do. I got tired of feeling bad about myself. There were times I couldn’t control it.” Despite undergoing aversion therapy, Adam continued to dress in feminine clothing. His wife divorced him when she found out, and Adam noted, “It felt degrading to her and me as well. The discovery certainly was unpleasant. And it didn’t feel good to me. It was shaming.” Rita could empathize with Adam’s despair, having experienced two painful divorces. The northern Indiana police officer considered ending his life. Unlike Adam, Rita ultimately concluded that, despite having to keep the crossdressing aspect of his life private, “I wouldn’t give it up. If there was a magic pill, I wouldn’t take it.” The Star profile noted that Rita had begun wearing feminine clothing in elementary school. While in the Marines, he was able to shave his arms and legs “without attracting undue attention from his fellow leathernecks.”
Despite their personal struggles with shame and acceptance, gay bars afforded gender non-conforming Hoosiers a degree of shelter from harassment and discrimination. The Star noted that the venues were particularly important to this minority group because they provided a “place where men won’t try to pick them up.” However, these spaces dwindled when the 21 Club and G.G.’s closed, which according to the New Works News, prompted an influx of gender non-conforming patrons to other local gay bars. As demographics changed, some bar owners implemented exclusionary policies, perhaps reflecting the assertion of transgender activist Evan Greer in her 2018 piece for The Washington Post, that historically “the predominantly white, cis, gay, male leadership saw trans people as a threat to their slowly but surely growing social and economic political power.” Perhaps these discriminatory measures were an attempt to safeguard this hard-fought increase in social “legitimacy.”
In 1989, the New Works News reported on the fallout of the bar closings. Articles reported instances in which bar owners refused to serve cross-dressing and transgender individuals like Roberta Alyson and Kerry Gean. Dressed as the “woman I am deep inside of my biological male self,” Gean and friends went to the Varsity Lounge in February 1989. After they were seated, their server singled out Gean with a request for identification. The server then informed her that she was breaking the law because the photo on her I.D. did not identically match her face. Humiliated and hurt, she returned home, changed into “male” clothes, and upon return was immediately served.

By June, things were no better for Roberta Alyson, described by The Works as a “pre-operative transsexual.” Alyson was denied entrance to the gay bar Our Place on the grounds of not meeting dress code and identification not matching Alyson’s face, despite having a doctor’s note confirming the necessity of dressing as a woman. Bar officials got an off-duty officer who worked security to check the 31-year-old’s ID. The officer crumpled up the doctor’s note and Alyson “regrettably began to panic,” walking away from the parking lot. The officer pursued and arrested Alyson, who later said one of the back-up officers was abusive and tried to lift Alyson’s skirt. Alyson was charged with and fined for fleeing an officer. Alyson addressed the implications of such discrimination in a letter to the editor of The New Works News, noting Our Place’s dress code “flies in the face of the Stonewall Riots and sends a terrifyingly repressive message to the ‘straight’ community.”
Alyson received assistance from IXE, of which she was a member. That year, IXE had “joined Justice, Inc., a statewide umbrella organization for support and activist groups working in and with the gay/lesbian community. Justice has a full time lobbyist at the state capital.” Forging such partnerships would prove critical in challenging discrimination. With Justice’s help, IXE initiated a series of meetings with bar owners, excise police, and allies like the Indiana Civil Liberties Union. These gatherings provided a forum to exchange perspectives and to gain a better understanding of excise laws.
The groups initially gathered in July for a meeting facilitated by police officer and community liaison Shirley Purvitis. Remarking on the conflict within the queer community, she noted in the Star profile that crossdressers are “‘professional people with good jobs. They’re taxpayers. A lot of them have families. It’s time we started learning about them.'” As expected, the meeting was tense. Some owners claimed that they implemented policies, like denying entrance to those whose photo I.D.s did not reflect their apparent gender, because they feared breaking excise laws and making their businesses vulnerable to legal issues. Responding to these concerns, Excise Chief Okey reassured that “the only requirement that excise has for a person being served alcohol is that they be 21 years of age or older. . . . crossdressing, either male or female, is not grounds for refusal of service.”

Other bar owners stated blatantly that they refused to admit these patrons because they intended to “‘preserve the established atmosphere of their bars.’” A 501 Tavern spokesperson stated that these individuals “‘were not wanted there,’ and if they had been admitted violence might have resulted. The bar owners also voiced the fear that if they admitted people in drag their regular patrons might leave.” Our Place owner David Morse sympathized with the 501 Tavern representative. He complained at a later meeting that new patrons had filled his bar with “boisterous, outrageous drag queens in double Dolly Parton wigs and that their presence was very disruptive” to the bar’s masculine ethos.
Works writer E. Rumbarger came away from this first meeting with a greater understanding of those who had been excluded from gay bars. Prior to attending, he had mused, “Did they eat their young? . . . Did they have two heads?” However, he was “very surprised and pleased to find that they were simply a group of very relaxed and congenial people who were ‘doing their own thing. . . . These men quite simply looked and acted like women or to be more precise—ladies.” He added that he could not fathom how any establishment would “object to their presence” and urged that “Greater knowledge and understanding is needed (and quickly) in the gay community regarding the wide diversity of groups that make up the community.” Similarly, Stan Berg, Works publisher and owner of the Body Works bath house, addressed Dee Gordon’s editorial, which criticized the push for greater inclusion. Berg opined that Gordon had articulated the:
feelings and actions of another owner of a gay business who, at one time, and for many years, kept out drags. Now, whether old age, an increasing tolerance for gays of all persuasions, or just the realization that bigotry was wrong, actually changed this business owner’s mind, I can’t tell you. But, that business owner is me. The bottom line is that your arguments are bigoted bullsh*t. My own reasons for keeping drags out of THE WORKS for seven years were also bigoted bullsh*t.

While the initial meeting spurred greater understanding among certain individuals, it failed to resolve turmoil within the broader community or result in specific policy reform. Upon IXE’s request, Justice, Inc. conducted a survey of those parties involved in the conflict and hosted a subsequent workshop in September. This workshop provided an opportunity to discuss injustices experienced by various groups within the community. Many voiced their anguish about discrimination within the lesbian community, against persons with AIDS, and along racial lines. At the center of the meeting, however, remained the exclusion of gender non-conforming individuals. IXE vice president Sharon Allan detailed the trials faced by crossdressers and drag queens, noting that they “are currently experiencing problems which the gay community faced years ago.”
However contentious, these meetings led to the reversal of policies at some bars and helped open the door to acceptance for other gender non-conforming individuals in Indianapolis. IXE members reported in September that they encountered less hostility at local establishments. Although bars like The Varsity maintained stringent policies, Tomorrow’s was much more welcoming. And while Jimmy’s did not reverse its I.D. policy, employees were more lenient about its enforcement. Roberta Alyson patronized the bar with a friend, who was also dressed in “female attire.” When the server approached, this friend instinctively searched their purse for identification, to which their server said “’Don’t worry about that, honey, we don’t do that kind of discriminating here.’” The Works noted that this action “on the part of Jimmy’s shows that people can change their mind” and should be commended for doing so.
As the 1980s came to a close, the queer community seemed more tolerant—and perhaps welcoming—of gender non-conforming individuals. The Works announced in January 1990 that the owner of the 21 Club was opening 3535 West, which would “cater to all segments of the gay community.” The piece added, “Now that Indianapolis will finally have a gay meeting place where everyone is welcome, perhaps our gay visitors from out of town who have avoided coming here in recent months because of all the discriminatory nonsense taking place in some of the local bars, will once again return to Indy for a renewal of good times shared in the past.”
In 1990, at the first large outdoor Pride celebration, which took place on Monument Circle, people who staffed IXE’s booth reported that they were generally accepted, if not entirely understood. An unidentified member mused in the Works:
‘We all had lots of fun watching and talking. More often than not people would come up to our table and say hello and then look at what was on display and read the titles of the magazines and books, see the word ‘crossdressing’ and then look up at us and then down at the book and then back at us as a look of surprise and realization passed across their faces. . . . One girl was talking with Emily for five minutes before she looked down and saw the title ‘Understanding the Crossdresser’ and said with utter surprise, ‘Oh, I get it! You’re a guy! That’s cool. You know, I never understood why I can wear anything I want and guys can’t wear skirts.’
Similarly, public acceptance of crossdressers increased slightly following media profiles like that published by the Indianapolis Star about IXE. The feature’s author marveled that not only did she not receive vitriolic phone calls from readers after its publication, but got calls asking for more information about IXE. Indeed, Genny Beemyn contended in “Transgender History of the United States,” that in the early 1990s a “larger rights movement” emerged. Beemyn noted that this movement was “facilitated by the increasing use of the term ‘transgender’ to encompass all individuals whose gender identity or expression differs from the social norms of the gender assigned to them at birth.”

Reflecting this movement, the Louisville Gender Society was formed in 1992, serving people living in southern Indiana and Illinois, as well as Kentucky. At the same time, IXE’s membership notably increased, as gender non-conforming Hoosiers searched for solidarity. In a 1991 Tapestry issue, Gloria C., a 33 year-old “transvestite” who lived in a small town, pleaded “I’m lonely! Please Write.” The auto racing and fishing fan hoped to meet “TV/TS” friends. IXE drew members like Michelle Michaels, a 40-year-old self-described transvestite who struggled with addiction resulting from the “guilt, shame, & confusion” of crossdressing. After getting sober, Michaels—who had three children and a supportive wife—joined IXE because of an ongoing struggle with “acceptance, self-esteem and balance.” Member Vickie Mansfield, “a young 47,” was involved in the Catholic Church, enjoyed “fine wines,” and was only “recently out of the closet.” Dan Riley, a 40-year-old “female-to-male” crossdresser, who enjoyed hiking and t’ai chi, joined the organization, in part, because Dan liked “helping others ‘coming out.’” Indianapolis funeral service supplier Yvonne Cook was not only a lifetime member IXE, but a leader and board member of the International Foundation for Gender Education.
IXE served such members until at least 2005. Although, no longer an organization as of 2023, IXE provided solidarity to so many Hoosiers in distress or suffering from loneliness. Additionally, its members’ activism and willingness to facilitate discussion helped change public perceptions about gender non-conforming individuals and contributed to greater inclusivity within the LGBTQ community. The struggle to obtain societal acceptance and secure civil rights in Indiana endures, as evidenced by recent debates about gender-affirming medical practices. Like the Indiana Crossdresser Society, groups like Trans Solutions Resources and Research, continue to fight, in the words of Sharon Allan, for “‘Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. It’s a fundamental right.'”
Sources:
Genny Beemyn, “Transgender History in the United States,” in ed. Laura Erickson-Schroth, Trans Bodies, Trans Selves, p. 28, accessed UMass Amherst.
Cross-Port InnerView (March 1987, June 1987, July 1987, August 1987, December 1987, July 1988, November 1988, January 1991, August 1991, September 1991, December 1992, June 1995, June 1996), Digital Transgender Archive.
Cross-Talk: The Transgendered Community’s Newsletter (September 1991, July 1992), Digital Transgender Archive.
Editorial, Jim Chaffin, “‘Hoosier Gay Boy, Come on Down!,'” The Works (October 1984): 7, accessed Chris Gonzalez GLBT Archives, IUPUI Library.
“Indiana,” Tapestry: The Journal for All Persons Interested in Crossdressing and Transsexualism 78 (Winter 1996): D38, accessed Digital Transgender Archive.
“National Gender News,” Renaissance News 3, no. 1 (January 1989): 9, accessed Digital Transgender Archive.
Kyle Niederpruem, “Cross-dressers Seek Society’s Acceptance,” Indianapolis Star, November 26, 1989, 115, accessed Newspapers.com.
“North American Support Groups,” Lady Like (Winter 2005): 44, accessed Internet Archive.
Editorial, Roy Pershing/LaNora Takie, “Darts from a ‘Drag,'” The Works (November 1984): 6, accessed Chris Gonzalez GLBT Archives, IUPUI Library.
JoAnn Roberts, “The Iconoclast,” Renaissance News 6, no. 9 (September 1992): 7, accessed Digital Transgender Archive.
Tapestry: The Journal for All Persons Interested in Crossdressing and Transsexualism 58 (1991): 129-130, accessed Digital Transgender Archive.
Nicole Poletika, “’Walk a Mile in Their Pumps:’ Combating Discrimination within Indy’s Queer Community,” October 7, 2020, accessed Untold Indiana.
Draft, Nicole Poletika, “’Walk a Mile in their Pumps:’ Combating Discrimination within Indianapolis’s Queer Community,” 2022 Queer History Conference paper, accessible here.