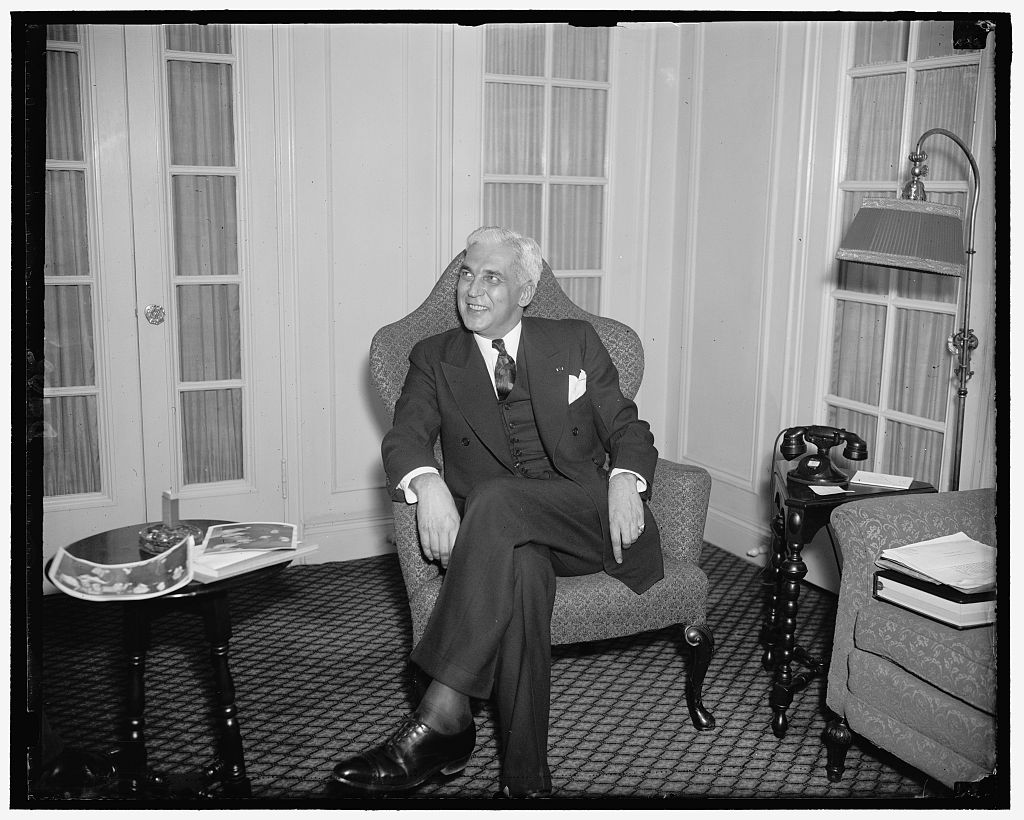
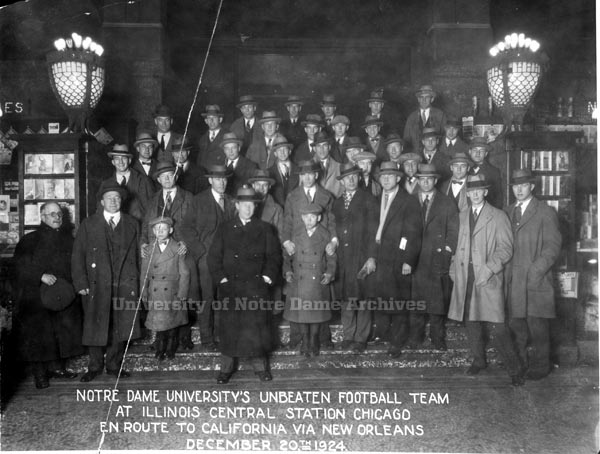
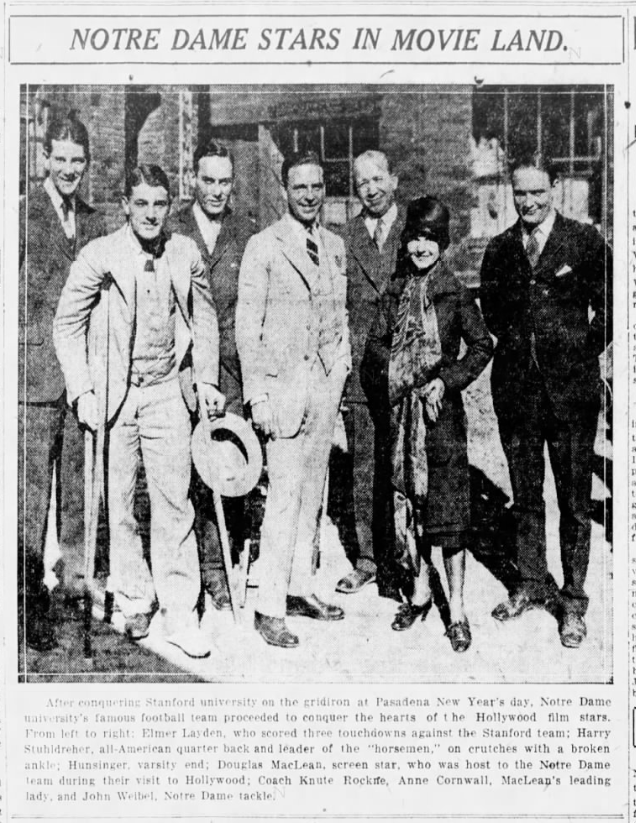
One of the most dynamic political careers of any Hoosier belonged to Governor Paul V. McNutt. He set his sights on the U.S. presidency as early as the 1920s, when he was the state and national commander of the American Legion. His advocacy of human rights, particularly for the Jewish people during his time as Governor and High Commissioner to the Philippines, put his moral arc far beyond some of his peers. In the 1940 presidential election, McNutt was also considered a Democratic “Dark Horse” candidate before Franklin D. Roosevelt decided to run for an unprecedented third term. McNutt’s progressive, internationalist political identity squared well with the New Deal Era and growing American involvement in World War II. While his chance to become president never materialized, McNutt’s decades of public service revealed a man dedicated to democracy and humanitarianism.

Paul Vories McNutt was born on July 19, 1891 in Franklin, Indiana. His father, attorney John Crittenden McNutt, served as a librarian for the Indiana Supreme Court and exposed his son to law and politics at a young age. When Paul was seven, the family moved to Martinsville, where he graduated from high school in 1909. He then attended Indiana University, earning a BA in English in 1913. McNutt attended IU at the same time as another influential Hoosier who would also have ambitions for the presidency: Republican businessman Wendell Willkie. While at IU, they both held leadership roles, with McNutt the President of the Student Union and Willkie the President of the Democratic-aligning Jackson Club. Willkie even helped McNutt win his Student Union presidency and biographer I. George Blake noted that they were “very good friends.” After his time at IU, McNutt pursued a career in law, receiving a Bachelor of Laws from Harvard University in 1916.

After a year of private practice with his father, McNutt joined the Indiana University law school faculty in 1917. However, World War I disrupted his teaching and in the spring he registered for military service. By November, the South Bend News-Times reported he attained the rank of Captain. He spent most of the war at bases in Texas, and while he “exuded pride in his contribution,” historian Dean J. Kotlowski noted that the war’s end dashed his chance to fight in Europe. He also met his future wife, Kathleen Timolat, during his time in Texas. He proposed marriage to Kathleen in 1918 and they married three months later. His only child, Louise, was born in 1921.
After the war, McNutt returned to teaching at the IU Law School faculty in 1919 and in 1925 was formally installed as the school’s Dean. Under his tenure, the Law School streamlined its administration, expanded its enrollment, and oversaw the launch of the Indiana Law Journal. He held this position until his inauguration as Governor in 1933.

His career trajectory sharply pivoted once he got involved with the American Legion. The organization served as a vehicle for his political ambitions and provided him with the infrastructure to win the governorship. According to its website, the American Legion:
evolved from a group of war-weary veterans of World War I into one of the most influential nonprofit groups in the United States. Membership swiftly grew to over 1 million, and local posts sprang up across the country. Today [2022], membership stands at nearly 2 million in more than 13,000 posts worldwide.
McNutt joined the Bloomington post of the American Legion shortly after its founding in 1919. In the years leading up to his role as State and National Commander, McNutt had little interest in the Legion other than as a social club. This changed around the time he became Dean of the IU Law School; McNutt’s desire for higher office motivated his involvement in Legion leadership. Thus, he became one of the organization’s indispensable leaders and rose quickly through the ranks, being elected State Commander in 1926.

As State Commander, he lobbied for veterans, urging state banks to provide personal loans to WWI veterans based on their future retirement compensation. An American Legion Monthly piece credited McNutt with growing the Indiana department of the Legion from 18,336 to 25,505 by 1929. After rigorous campaigning and substantial support at the American Legion’s National Convention, McNutt was elected National Commander in 1928. In this role, McNutt continued to expand national membership, organized events, and offered advice on foreign policy and veteran’s affairs. McNutt’s outspoken views on military preparedness ignited a very public feud with President Herbert Hoover. In 1929, the Hoover Administration agreed to scrap two British Naval Ships, a decision McNutt vehemently disagreed with in a telegram published in the New York Times. McNutt believed it made America more open to attack if “naval parity with Britain” was lost. McNutt’s internationalist view of foreign policy, which would serve him well during the 1940s, clashed with the isolationist current of the 1920s.
In July 1929, McNutt traveled to France, Hungary, and Yugoslavia on a trip as National Commander. He visited the Legion’s world headquarters in Paris and attended gravesites for those killed in World War I. In October, his one-year term limit expired, and McNutt was replaced as National Commander. Following his tenure, the Legion appointed McNutt as “legal advisory council of the [U. S.] Veteran’s Bureau,” which advanced his policy experience. Overall, McNutt’s time in the American Legion provided the logistical tools and political network necessary to run for higher office.

In 1932, Hoosier voters elected McNutt as the state’s first Democratic governor in twenty years, the same year Franklin Delano Roosevelt first won the presidency. In his inaugural address on January 9, 1933, McNutt advocated for broad political reform, especially relief for those affected by the Great Depression, something he vigorously campaigned on. He called for investments in public education, infrastructure, care for the elderly and infirm, and a reorganization of government functions. The next day, McNutt gave another address to the General Assembly detailing his proposals, which included consolidation of government agencies, a personal income tax, tighter regulation of public utilities, the end of alcohol prohibition, and balancing the state budget.

During his four years as governor, McNutt achieved many of his policy proposals. According to historian Linda C. Gugin, his signature achievement during his first year of office was the Executive Reorganization Act, passed by the General Assembly on February 3, 1933. It reorganized more than 100 separate divisions of government into eight departments, directly overseen by the Governor. This law was seen as a controversial power grab by many Republicans; one critic of McNutt, State Senator William E. Jenner, called him “Paul the Fifth” in a speech, as if he was a monarch rather than a Governor. Nevertheless, McNutt’s reorganization plan proved popular, and Democrats fared well in both the 1934 and 1936 elections. He also kept his promise on Prohibition. According to the New York Times, the General Assembly repealed the state’s prohibition law on February 25, 1933 and Governor McNutt “recommended pardons for those convicted of liquor law violations other than public intoxication and driving while intoxicated.”

Perhaps most notably, Governor McNutt proved to be an early champion of human rights for European Jews persecuted by the iron-fisted rule of Adolf Hitler and the Nazis. McNutt delivered the keynote address at a Chicago anti-Hitler meeting on March 27, 1933, condemning the Nazi treatment of German Jews. Thousands of attendees filled the theater and those unable to get in wrapped around the block, listening through loudspeakers. In his address, as recorded by the New York Times, he stressed the need to combat Germany’s injustice:
Indiana joins the protest against this persecution. This is a prayer for the freedom of the world. Are we to join with the traitors of brotherhood, or to enlist in the war of justice?
What nation would deny its pioneers and a people who have made such contributions to culture? No government can long endure that fails to guarantee to its people the right to live as human beings. The present government of Germany thus writes its own destruction.
During the convention, a resolution introduced by Dr. Paul Hutchinson, editor of the Christian Century magazine and one of the event’s organizers, was adopted “amid wild applause.” It called for the United States to end its diplomatic relations with Germany until an independent investigation was conducted regarding the status of Jewish residents. This event was one of multiple examples of his advocacy of the Jewish people. (To learn “what Hoosiers knew when” about the Holocaust, see IHB historian Jill Weiss Simins’s History Unfolded blog series).
Furthermore, McNutt advocated for Americans ravaged by the Great Depression. According to Bradford Sample’s 2001 Indiana Magazine of History article, in the early years of the Depression, Hoosiers received minimal help from local and state government, relying instead on aid from civic and charitable organizations. Espousing traditional Hoosier principles of small government and self-sufficiency, McNutt’s predecessor Governor Harry G. Leslie refused to authorize relief bonds. According to the Evansville Press, the Republican governor balked at requests to call a special legislative session in March 1932, fearing an unemployment relief bill would be introduced and that it would “‘be hard for any legislator not to vote for it.'” Gov. Leslie opined that “such a procedure would demoralize the relief work now being done in committees. People now giving to unemployment relief would assume that their help was not needed if the state began making donations.'” He also refused to accept federal relief funds, viewing them as “direct threats to the tradition of local autonomy for relief in Indiana,” according to historian James H. Madison. McNutt worked to reverse the previous administration’s inaction.
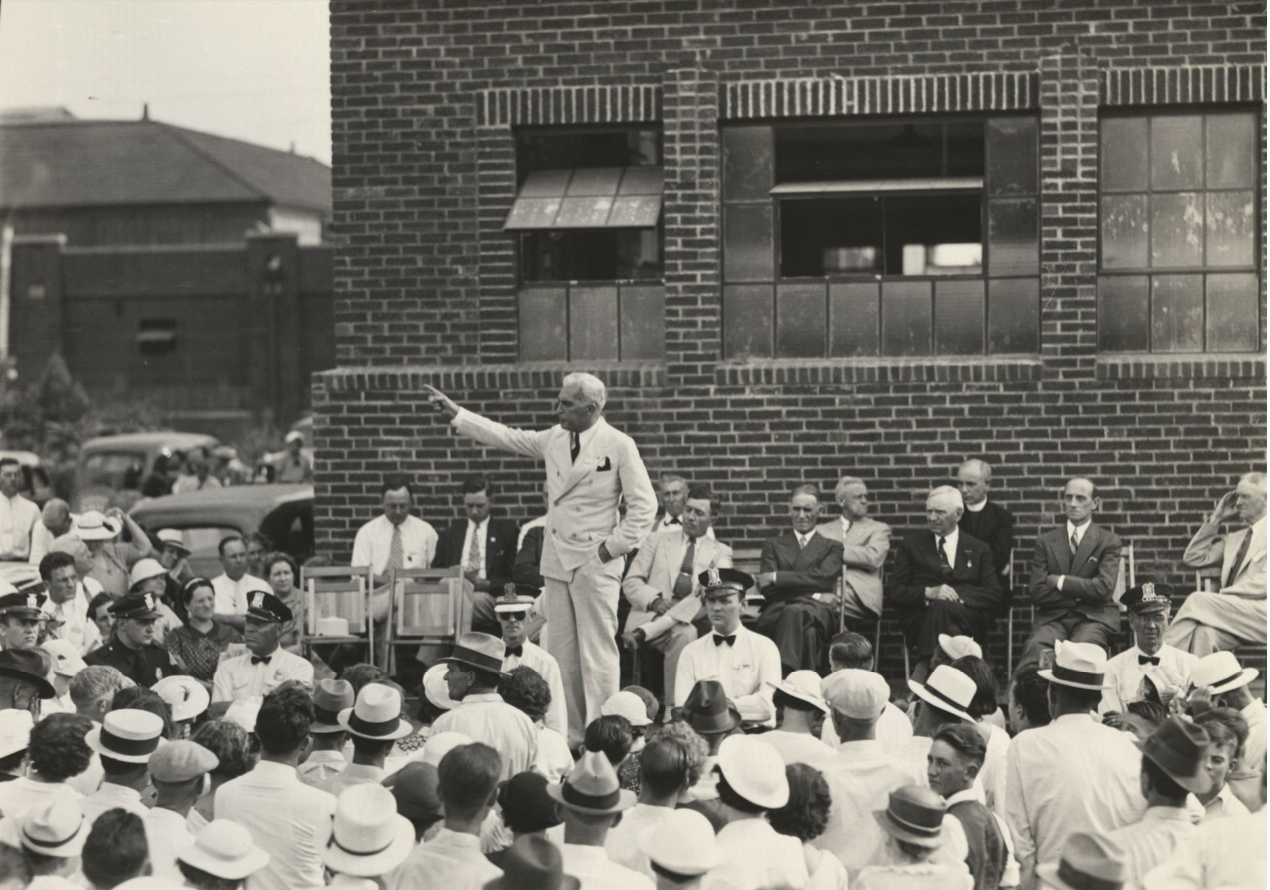

While bank runs ravaged the country’s financial health, McNutt argued against a bank holiday for the state, despite states like Michigan had already passed one. This move ensured more stability to the banking system in the state. In late 1934, McNutt gave a policy speech defending his state’s old age pension program and a national plan for old age pensions, which paralleled President Roosevelt’s Social Security proposal:
In any future program will be included three great objectives: the security of the home, the security of livelihood and the security of social insurance. Such a program would be a great step toward the goal of human happiness. The first duty of government is to protect the humanity which it serves.
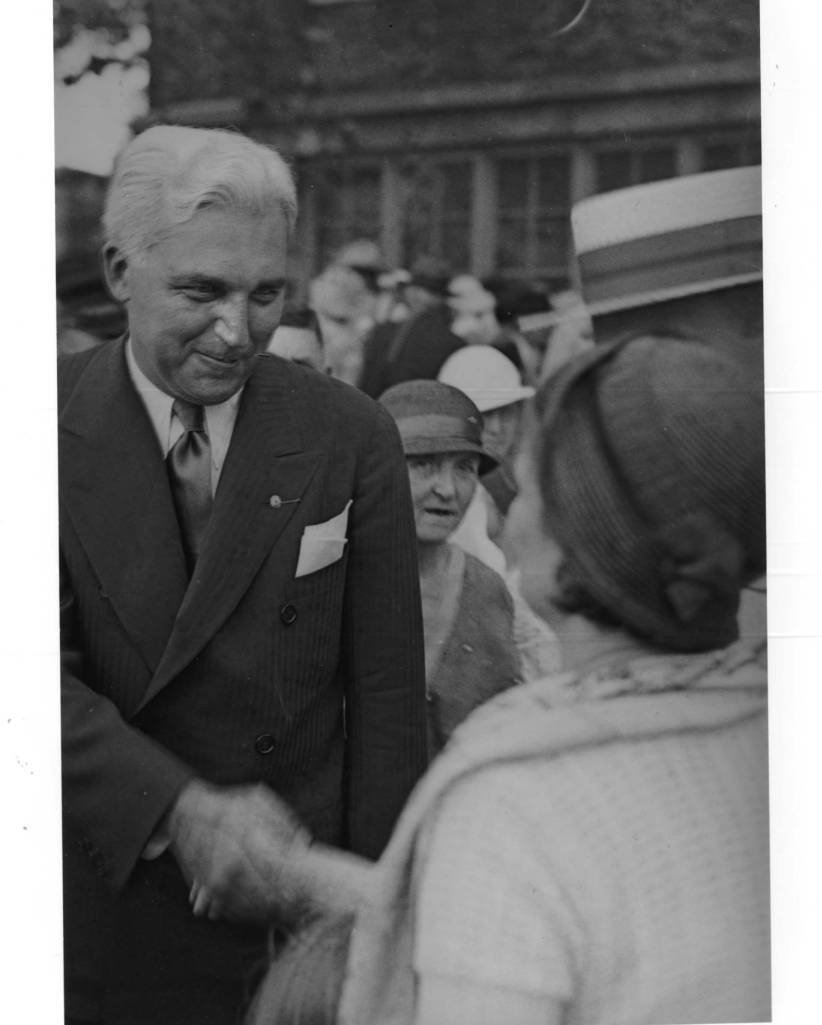

Once the Social Security Act was passed in 1935, McNutt’s administration aligned Indiana’s policies with the national program through the “Unemployment Compensation Act, the Public Welfare Act, and the Child and Maternal Health Act. Like Roosevelt, McNutt’s progressive policies highlighted his belief in “economic security for Americans at home as well as national security for America abroad.”
Despite his broader liberalism on many issues, Governor McNutt received criticism for how he wielded his political power. In the fall of 1933, Governor McNutt ordered Sullivan County under martial law and sent National Guard Troops to deal with unrest at the Starburn Shaft Mines following a labor contract dispute. He also garnered criticism for his actions during the 1934 midterm elections. McNutt used his influence within the Democratic Party to ensure that Sherman Minton was the Democratic nominee for Senate, rather than R. Earl Peters, a vocal opponent of the McNutt administration and its policies. These actions, alongside his consolidation of state government agencies, ironically garnered him the nickname the “Hoosier Hitler” among many within the labor movement.
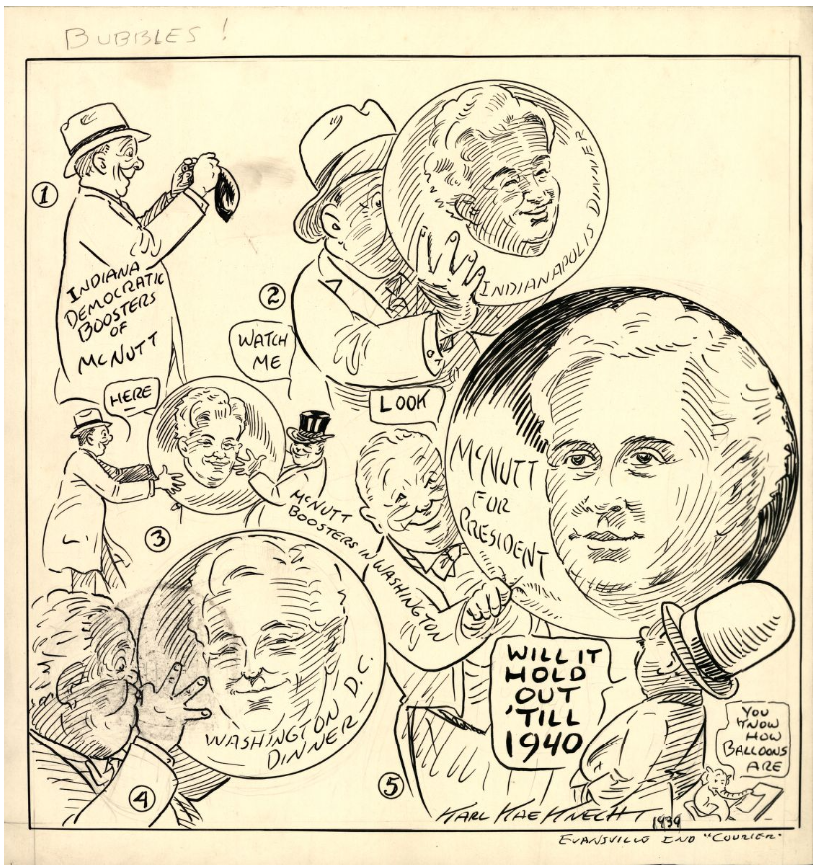

He spent the later years of his term as governor championing his reforms of state government and maintaining a progressive agenda. His second legislative message to the Indiana General Assembly called for the expansion of relief efforts within state government and new reforms for taxes, highways, and the sale of alcohol. In a 1935 address, McNutt championed the new Utilities Commission, whose tighter regulations on energy companies saved the Hoosier public over $5,000,000 in just two years—a crucial difference during the lean Depression years. These new regulations ensured that rural areas of the state received electricity for the first time, something McNutt counted as one of his greatest gubernatorial accomplishments. In his final weeks of office, McNutt was honored with a dinner hosted by Democratic Party leaders, who had begun to see him as a presidential candidate. Senator Sherman Minton said to McNutt that, “As we bid you good-bye to the State House, we bid you godspeed to the White House.” In his book, Indiana Through Tradition and Change, historian James Madison emphasized that McNutt’s governorship was one of the most dynamic and influential administrations in Indiana history. Not since Civil War Governor Oliver P. Morton had a governor left such an impact on the lives of Hoosiers.
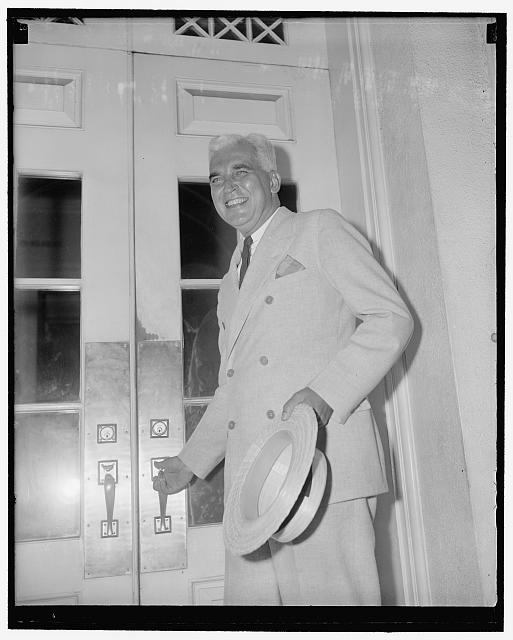

After his time as Governor, McNutt served as High Commissioner to the Philippine Islands from 1937-1939, and then again from 1945-47, becoming the Philippines’s first Ambassador to the United States after it gained independence in 1946. He was nominated for the position in 1937, roughly a month after he finished his term as Indiana’s Governor. His nomination surprised the Philippine public, to whom McNutt was relatively unknown. However, his diplomatic record reportedly earned their trust. Nevertheless, his nomination also drew criticism in the United States. Frederick J. Libby, executive secretary of the National Council for the Prevention of War, saw McNutt’s use of national guard troops as governor during labor disputes as a serious concern which he addressed in a letter to President Roosevelt. The criticism continued after his appointment, specifically in his handling of ceremonial functions. An article by James Stevens in the American Mercury noted that McNutt’s insistence on toasting décor during official functions as High Commissioner: “As the new High Commissioner to the Philippine Commonwealth, he recently issued an ukase [word for Russian edict] on precedence in public toasts and thus assured himself of front-page fame.” Regardless of the criticism, McNutt proved to be a key ally to President Roosevelt, and the office became a political asset.

Much like during his governorship, McNutt’s commitment to the protection of European Jews extended to his role as High Commissioner. McNutt denounced the horrific policy of Kristallnacht, a nationwide pogrom the Nazi regime launched against German Jews in November 1938. Mobs smashed and looted Jewish shops and burned hundreds of Jewish synagogues. According to the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, approximately 30,000 Jewish males were arrested and transferred from local prisons to concentration camps, mainly Dachau. German officials reported 91 Jewish deaths during Kristallnacht, but numbers were likely much higher. In the months following the “Night of Broken Glass,” thousands of Jews emigrated from Germany to other countries. McNutt ensured the escape of “1,200 German and Austrian Jews” to the Philippine Islands. His policies stood as an outlier for American policy during the 1930s, as entering the United States was often difficult for Jewish refugees fleeing fascism, even for such luminaries like Albert Einstein. Nevertheless, as acts of political conscience, these policies remain one of McNutt’s enduring legacies.
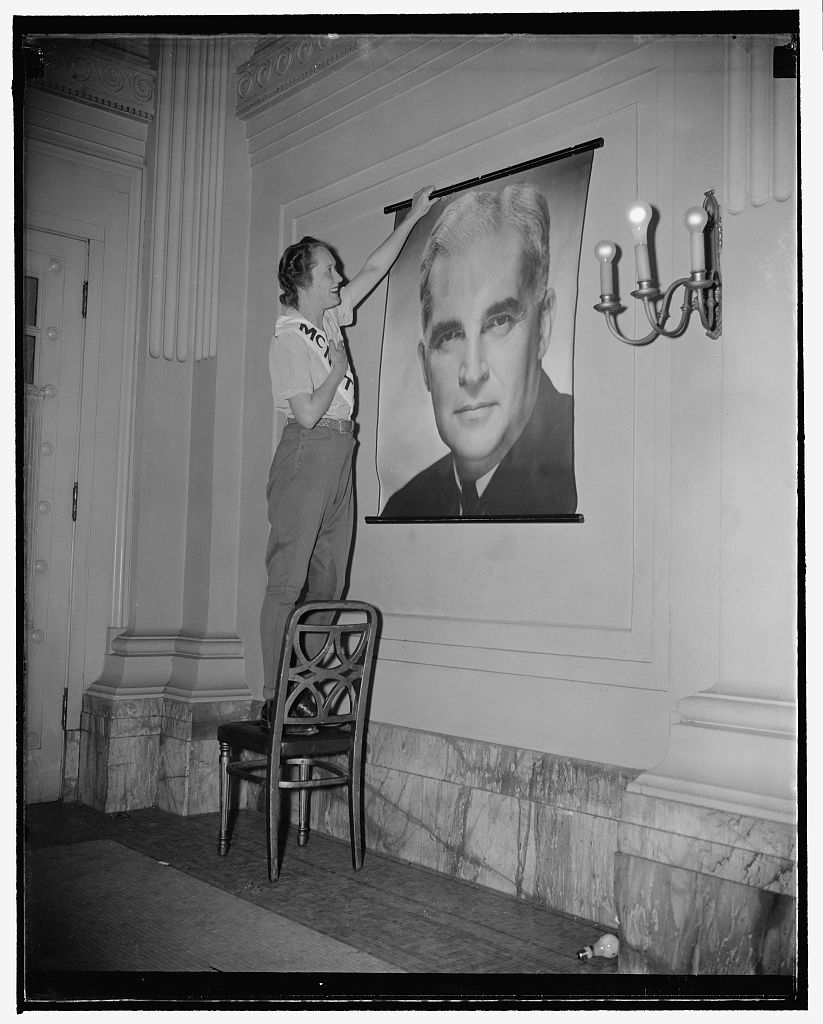

During his time as Commissioner, some Democrats began touting him as a candidate for the party’s 1940 presidential nomination. Franklin Roosevelt, nearing the end of his second term as president, initially displayed ambivalence about a third term. This forced many within the Democratic Party to seek out a candidate, and McNutt received serious consideration. During his February 1938 visit to the U.S., the Indiana Democratic Editorial Association, a meeting of 300 Democratic leaders in Washington, D.C., endorsed him for President. Two national publications also placed him front and center. A Life magazine piece by Jack Alexander highlighted the Indiana Democratic Party’s use of “McNutt for President Clubs,” local organizations that campaigned for the former Governor, as integral to his electoral success. Alva Johnston’s piece in the Saturday Evening Post highlighted his prominence next to Roosevelt and saw his chances of election as strong. If Roosevelt did not seek a third term, McNutt believed he had the political resources to win the Democratic nomination.
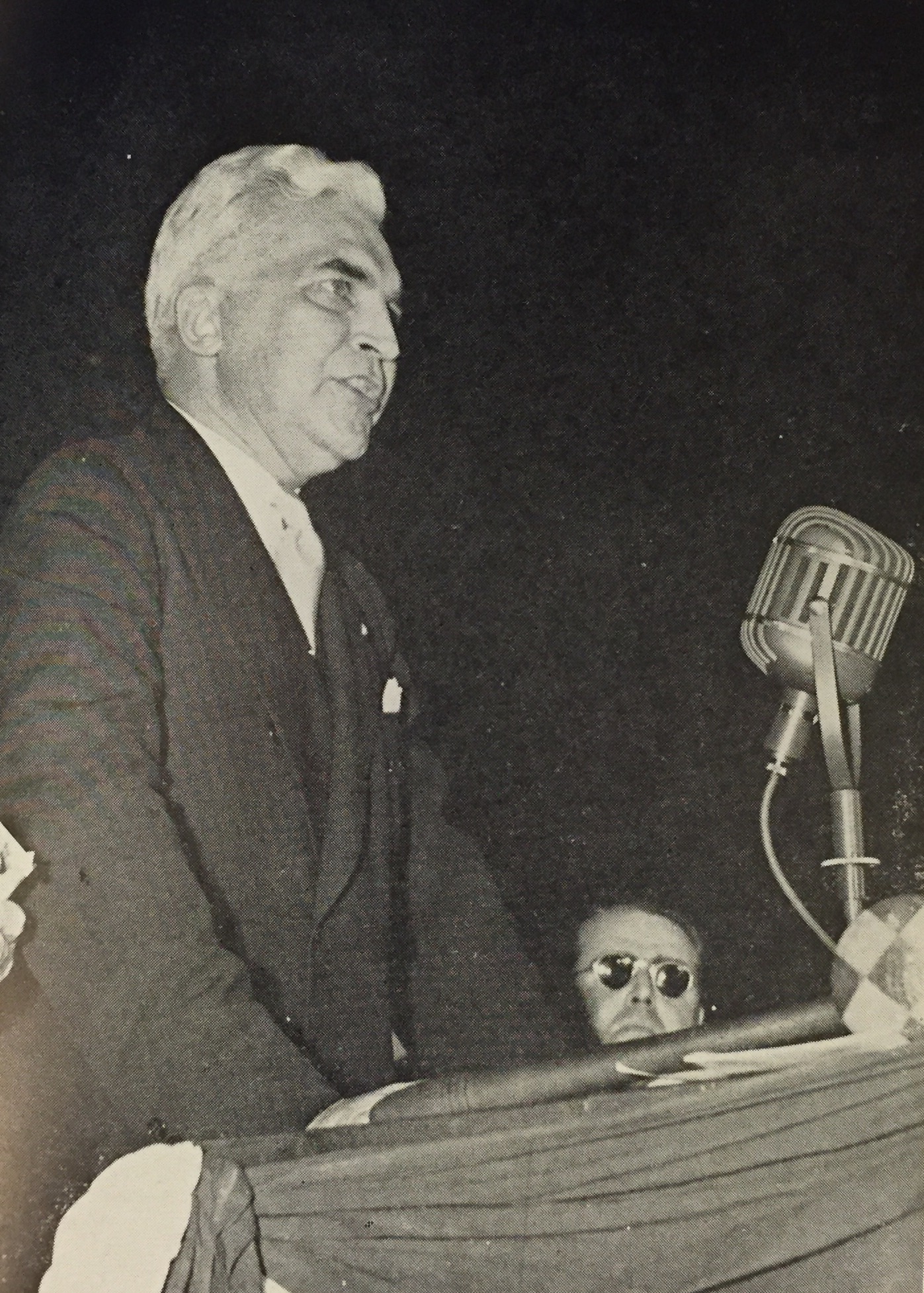

However, when Roosevelt decided to run for a third term, McNutt dropped out of the race for the Democratic Nomination in the hopes that he would be considered for the Vice Presidency. When Henry Wallace, Secretary of Agriculture, became Roosevelt’s choice for the Vice Presidency, McNutt conceded again to the wishes of the President. With a nomination for the presidency or vice presidency out of his grasp, McNutt ended his ambitions for the White House and he never held another elected office. Later that year, his friend and political rival Wendell Willkie secured the Republican nomination, but would lose to Roosevelt in November.
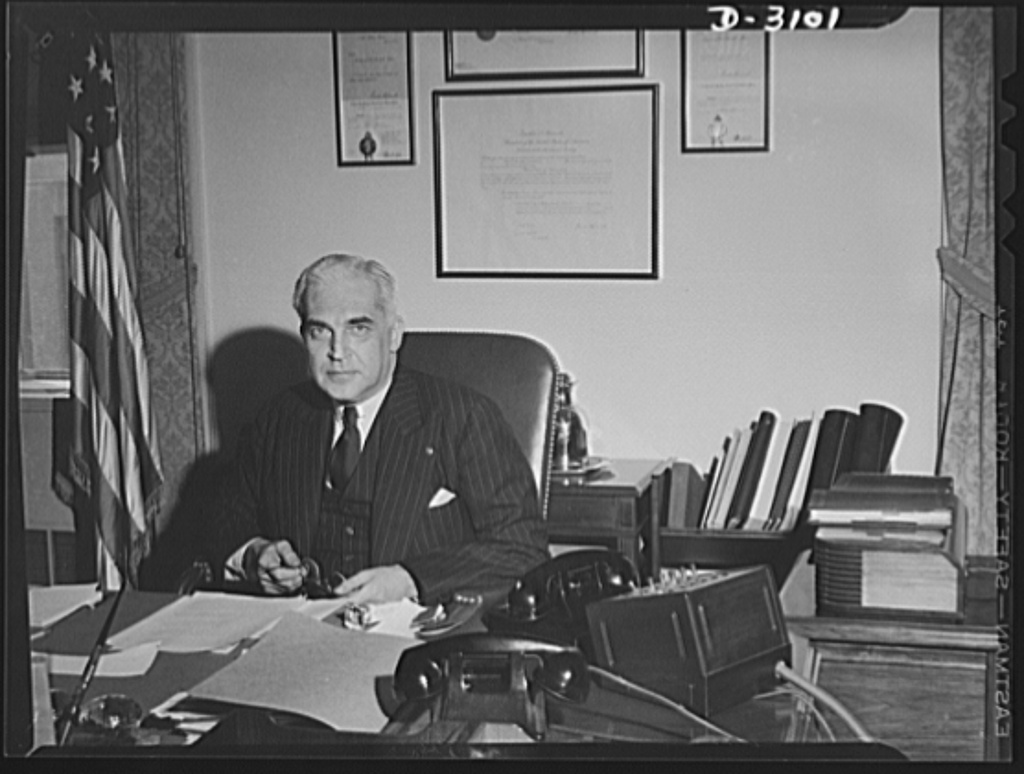


After his unsuccessful presidential campaign, McNutt continued public service as a loyal lieutenant for Roosevelt during World War II. He served as the Administrator for the Federal Security Agency from 1939-41, overseeing war efforts in infrastructure, health, and education, as well as the implementation of Social Security. In 1942, he was the Director of the Office of Defense Health and Welfare Services, part of the larger Office of Emergency Management. His final war post was as Chairman of the War Manpower Commission from 1943-1945. During his tenure, McNutt became an advocate for agricultural issues and their impact on the war effort, urging the need for food preparedness and the importance of student agricultural sciences.
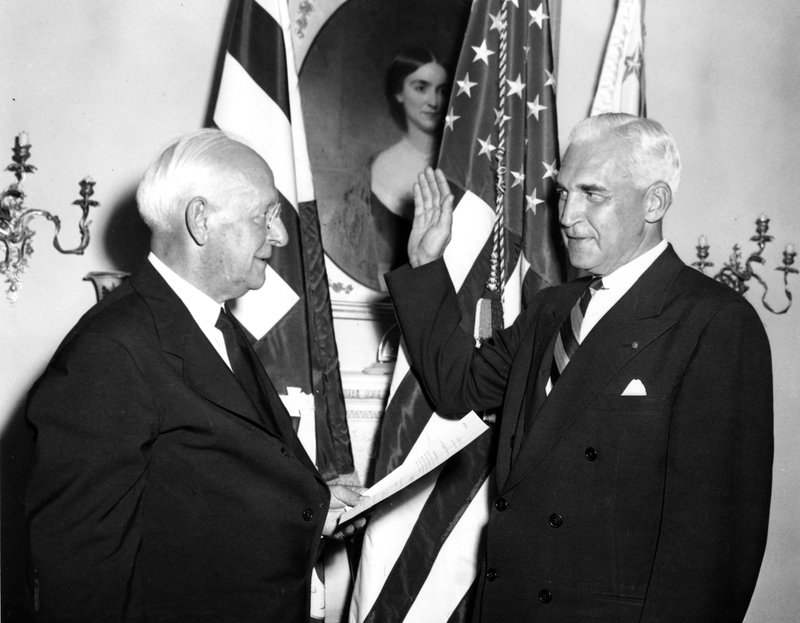

Near the war’s end, at President Harry Truman’s personal request, McNutt returned as High Commissioner to the Philippines in 1945 and, once they secured independence, appointed their first U.S. Ambassador in 1946. McNutt represented President Truman at the Philippine Independence ceremony on July 4, 1946, sharing the ceremonial duties with Philippine President Manuel Roxas and General Douglas MacArthur. He retired from this post in 1947. After his final post to the Philippines, the former governor, diplomat, and administrator took on a variety of projects, including unsuccessful stint as chairman of the United Artists Film Corporation in 1950- 51, buying out the controlling shares from Hollywood legends Charlie Chaplin and Mary Pickford. Unable to save the company from losses, McNutt was eventually bought out by movie mogul Arthur Krim, whose subsequent leadership spearheaded such classic films as The African Queen (1951) and High Noon (1952).
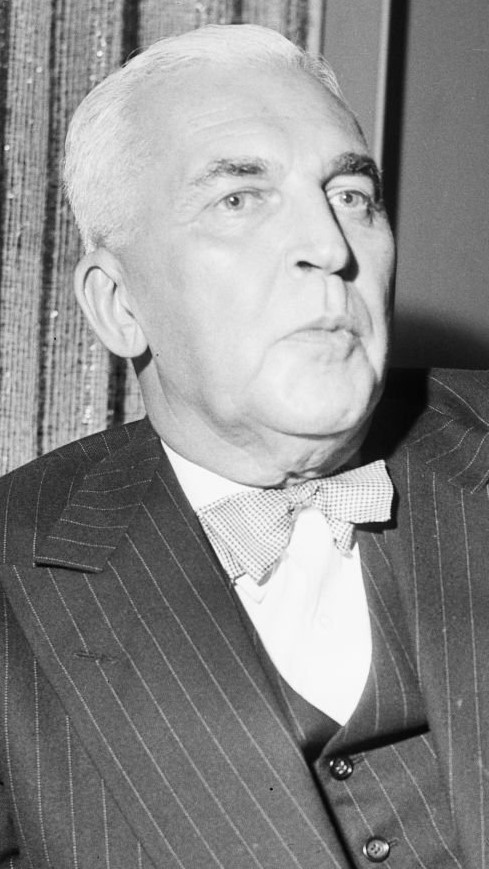

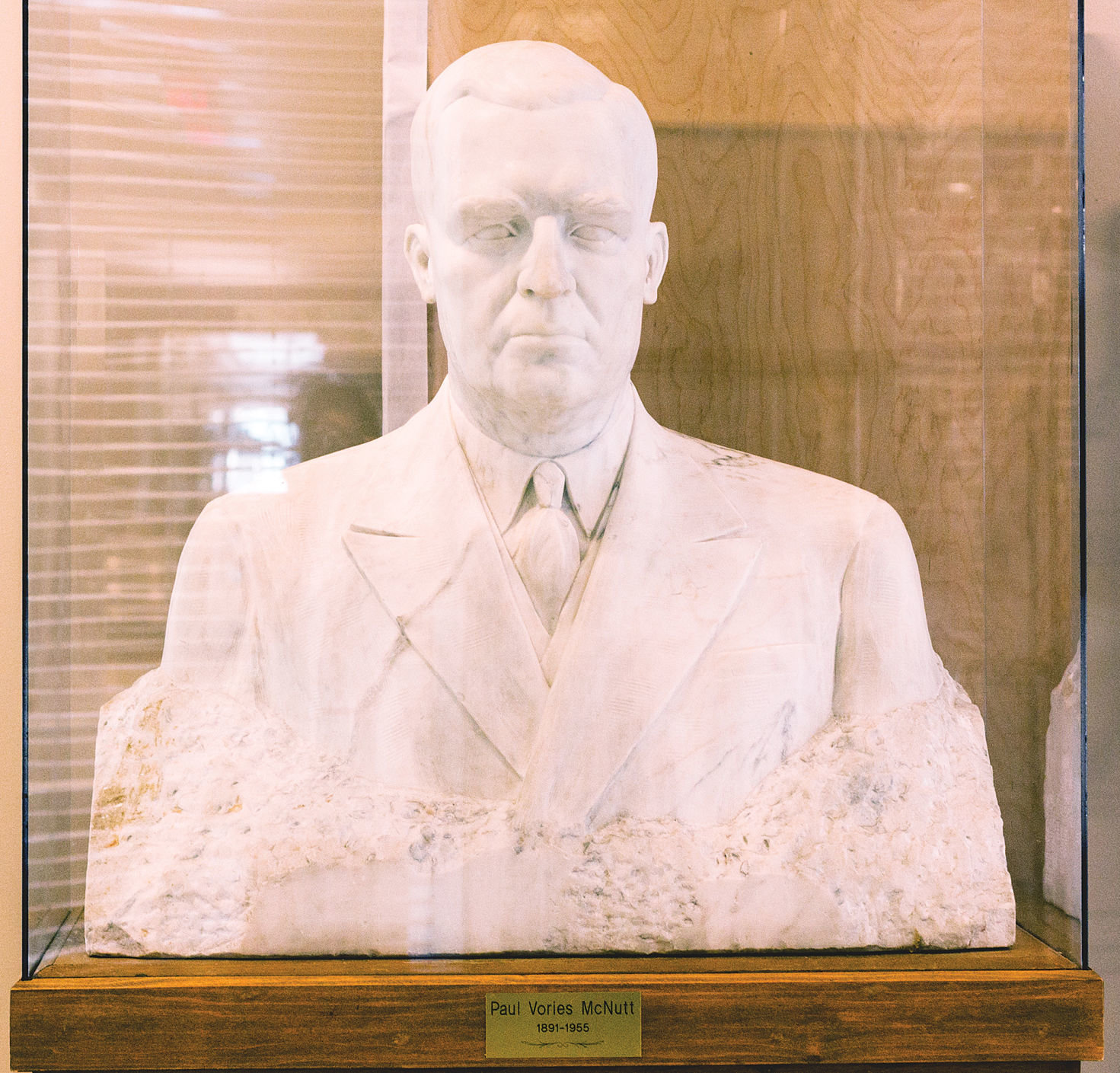
By 1954, McNutt’s health began to decline, most likely due to complications from surgery on a “throat ailment,” and on March 24, 1955 he died in his Manhattan apartment at the age of 63. He was interred at Arlington National Cemetery on March 28, 1955 with full burial rites. Herman B Wells, then president of Indiana University, performed the eulogy. In honor of his contributions to Indiana University, a residence hall complex at the Bloomington campus is named Paul V. McNutt Quadrangle and a bust of him resides in the front foyer of the main building.

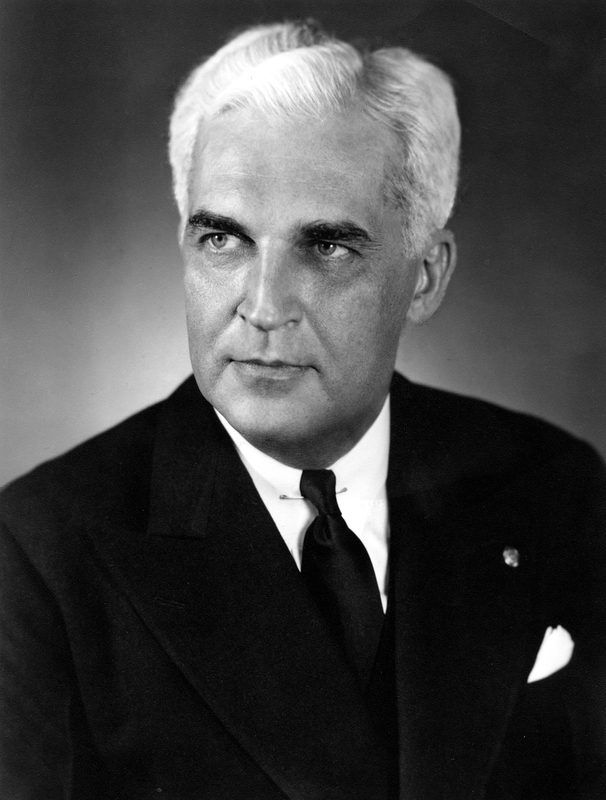
Paul V. McNutt’s decades of public service—as head of the American Legion, governor, diplomat, and administrator—left an indelible mark on the state of Indiana, the United States, and even the world. His commitment to human rights, political and social equality, and an internationalist view of foreign policy remain relevant today. His steadfast dedication to the protection and rights of the Jewish people during the hour of their extreme oppression serves as a model for us.

Above all, McNutt was committed to the cause of democracy. Like today, the challenges of McNutt’s era led many to question the relevance of the democratic ethos, whether we could have a government of the people, by the people, and for the people. In his inaugural address as Governor on January 9, 1933, Paul V. McNutt reflected on the importance of, and obstacles to, democracy:
It is possible to know the truth without fear, to meet a crisis with indomitable courage. Our proud heritage from the Indiana pioneers, who came here over a century and a half ago to build homes in the wilderness, should give us that power. Yet there are those among us who are afraid, who listen to prophets of evil. They profess to see the end of representative government, now rudely challenged by Communism, Fascism, and, some think, by Technocracy. They say that democracy in theory is not democracy in practice, that popular sovereignty is an elusive concept, that the right to have a voice in government is not a prized possession.
I wish to be counted among those who deny such a doctrine. I believe in the destiny of democracy as a system of government, believe in it more profoundly than in anything else human. . ..
This is a testing time for representative government. Our high enterprise is to prove it sufficient in every circumstance and for every task which can come to free people. We face a magnificent opportunity in which we, as lovers of freedom, dare not fail.
McNutt’s life and work demonstrate that democracy is a living, breathing process, one shaped by a resolute faith in the power of self-government. Hoosiers, and Americans broadly, are living through a “testing time” of their own, but the successes, and failures, of the life of Governor Paul V. McNutt provide a clear, historical example of robust and democratic leadership.

To learn more about Governor Paul V. McNutt, visit the Bureau’s marker page : http://www.in.gov/history/markers/165.htm.