
Indiana native Melba Newell Phillips pioneered new physics theories, studied under the famous J. Robert Oppenheimer, worked passionately to improve science education, and advocated for women’s place at the forefront of science research. After the U.S. dropped atomic bombs on Japan at the end of World War II, Phillips and other scientists organized to prevent future nuclear wars. She took a great hit to her career during the Cold War as she stood up for the freedom to dissent in the oppressive atmosphere of McCarthyism. Colleagues and students have noted her “intellectual honesty, self-criticism, and style,” and called her “a role model for principle and perseverance.”
Phillips was born February 1, 1907 near Hazleton, Indiana. According to Women in Physics, Phillips graduated from high school at 15, earned a B.S. from Oakland City College in Indiana, taught for one year at her former high school, and went on to graduate school. In 1928, she earned a master’s degree in physics from Battle Creek College in Michigan and stayed there to teach for two years. In 1929 she attended summer sessions on quantum mechanics at the University of Michigan under Edward U. Condon. When she sought Condon’s help on a physics problem, her solution, rather than his, ended up being the correct one. This led to a lifelong friendship and Condon recommended Phillips for further graduate study at the University of California, Berkley. Here she pursued graduate research under Oppenheimer and earned her Ph.D. in 1933. Within a few years she was known throughout the physics world because of her contribution to the field via the Oppenheimer-Phillips effect.
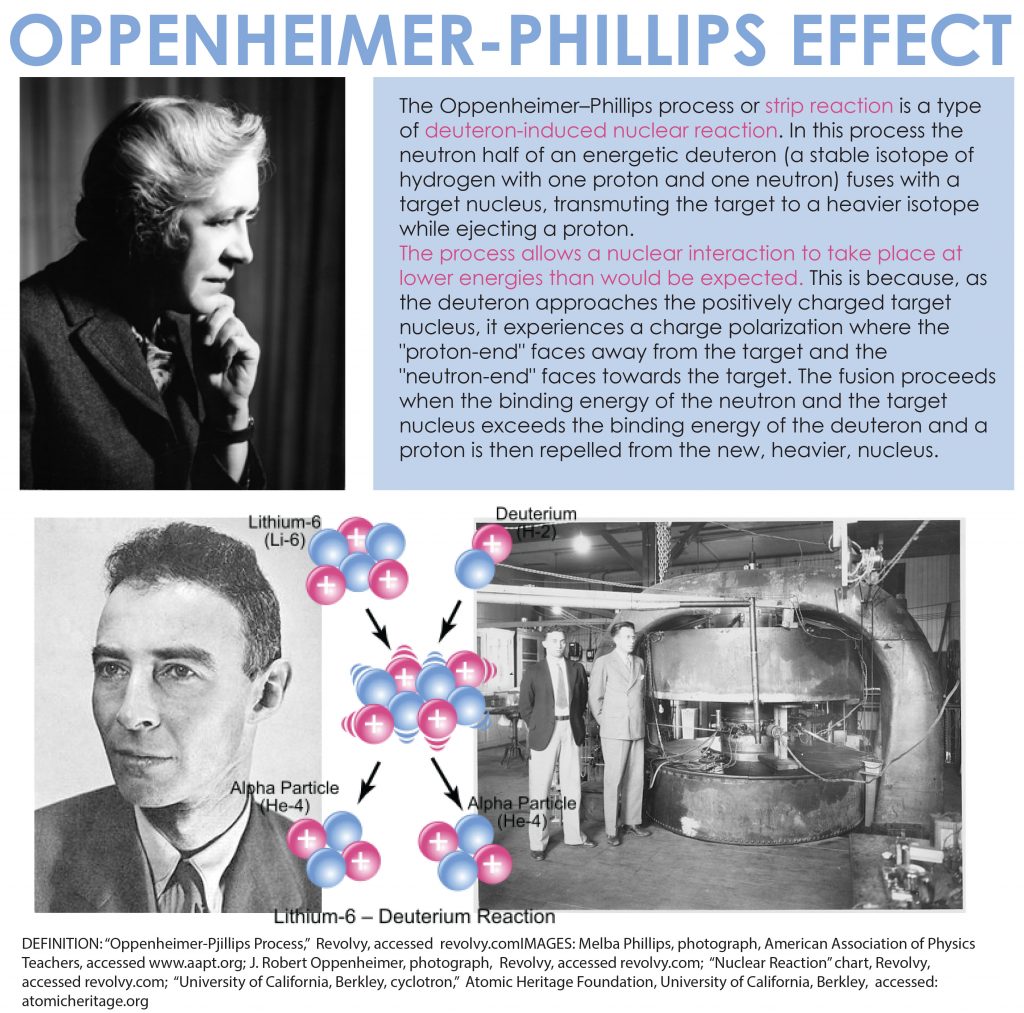
The 1935 Oppenheimer-Phillips Effect explained “what was at the time unexpected behavior of accelerated deuterons (nuclei of deuterium, or ‘heavy hydrogen’ atoms) in reactions with other nuclei,” according to a University of Chicago press release. When Oppenheimer died in 1967, his New York Times obituary noted his and Phillips’s discovery as a “basic contribution to quantum theory.” Manhattan Project scientist and professor emeritus of chemistry at the State University of New York, Stony Brook Francis Bonner explained in the release that normally such an accomplishment, now considered “one of the classics of early nuclear physics, “would have meant a faculty appointment. However, Phillips received no such appointment, perhaps due in part to the Great Depression, but also likely because of her gender.
Instead, Phillips left Berkley to teach briefly at Bryn Mawr College (PA), the Institute for Advanced Study (NJ), and the Connecticut College for Women. On February 16, 1936, the New York Times reported that she was one of six women to receive research fellowships for the 1936-1937 academic year as announced by the American Association of University Women. The announcement read: “Melba Phillips, research fellow at Bryn Mawr, received the Margaret E. Maltby fellowship of $1,500 for research on problems of the application of quantum mechanics to nuclear physics.”

In October of 1937 Phillips served as a delegate to the fall conference of the association at Harvard, where the discussion centered around the prejudices against women scientists that halted not only their careers, but scientific progress more generally. According to a 1937 New York Times article, Dr. Cecelia Gaposchkin, a Harvard astronomer, detailed the “bitter disappointments and discouragements” that faced women professionals in the field of science. Certainly, Phillips related, as her career moved forward slowly despite her achievements in physics.

Finally, in 1938, she received a permanent teaching position at Brooklyn College. In 1944, she also began research at the Columbia University Radiation Laboratory. Phillips was highly regarded as a teacher and Bonner noted she became “a major figure in science education” who “stimulated many students who went on from there to very stellar careers.”
Meanwhile, the U.S. officially entered World War II with the December 7, 1941 bombing of Pearl Harbor. No previous war had been so dependent on the role of science and technology. From coding machines to microwave radar to advances in rocket technology, scientists were in demand by the war effort.
In July 1945, the Manhattan Project scientists successfully detonated an atomic bomb in the desert of Los Alamos, New Mexico. In August 1945, the U.S. dropped two atomic bombs on Japan, forcing the country to surrender and effectively ending World War II. Over 135,000 people were killed in Hiroshima and 64,000 in Nagasaki. Many thousands more died from fires, radiation, and illness. While a horrified public debated whether the bomb saved further causalities by ending the war or whether it was fundamentally immoral, scientists also dealt with remorse and responsibility.
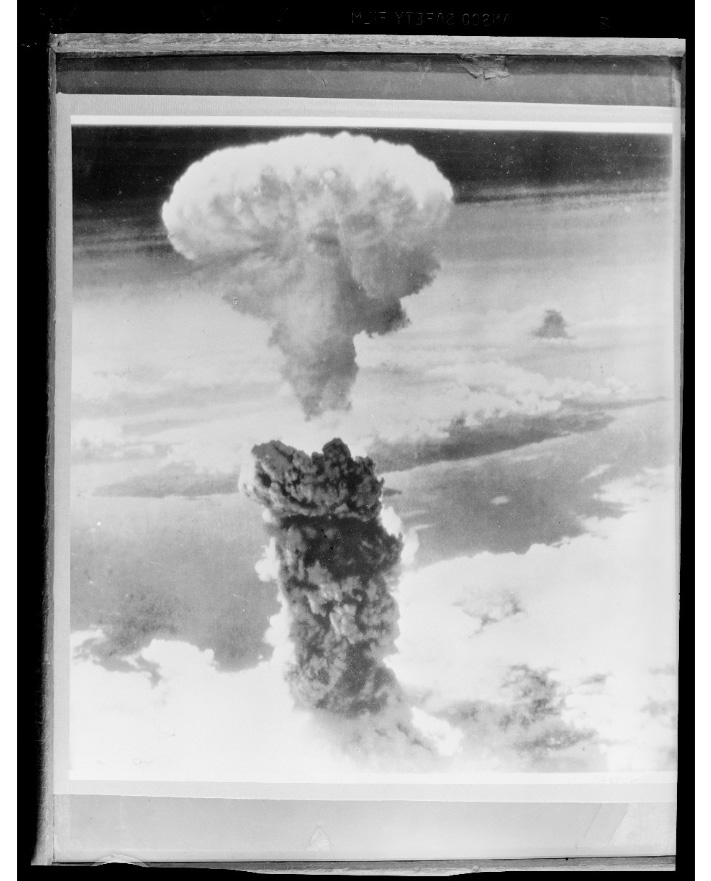

Henry Stimson, Secretary of War in the Truman administration, stated, “this deliberate, premeditated destruction was our least abhorrent choice.” Oppenheimer, however, reflected, “If atomic bombs are to be added as new weapons to the arsenals of a warring world, or to the arsenals of nations preparing for war, then the time will come when mankind will curse the names of Los Alamos and of Hiroshima.” More bluntly, Oppenheimer told Truman, “Mr. President, I feel I have blood on my hands.” Many physicists retreated to academia, but some became politically active, especially in regard to preventing further destruction through scientific invention.
Representing the Association of New York Scientists, Phillips and leading Manhattan Project scientists helped organize the first Federation of American Scientists meeting in Washington, D.C. in 1945. The goal of the Federation was to prevent further nuclear war. That same year Phillips served as an officer in the American Association of Scientific Workers, an organization working to involve scientists in government and politics, to educate the public in the science, and to stand against the misapplication of science by industry and government. On August 16, 1945 the New York Times reported that Phillips and the other officers of the Association signed a letter to President Truman giving “eight recommendations to help prevent the use of atomic bombs in future warfare and to facilitate the application of atomic energy to peacetime uses.”
By the end of the 1940s, Melba Phillips’s accomplishments in physics and science education were well-known throughout the academic physics community. However, by the early 1950s, she was accused of being affiliated with communist subversives and fired from her university positions. What happened to this Hoosier physics pioneer?
Find out with Part Two, Melba Phillips: Leader in Science and Conscience.
