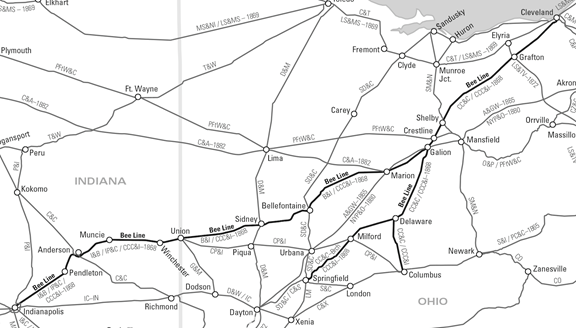
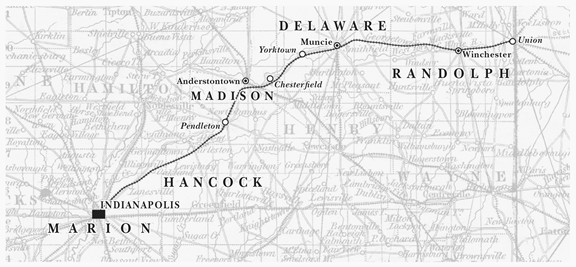
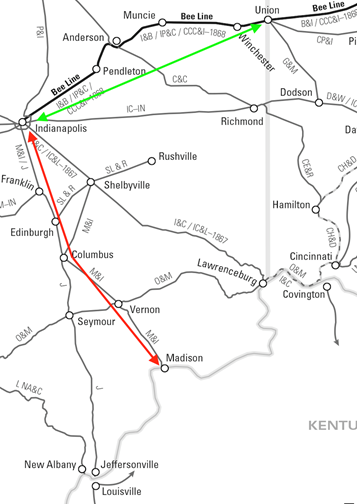
See Part VI to learn how the Hoosier Partisans moved for autonomy as the Cleveland Clique tightened its grip on the Bee Line railroad.
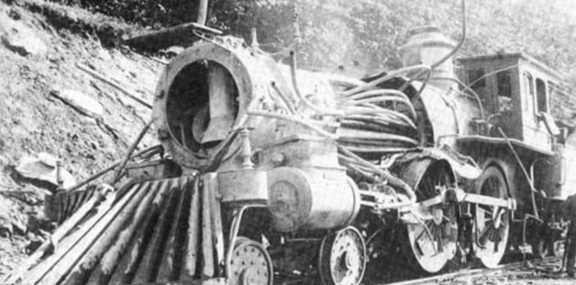
In the summer of 1859, the Indianapolis, Pittsburgh and Cleveland’s (IP&C’s) Madison locomotive exploded near Kilgore Station in Yorktown, Indiana – killing the engineer and fireman. A month later, near the same location, an intoxicated man fell from the station’s platform and was killed by a passing train.
These tragic events occurred just weeks after the Hoosier Partisans’ scheme to achieve their independence, by leveraging on the IP&C’s strategic position as a funnel to the West, had failed. The accidents seemed eerily suggestive of the Hoosier Partisans’ plight in the face of the Cleveland Clique’s mustered financial power.
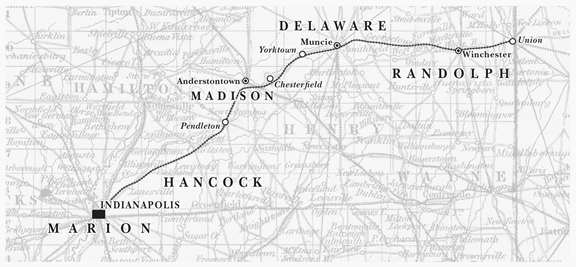
By the IP&C’s May 1860 board meeting the Partisans were resigned to their fate: “we know of no other means by which we can extricate ourselves from our monetary difficulties and save the road . . . We deem it best to extend and continue said [joint operating] contract with said Bellefontaine and Indiana Railroad (B&I).”
Indiana board members had again faced the reality that the railroad business, on many levels, could be a perilous endeavor. The push and pull of the Hoosier Partisans and Cleveland Clique would ultimately result in the legal consolidation of the Bee Line Railroad components roads.
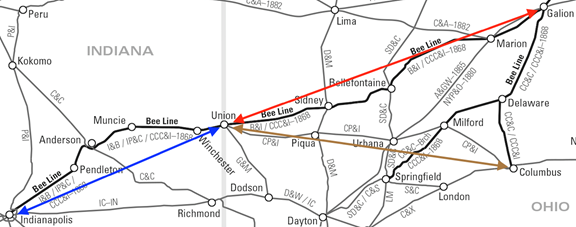
Incredibly, Brady was able to pull off what the Hoosier Partisans had been unable to accomplish in their effort to effect a divorce from the Cleveland Clique – at least until 1863 when the CP&I was once again reorganized.
Ironically, the advent of the Civil War in 1861 would bring prosperity to the anemic component roads of the Bee Line – now operating jointly as the Bellefontaine Line. The combination of enhanced demand for grain to feed the troops and bolster poor harvests on the European continent spelled profits for the railroads.
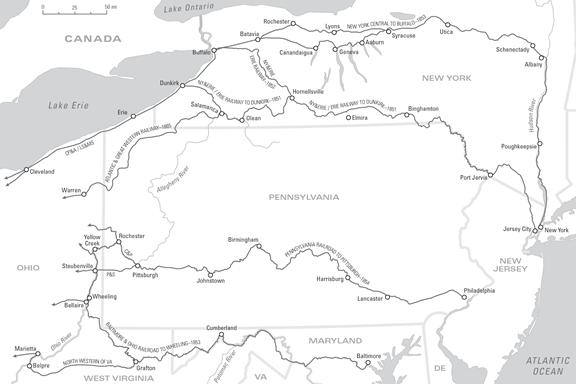
The demands of war pushed operational efficiency forward – driven by the trunk lines. The resulting more integrated rail networks also led to enhanced profitability, and opened the door for the Eastern trunk lines to expand their footprint west.
The Bee Line roads finally got their financial houses in order. By June 1863 the IP&C declared its first dividend in years—3 percent. Taking advantage of newfound prosperity, it declared another 3 percent dividend in December and voted to increase capital stock by $300,000.
Ostensibly this was done to pay for new equipment, new terminals, and road improvements. In reality it provided a convenient opportunity for the Cleveland Clique to increase their stock position and thereby dominate upcoming shareholder votes. To that end they determined, once and for all, to quell the IP&C board’s irritating Hoosier independence.

Courtesy of the Clique’s voting block, John Brough returned as IP&C president at the February 1863 annual meeting – following Hoosier figurehead Thomas A. Morris’ 3½-year tenure. In a last-ditch effort to stem the Clique’s board dominance, Alfred Kilgore—Yorktown’s first station agent, son of director David Kilgore, and an Indiana state legislator— introduced a House bill in January 1863. Had it passed, all Indiana railroad corporations would have been required to elect three-quarters of their board from stockholders resident in the state. It died in committee.

Beyond Brough’s return to the IP&C’s presidency, he emerged as the front-runner in Ohio’s governor’s race in the summer of 1863. Orchestrated by the Cleveland Clique, Brough’s candidacy leveraged on his earlier but noteworthy Ohio political career and effective pro-Union speechmaking style. The War Democrats and Republican Union parties joined forces to secure his nomination. He was overwhelmingly
elected in October 1863.

Stillman Witt, Cleveland Clique heavyweight and by then the second-largest individual holder of Bee Line roads stock, had encouraged and supported his close friend’s candidacy. On Brough’s election as governor Witt volunteered to fulfill his duties as president of the Bee Line roads. He insisted Brough draw his IP&C presidential salary while serving as governor.
During 1864 Witt steered the Bee Line roads toward a brisk legal consolidation. At the IP&C’s June board meeting a committee was appointed “to agree upon mutual and just terms for consolidating the capital stock of this company with that of the B&I.” Reprising its once central role in the history of both the IP&C and B&I, Union and its Branham House was chosen as the site for the decisive shareholder consolidation vote.
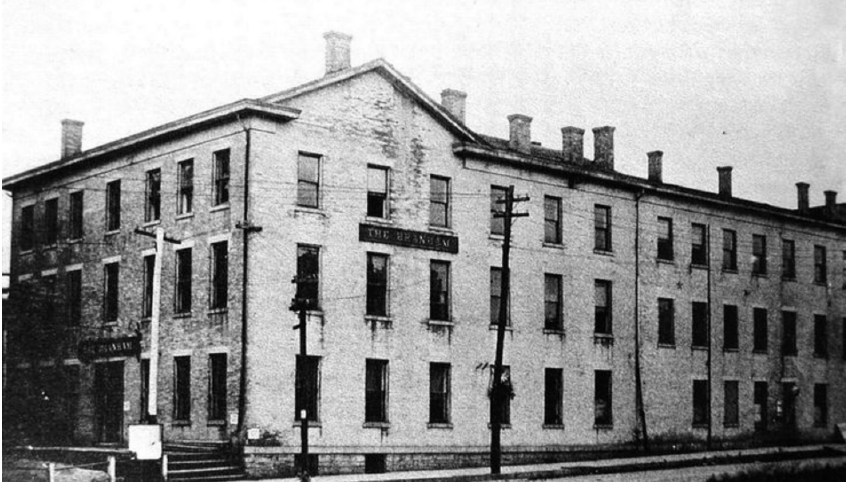

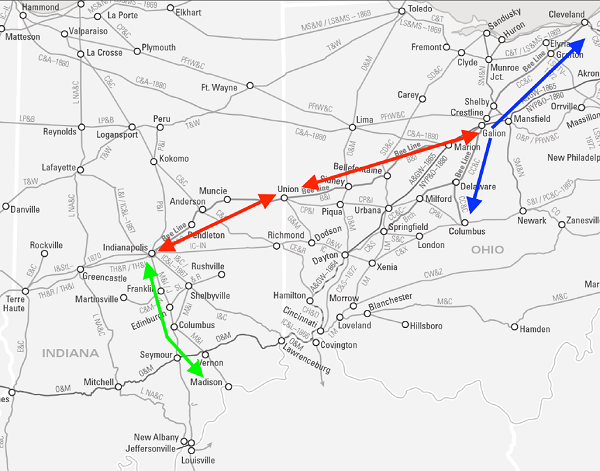
Finally, after years of Hoosier Partisan and Cleveland Clique push and pull, the two lines were legally consolidated on November 24, 1864 – emerging as the Bellefontaine Railway Company. For the first time since its inception in 1848, the railroad extending from Indianapolis to Union failed to exist as a stand-alone Hoosier-based—if not completely controlled—entity.
Brough was elected the new entity’s first president at its inaugural meeting in Union on December 22nd. It would be a short tenure, however, as Brough died in office on August 29, 1865 while also serving as Ohio’s last wartime governor.
After Brough’s death, Witt officially assumed the role he had been occupying as Brough’s proxy. His style was businesslike and close to the vest. Board minutes reflected meetings run with a limited agenda, focused on few topics, and with little discussion noted.
Witt saw to it that the Cleveland Clique began to recoup investments made in the road’s predecessor lines. Hardly a board meeting would go by over the next three years in which a dividend was not declared. And there were up to three board meetings a year.
The Cleveland Clique was not done tightening its grip on the Bee Line. In addition to Brough’s election as president in December 1864, a landslide of Cleveland Clique members took eight of eleven seats on the Bellefontaine Railway’s board. Included among this number was an individual destined to alter the Bee Line’s future trajectory: Hinman B. Hurlbut.
Hoosier David Kilgore, the only surviving original director from the Indianapolis and Bellefontaine Railroad (I&B) days, assumed one of the three crucial executive committee positions.

By the spring of 1868 the Cleveland Clique decided to finally consolidate all three of the original Bee Line component roads – then comprised of the Bellefontaine Railway and the Cleveland, Columbus and Cincinnati Railroad (CC&C). The need for additional monies to restructure debt and fund an expanding footprint was justification enough to tap the CC&C’s solid financial underpinnings.
In reality the freed and raised cash by the consolidation would be spent on both business expansion and personal enrichment. To a greater extent than marketed to the public the new road was being recast, like many others in the post-Civil War era, as a “financiers’” railroad.

On May 13, 1868, the Cleveland, Columbus, Cincinnati and Indianapolis Railway (CCC&I) sprung to life under the leadership of former CC&C president Leander M. Hubby. Hubby had established a long, profitable, and almost patriarchal reputation among his management team over the course of more than a decade at the helm of the CC&C. He and the newly recast Bee Line faced two immediate and significant obstacles to their future viability.
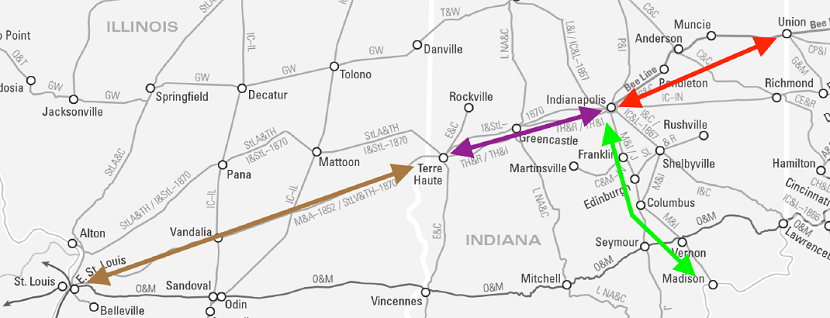
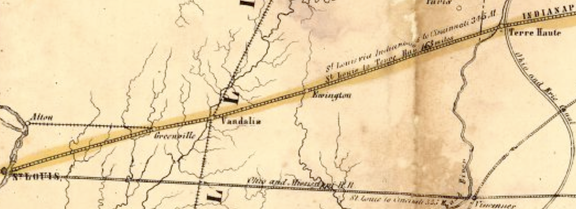
One challenge was to finally complete and/or control a rail line between Indianapolis and St. Louis. By 1867, the Cleveland Clique had assembled what it thought was a consortium of six similarly-interested rail lines to sign an expensive long-term lease of a road between Terre Haute and St. Louis. It proved to be otherwise.
The poorly engineered, indirect, and financially tenuous St. Louis, Alton and Terre Haute Railroad (StLA&TH) was its only option. And by the time the lease was signed the original consortium had essentially dwindled to two: the Bee Line and another Clique-affiliated railroad.
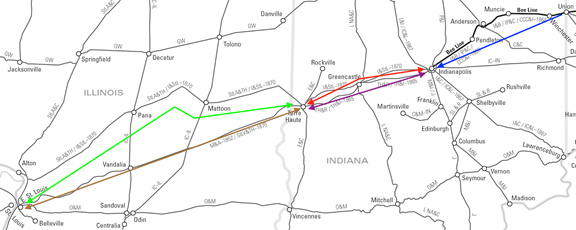
More to the point, as the consortium disintegrated, the road between Indianapolis and Terre Haute – by then called the Terre Haute and Indianapolis Railroad (TH&I) – backed out. Instead, it would align with Pennsylvania Railroad interests to complete John Brough’s dream of a direct line to St. Louis, under the colloquial Vandalia Line moniker. As a result, consortium participation with competitors made no sense.
However, the TH&I’s realignment with Pennsylvania Railroad interests meant the Bee Line was left without a link between Indianapolis and Terre Haute. And the TH&I would not entertain an arrangement to let the Bee Line utilize its tracks.
By the fall of 1867 the Clique’s Bee Line board made the financially difficult decision to build its own parallel line between Indianapolis and Terre Haute. The Indianapolis and St. Louis Railroad (I&StL), headed by Thomas A. Morris, would be built in less than three years. And soon, it would fold and operate the StLA&TH under its banner. But it had been a costly decision.
Hubby’s other immediate Bee Line challenge was more sinister in its design. And, at least initially, Hubby would be unaware of its existence. But, in fact, it would threaten the Bee Line’s very survival and that of its Cleveland Clique benefactor.
Check back for Part VIII, the final blog in the Bee Line series, to learn more about how the national aspirations of other railroads, and their financial chicanery, recast the Bee Line Railroad’s ultimate destiny.
Interested in the Bee Line?


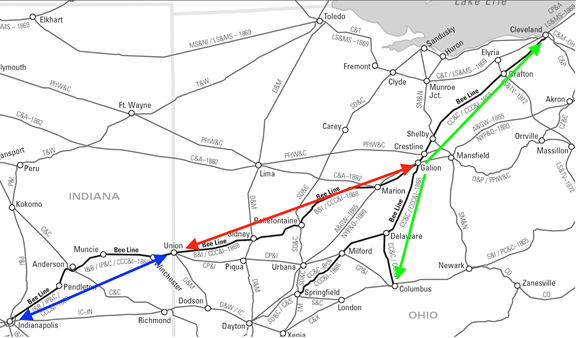











![Midwest Railroads Map, circa 1860, showing the Madison and Indianapolis [M&I], Terre Haute and Richmond [TH&R], and component roads of the Bee Line: Cleveland, Columbus and Cincinnati [CC&C]; Bellefontaine and Indiana [B&I]; Indianapolis and Bellefontaine](http://blog.history.in.gov/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Midwest-Railroads-Map-c1860.png)

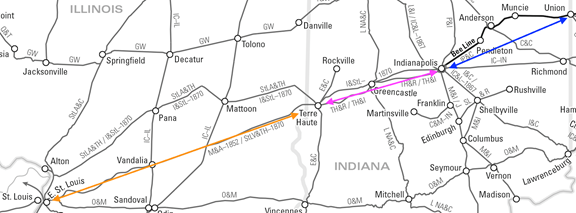
![Railroads west from Indiana, including the Terre Haute and Richmond [TH&R], Ohio and Mississippi [O&M], Mississippi and Atlantic [M&A], and St. Louis, Alton and Terre Haute [StLA&TH]](http://blog.history.in.gov/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Railroads-West.png)

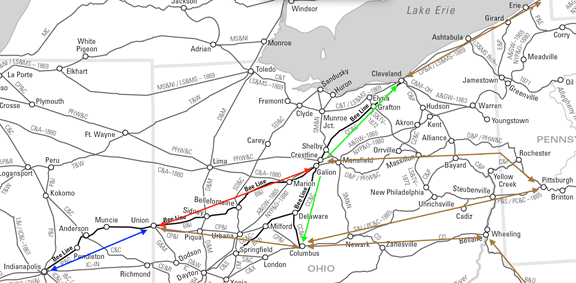
![image of The Madison and Indianapolis Railroad [M&I] and involved roads: the Peru and Indianapolis Railroad [P&I], extending north from Indianapolis, and the Mississippi and Atlantic Railroad [M&A], extending west to St. Louis. Terre Haute and Richmond [TH&R]](http://blog.history.in.gov/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/MI.png)