This blog post is an expanded version of Nicole Poletika’s original marker review essay, which can be viewed here.
The presidency of the United States is seen by many as the ultimate prize in American politics. It has been held by lawyers, philanthropists, and even actors. The State of Indiana has been at the center of presidential history, claiming Hoosier Presidents Benjamin Harrison and his grandfather, William Henry Harrison. However, one year sticks out more for what didn’t happen than what did: 1940.
That year, Hoosier natives Wendell Willkie and Paul V. McNutt, came very close to winning the presidency but ultimately lost, in their own ways, to Franklin Delano Roosevelt (FDR). This is the first of two blogs dedicated to the Indiana men who ran for the highest office in America.


Wendell Willkie, the 1940 Republican Candidate for President, was born in 1892 in Elwood, Indiana. Willkie attended Indiana University, where he became friends with another budding young student, Paul V. McNutt. When McNutt was the President of the Student Union, Willkie was the President of the Jackson Club, a Democratic leaning political group. Their paths continued to cross throughout the rest of their lives. Willkie received his law degree from Indiana University in 1916. In 1929, after practicing law in Akron, Ohio for the Firestone Tire Co, he provided legal counsel for The Commonwealth & Southern Corporation, a large public utilities company, of which he later became president.
As company president, he fought against FDR’s federally funded New Deal program to establish the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), which intended to provide employment to the many jobless during the Great Depression. Willkie opposed the TVA because it would directly compete with The Commonwealth & Southern Corporation and because he opposed both governmental and private monopolies. While Willkie lost, he gained notoriety as “the most articulate, vigorous spokesman for the business community.”

After gaining the attention of Republican politicians with his outspoken belief in free enterprise, Willkie was nominated as the Republican presidential candidate to run against FDR in 1940 in what was described by the Indianapolis News as “one of the most dramatic events in American political history.” Despite never holding political office, much like modern Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump, Willkie was nominated after the sixth ballot was taken at the Republican National Convention. He defeated well-known political figures such as Governor Thomas E. Dewey and Senator Robert A. Taft. It was here that he earned the campaign moniker of “Dark Horse,” since his candidacy was such a political upset. Republicans sought a fresh candidate to represent the party as World War II intensified abroad and Americans became more determined than ever to avoid war at home.
Around this same time, his IU colleague and friend Paul McNutt, dropped out of consideration for the Democratic nomination, giving in to Roosevelt’s desire for an unprecedented third term. Had McNutt been nominated, both major party candidates for President would have been from the State of Indiana.
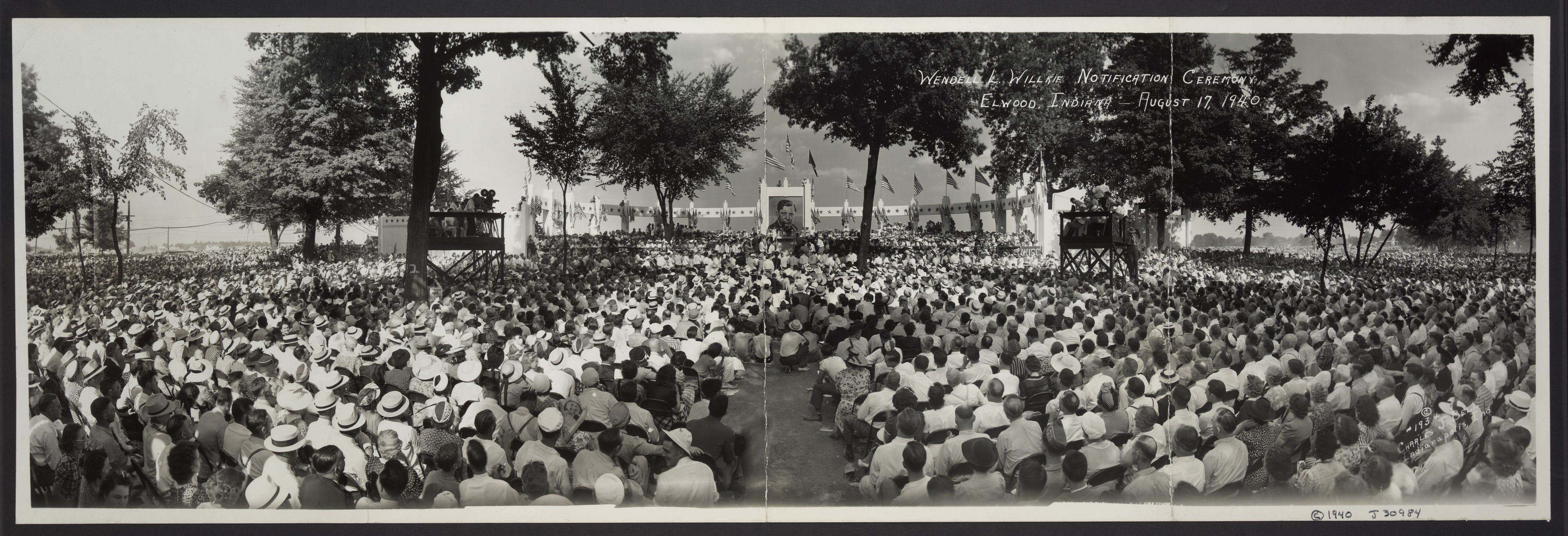



Despite a well-fought campaign, Willkie lost the election to Roosevelt in a landslide, earning only 82 electoral votes to Roosevelt’s 449. He also lost the popular vote by nearly five million. Many commentators thought that his progressive position on civil rights and support of liberal internationalism alienated him from his party. Voters also struggled to identify his position on major causes because he covered a wide range of issues briefly.

Even though he lost the presidential election in 1940, Willkie and FDR became friends and political allies, as they held similar views on foreign policy and civil rights. In particular, Willkie, both during and after the campaign, went against many in his party with his support of FDR’s policy to dispatch war aid to Britain in 1940, as opposed to fighting abroad or remaining isolated from the war. Historian Justin H. Libby describes Willkie’s support of war aid as the “forerunner of the bipartisan policy.”
Willkie’s support for aid eventually gained favor among the general public, allowing FDR to pass the Lend-Lease Bill in 1941, which postponed U.S. involvement in the war. He also served the President by traveling the globe as a U.S. emissary to observe the war abroad and meet with foreign leaders, reporting on his experiences. As an internationalist, Willkie worked for “world peace,” presenting a bipartisan resolution to the Republican National Committee in 1942 that was eventually passed.

On the home front, Willkie avidly defended the rights of African Americans and publicly advocated for the improved housing, education and health of black citizens. He was widely concerned with the treatment of African Americans in the Armed Forces, arguing in various articles that they should be afforded the same freedom at home that they fought for abroad.
In his 1944 article “Citizens of Negro Blood” for Collier’s Magazine, Willkie stated that World War II “has made us conscious of the contradictions between our treatment of our Negro minority and the ideals for which we are fighting. The equitable treatment of racial minorities in America is basic to our chance for a just and lasting peace.” He appealed to political figures to strengthen anti-lynching measures and to eliminate state poll taxes that often prevented African Americans from voting. Willkie ultimately brought attention to the struggles of all minority citizens, arguing in the New York Times that they were “rich assets of democracy.”

In 1943, Willkie wrote about his experiences traveling the globe in his best-selling book One World. He described his trip, in which he traveled with Army and Navy officials to over half a dozen countries. His observations, made during a period before the United States frequently worked and communicated with other countries, has been described as “extraordinarily perceptive and statesmanlike.” It spent four months on the New York Times bestseller list and was an influential text on the future United Nations.
Willkie sought the Republican presidential nomination in 1944, but dropped out of the race in April after a poor showing in the Wisconsin primaries. Constant comparisons to FDR, his liberal stance on civic and international issues, and general independence from other Republican members resulted in the loss of party support.

Willkie died October 8, 1944 and was buried in East Hill Cemetery in Rushville, Indiana. President Roosevelt issued a statement honoring Willkie as “one of the great men of our time.” In addition to the memorial erected at his gravesite, memorials to Willkie were dedicated in Elwood and in the State House Rotunda in Indianapolis. The Willkie Memorial Building, created to serve as a center for the Freedom House and other causes he supported, was dedicated in New York on the first anniversary of his death. Willkie, with the support of Eleanor Roosevelt, helped established Freedom House in 1941 as an organization that could “strengthen human rights and civil liberties in the United States.” As of 2016, the Freedom House still advocates for human rights.
Wendell Willkie’s ambitions for the White House never materialized, but his influence on American politics can still be felt, especially in his stances on international relations, civil rights, business, and foreign policy. His friendship and support of Franklin Roosevelt, even after losing to him, benefited the country during wartime. Willkie was a results man; he believed deeply in the power of institutions and people to get the job done right, whether in politics or in business. His bipartisanship and amiable demeanor earned him respect from leaders all across the country. In the end, the “Dark Horse” became a statesman on par with almost any President.