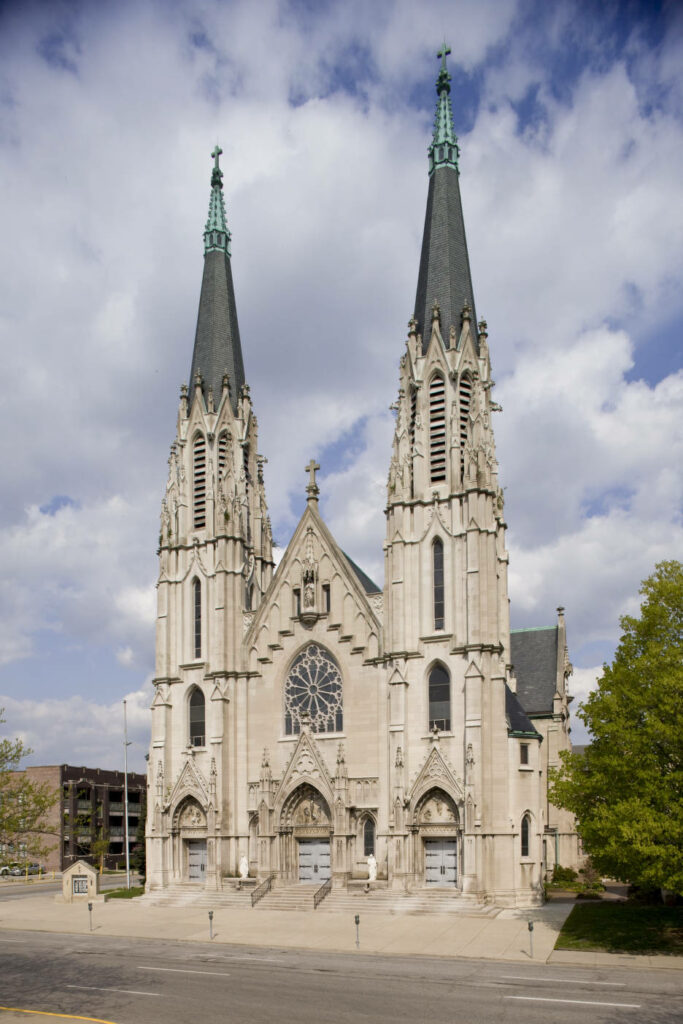
St. Mary Catholic Church is an architectural gem. Its gothic towers help define the downtown Indianapolis skyline, while its bells call the faithful to worship. For its congregation certainly, but also for those dining and shopping in the Mass. Ave. Cultural District, the cathedral provides a moment of stately beauty in the urban landscape. But St. Mary’s is more than an elegant building. It is a love story—one set into motion by a kind matchmaking priest.

Herman (also spelled Hermann) J. Gaul was born in Germany in 1869 and immigrated to the United States in the late 1880s.[1] He was a devoted Catholic who loved the architecture of Germany’s churches, especially the Cathedral of Cologne. From an early age, he aimed to bring this gothic vision to the Midwest. In the early 1890s, he began an apprenticeship with the renowned Chicago architect Louis Sullivan.[2] In 1891, Sullivan’s Chicago firm sent Gaul to Indianapolis for several months to supervise the building of a new plant for the Home Brewing Company.[3]
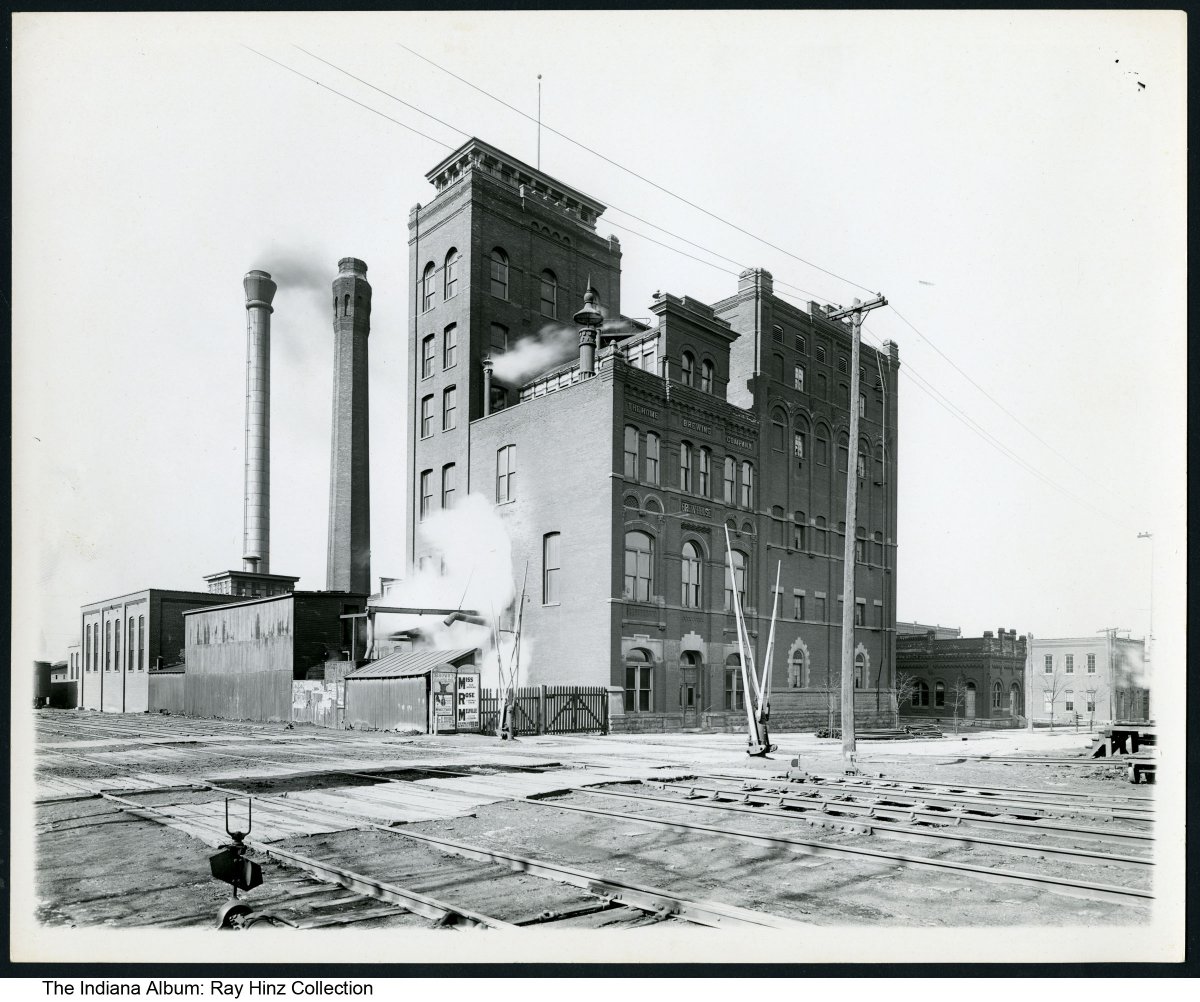

The beer company incorporated in the summer of 1891 with $200,000 in stocks from notable residents. Construction, at a cost of $70,000, began soon after. The company was influential enough to garner city permission to construct a switch that would allow shipping via railroad right out of its backyard—not without some objection over this “bow to the brewers” from temperance factions in the city. The Home Brewing Company began operations early in 1892 and was a huge financial success.[4]

For the local business community, this ambitious and visible project made Gaul a young architect to watch. For the ladies of Indianapolis’s German Catholic community, it would have made him a fetching romantic prospect. And luckily for Gaul, the 1890s were actually a great time to fall in love.

In previous eras, women’s labor was necessary for a couple’s survival and a man seeking a wife looked for someone who would make an economic contribution to the farm or family business—regardless of his personal feelings for her. On the flip side, a young woman’s family would make a similar financially-minded decision, using her to link two families together to build wealth — regardless of the bride’s feelings for her groom. Of course, financial concerns never disappeared from matchmaking, but by the eighteenth century, love became more central to a match, and romantic marriage became more common.
Nineteenth century conventions placed more emphasis on the husband as breadwinner and wife as homemaker. And while this social construct had some serious political and economic disadvantages for women, it did allow for the consideration of romantic love in choosing one’s spouse. [5] Gaul’s luck at being born in this period and his dedication to his faith soon led to his own romantic match.

When he arrived in Indianapolis in 1891, Gaul knew that he wanted to stay in the home of a respectable German Catholic family as opposed to a hotel or boarding house. He was also eager to find a spiritual home. He looked to St. Mary, the heart of the German Catholic community, located at that time on Maryland Street. Indianapolis German Catholics and regional Catholic leadership had organized this church for German-speaking congregants in the 1850s. In addition to serving the community’s spiritual needs, St. Mary was also the cultural hub for the local German immigrant community, hosting concerts, theatrical performances, and festivals featuring traditional German food and entertainment.[6]

Gaul’s first stop in his new city was the home of Father Anthony Scheideler, pastor at St. Mary since 1874. Father Scheideler knew his congregants well. So when Gaul asked him to recommend a nice family who might take him in as a boarder and who lived near the Home Brewing Company construction site, Scheideler immediately had the right fit: the Seiter family. They were also of German origin and described by Scheideler as “one of the best families in my parish.”[7] Christopher Seiter, the patriarch, owned a saloon, while his wife, Cecelia, took care of the home and their children. In his two months with the Seiters, the young architect fell in love with their daughter, Mary, who was about sixteen years old, seven years younger than Gaul. He was smitten but would have to be patient for several more years. With a smile on his face that the pastor remembered decades later, Gaul told Father Scheideler:
I am going back to Chicago, but I shall return soon. I have found the oldest daughter of Mr. Seiter very interesting.[8]
Father Scheideler was pleased with the match. It’s not clear how often Gaul returned to visit Mary or if they stayed in touch mainly by mail, but he kept his promise to return. On April 22, 1896, Father Scheideler officiated the wedding of Herman Gaul and Mary Seiter at St. Mary Catholic Church.[9]
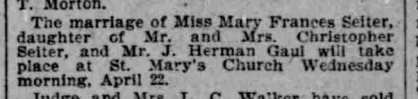
On his wedding day, Gaul thanked the pastor for connecting him “to such an estimable family” and told him he would never forget his kindness. He vowed:
If you ever build a new church, Father Scheideler, I will be the architect.[10]
It seemed like the kind of lofty promise a young man would make on an emotional day, and the pastor “laughed and thanked the enthusiastic young architect but gave no further thought to his promise.”[11]

Gaul and his new wife moved to Chicago. He opened his own architecture firm and grew his career over the following decade, building a half dozen churches as well as schools, orphanages, and hospitals for German institutions around the Midwest. One major commission, St. Nicholas Church in Evanston, Illinois, stood proudly on an elevated site with “romantic ambience.”[12]
Over the following years, Herman and Mary Gaul welcomed seven children. Unsurprisingly, Mary’s name doesn’t appear in newspapers outside of a real estate transfer (along with Herman’s name). She seems to have been busy taking care of her large family with little time to lead a literary or church club that would have landed her coverage in newspapers. But we can assume their marriage was a happy one, since Gaul still felt inspired by it to fulfill the promise he made in Indianapolis.[13]

Meanwhile in the Circle City, the German immigrant population continued to grow, as did the congregation of St. Mary Catholic Church. Father Scheideler knew he would soon need a bigger building. In 1906, the pastorate purchased land at the intersection of Vermont and New Jersey as a future investment with “no thought of building immediately entertained.”[14] Nonetheless, local newspapers printed news of the transfer.
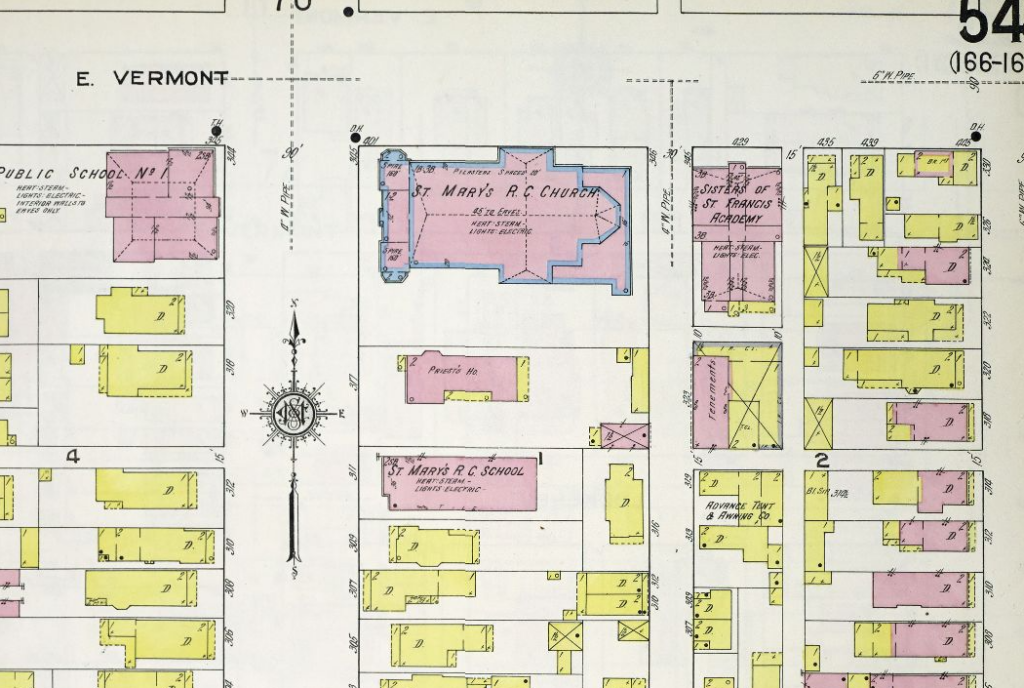
Father Scheideler may have “practically forgot Herman Gaul and his promise to draw the plans for a new St. Mary’s,” but Gaul had not forgotten. When the architect read about the new St. Mary property in the newspaper, he quickly left for Indianapolis. Father Sheideler opened his door and there was Gaul, again wearing that memorable smile. The architect said, “I have come to make good my promise to draw plans for a new St. Mary’s.” Father Sheideler told him that unfortunately they did not yet have the funding to build, but Gaul was undeterred. He replied, “Well, I am going to draw the plans anyhow, true to my word.”[15]

The two men spent hours chatting and catching up and soon discovered that they were both born near the Cathedral of Cologne in Germany. Gaul shared that he had dreamed of building a church like it since he was a boy—a building that would “bear the stamp of its beauty.” Father Sheideler doubted that such a feat was possible but the architect said simply, “Well, we shall try.”[16]
Several months later the driver of an express wagon arrived at the pastor’s door bearing a large package: Gaul’s plan for “a miniature cathedral of Cologne” in Indianapolis. Father Scheideler shared the plans with leading St. Mary congregants and “Herman Gaul’s dream for a new St. Mary’s spread through the parish.”[17]

In spring 1910, clergy and parishioners, assisted by hundreds of Catholic school children, broke ground on a new location for St. Mary’s at Vermont and New Jersey Streets.[18] That fall, the congregation laid the cornerstone.[19] By July 1912, the new building was complete. The Indianapolis News ran a feature on its architecture with the headline: “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge to Plan for the St. Mary’s Parish a Miniature Cathedral of Cologne.”[20]

While we don’t have a record of Herman’s love for his wife Mary in letters or diaries, we see their love reflected in his tribute to her and to his faith. Recorded for posterity in the architecture of St. Mary is one German immigrant’s joy at finding a partner to share his Catholic faith and German traditions, and with whom he built a family and home in addition to a church. And he owed it all to one savvy matchmaker, Father Scheideler, who just might have known what he was doing from the start.
Notes
[1] Passport Application, September 7, 1893, No. 4331, Roll 410, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; Twelfth Census of the United States, June 14, 1900, Chicago Ward 14, Cook County, Illinois, roll 262, page 13, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com. On his passport application, Gaul declared he immigrated to the U.S. in 1886.
[2] Edward R. Kantowicz, “To Build the Catholic City,” Chicago History 14, No. 3 (Fall 1985): 14, accessed Chicago History Museum.
[3] “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge to Plan for the St. Mary’s Parish A Miniature Cathedral of Cologne,” Indianapolis News, July 6, 1912, 13, accessed Newspapers.com.
[4] “Articles of Incorporation,” Indianapolis Journal, June 23, 1891, 8, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; “Minor City Matters,” Indianapolis Journal, August 26, 1891, 6, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; “Bow to the Brewers,” Indianapolis Journal, November 3, 1891, 8, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; “Industrial Notes,” Indianapolis Journal, January 4, 1892, 6, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles.
[5] “The History of Romance,” February 13, 2017, National Women’s History Museum, accessed https://www.womenshistory.org/articles/history-romance.
[6] “Religious Ceremony,” Indianapolis State Sentinel, August 26, 1857, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; “Laying of the Corner Stone of the German Catholic Church,” Indianapolis Daily Sentinel, September 1, 1857, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; No title, Indianapolis Daily Sentinel, May 14, 1858, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; “The German Catholic Church, Maryland,” Daily State Sentinel, August 13, 1858, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles; McEvoy’s Indianapolis City Directory and Business Mirror (Indianapolis: H. N. McEvoy Publisher, 1858), 219, accessed IUPUI Library Digital Collections; “Dedication,” Daily State Sentinel, September 12, 1859, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles.
[7] “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge,” 13.
[8] Ibid.
[9] “Personal and Society,” Indianapolis Journal, April 14, 1896, 3, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles.
[10] “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge,” 13.
[11] Ibid.
[12] Kantowicz, 14.
[13] Conclusion gleaned from searching census records and Chicago newspapers.
[14] “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge,” 13.
[15-17] Ibid.
[18] “Church Ground Broken,” Indianapolis Star, May 2, 1910, 3, accessed Newspapers.com.
[19] “Lays Cornerstone of New St. Mary’s,” Indianapolis Star, October 24, 1910, 12, accessed Newspapers.com.
[20] “After Twenty Years Herman Gaul Makes Good His Wedding Day Pledge,” 13.









