 Many people are looking for ways to channel the anxiety of our current crisis into something healthy and productive. For those of us with green thumbs, this has meant more time in the garden. And there is no better place for us to get some sage advice than from those Hoosier gardeners who came before us. Luckily, some of them shared their wisdom in an early-twentieth century column in the Indianapolis News titled “Of Interest to Farmer and Gardner.”
Many people are looking for ways to channel the anxiety of our current crisis into something healthy and productive. For those of us with green thumbs, this has meant more time in the garden. And there is no better place for us to get some sage advice than from those Hoosier gardeners who came before us. Luckily, some of them shared their wisdom in an early-twentieth century column in the Indianapolis News titled “Of Interest to Farmer and Gardner.”
Here are some April highlights.
The Pepper King
In 1912, the Indianapolis News columnist raved about the new Ruby King pepper (Capsicum annuum). The writer enthused:
There are a great many varieties on the market today; but there is only one kind of sweet pepper to grow for a large yield, fine appearance and good selling qualities — the Ruby King . . . when a farmer comes in [to market] with a load of Ruby Kings, what a difference there is and how quickly the buyers pick them up!

An exciting new find for the writer, we now consider the Ruby King an heirloom variety. According to several companies selling the pepper, it was first introduced in 1902. However, the American Garden: Illustrated Journal of Horticulture described the Ruby King in 1885. The American Garden writer explained that with the introduction of milder yellow peppers, people seemed to have “developed a taste for less pungency in this fiery vegetable.” This critic was not a fan of the yellow pepper, stating emphatically that “it cannot be denied that the correct color in a pepper seems to be red.” The only vegetable that fit the bill as both mild in taste and red in color was “Burpee’s Ruby King, now introduced by W. Atlee Burpee.” The writer called it a “a respectable Pepper . . . mild and pleasant to taste — unequaled, in this respect, by any other variety.”
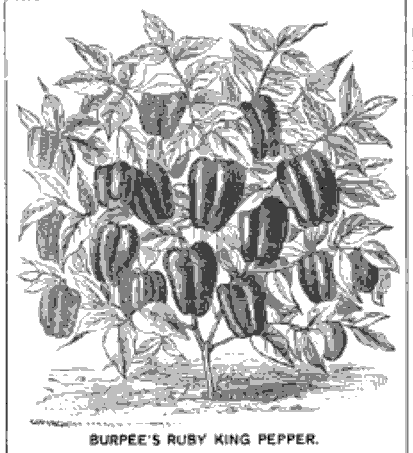

Burpee does not seem to offer the variety any longer, but you can add the Ruby King to your garden by ordering from heirloom sellers like the non-profit Seed Savers Exchange.
An Overlooked Bramble Berry

In the April 29, 1911 edition of the Indianapolis News, our gardening columnist gave some advice on introducing a low-maintenance bramble called a dewberry into the garden. While blackberries and raspberries were (and are) better known brambles, the writer gave several reasons to add dewberry, which is also native to Indiana. The dewberry does just fine in poor soil, doesn’t need fertilizer, and can produce in partial sun or full shade. While raspberries and blackberries need regular pruning, the dewberry doesn’t. It can be trained to a stake or a trellis, but doesn’t require any support. And while it doesn’t produce until its third or fourth year, the writer suggested that the plant benefits from mulch and frequent harvesting once it has berries. The Indianapolis News columnist had one more piece of advice for bramble growers in 1911: plant different varieties together. I was not able to confirm the science behind this, but the writer’s experience shows that dewberries grow better when planted with blackberries or raspberries.
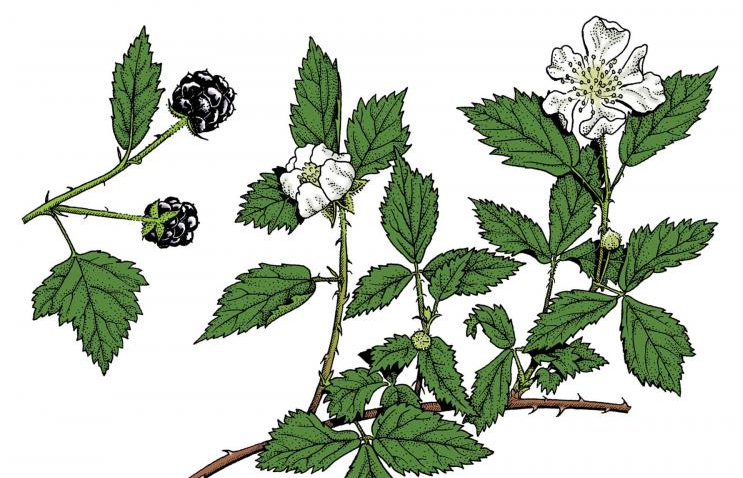

There are several varieties of dewberry, but one native to Indiana, according to the Ladybird Johnson Wildflower Center, is the Lucretia Dewberry (Rubus roribaccus). Writing for the Cornell University Bulletin in 1892, L. H. Bailey described the ease of growing the Lucretia Dewberry. Interestingly, this gardener-writer also recommended planting dewberry with blackberry and raspberry brambles. The main value of the dewberry was that of the three, it ripened first. Bailey also pointed out that dewberry is hardier than other berry plants, able to survive harsh winters without taking any special precautions. Birdwatchers might also want to plant this lesser known species. According to the Missouri Department of Conservation, dewberry is a favorite of catbirds, waxwings, and finches. I couldn’t find an Indiana farm selling Lucretia dewberry, but you can find them at DeGroot Nursery in Michigan, a family-owned farm in operation since 1957.
The Wolf Flower

The April 3, 1909 edition of the Indianapolis News column touted the beauty of lupines, recommending them to Indiana gardeners. The News columnist explained that this flowering plant works both in formal and more natural gardens, easily withstands the cold midwestern winters, and come in an array of colors and varieties, both annual and perennial. Lupine seeds should be direct sown in April after frost and will flower in June, “and if cut frequently so that the plants can not go to seed, their flowering period continued almost up to the first frost.” An added bonus: lupine returns nitrogen to the soil. (You can learn how here). Beyond gardens, Hoosiers can also keep a look out for lupine in the wild, or even by the side of the road.

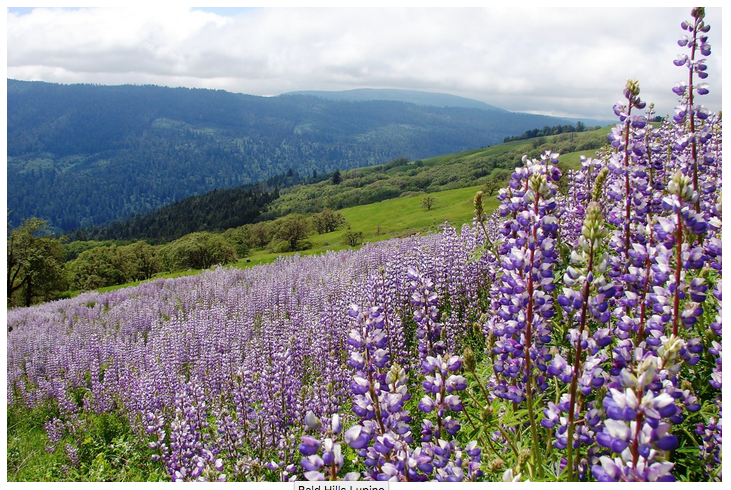
Beautiful white, blue, and purple wild lupine (Lupinus perennis) thrives in the sandy soil of the Indiana Dunes and the larger Calumet Region. Here they support the life cycles of three different butterflies that only eat lupine. One of these is the endangered Karner Blue butterfly. At the Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore, the National Park Service uses controlled burns that encourage lupine growth, in order to improve the Karner Blue’s habitat. While much has been done to improve the chances of this endangered species, climate change is also proving to be a threat, according to the NPS. In response, scientists are working to create lupine-filled microclimates.
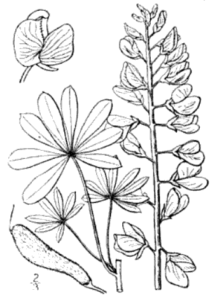
Butterflies aren’t the only species that eat lupine. While the flowers are not edible (in fact they are poisonous), the nut-like seeds are edible for humans once soaked to remove the toxic chemicals and historically have been ground into a flour for cooking. According to the Old Farmer’s Almanac, lupine seeds were “a favorite food for traveling troops in ancient Europe.” The historical lore around this flower’s name is also rich. “Lupine” is latin for “wolf.” While we now know that lupines add nitrogen, the opposite was once thought true, that they “wolfed” nitrogen from the soil to get their color. Others have claimed the that the flower got its wolfish name, from the barren habitat in which it thrives. After a prairie, the lupine could be seen thriving among the burnt landscape, like a lone wolf. But it is lupine’s intense color, especially the blue, that has captured the imaginations of poets, artists, and writers through the ages. Let’s close then with an 1851 journal entry by Henry David Thoreau:
June 5. The lupine is now in its glory. It is the more important because it occurs in such extensive patches, even an acre or more together, and of such a pleasing variety of colors, — purple, pink, or lilac, and white, — especially with the sun on it, when the transparency of the flower makes its color changeable. It paints a whole hillside with its blue . . . No other flowers exhibit so much blue. That is the value of the lupine. The earth is blued with them. Yet a third of a mile distant I do not detect their color on the hillside. Perchance because it is the color of the air.

Sources:
* All newspapers accessed Newspapers.com.
The Pepper King
American Garden: Illustrated Journal of Horticulture 6:2 (February 1885), 23, accessed GoogleBooks.
“Of Interest to Farmer and Gardener: Suggestions for Growing Peppers,” Indianapolis News, April 13, 1912, 17.
An Overlooked Bramble
L. H. Bailey, “The Lucretia Dewberry,” Cornell University Bulletin, reprinted in American Gardening 8:5 (May 1892), 274-75, accessed GoogleBooks.
Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center, “Rubis Roribaccus,” University of Texas at Austin, https://www.wildflower.org/plants/www.utexas.edu.
Missouri Department of Conservation, “Dewberry,” Field Guides, https://nature.mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/dewberry.
“Of Interest to Farmer and Gardener: How to Grow Successfully the Bramble Berries in the Small Garden,” Indianapolis News, April 29, 1911, 22.
The Wolf Flower
“Growing Lupines,” Old Farmer’s Almanac, accessed https://www.almanac.com/plant/lupines.
Sarah Fuller, “Wild Lupine,” Indiana Dunes, accessed http://www.indianadunes.com/beaches-and-beyond/blog/wild-lupine/.
Nathaniel Lord Britton, Illustrated Flora of the Northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions, vol. II (New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1897), 269, accessed GoogleBooks.
Kim Mitchell and Cathy Carnes, “Wild Lupine and Karner Blue Butterflies,” Midwest Region Endangered Species, U. S. Fish & Wildlife Service, accessed https://www.fws.gov/midwest/endangered/insects/kbb/lupine.html.
National Park Service, “Impact of Climate Change on the Karner Blue Butterfly,” 2010, accessed nps.gov.
“Of Interest to Farmer and Gardener: Perennial and Annual Lupine,” Indianapolis News, April 3, 1909, 20.
Henry David Thoreau, The Complete Works of Henry David Thoreau, vol. 36 (Hastings, East Sussex, United Kingdom: Delphi Classics, 2017), accessed GoogleBooks.
“Wild Lupine,” Save the Dunes, accessed https://www.indunesguide.com/lupinusperennis.
