
For many people, the first thing that comes to mind when thinking of the early Pure Food movement is Upton Sinclair’s 1906 book The Jungle. However, Hoosier Harvey Wiley’s work in the field was already at its apex when Sinclair’s exposé was released. When Dr. Wiley started his career in the mid- to late-19th century, the production of processed foods in the US was on the rise due to the increasing number of urban dwellers unable to produce their own fresh food. With little to no federal regulation in this manufacturing, food adulteration was rampant. Dr. Wiley made it his mission prove the importance of food regulation. With the help of a group of men known as the Poison Squad, he did just that.
Harvey Washington Wiley was born on a small farmstead near Kent, Indiana on October 18, 1844. He attended Hanover College from 1863-1867, with the exception of a few months in 1864 when he served in Company I of 137th Indiana Volunteers during the Civil War. After graduating in 1867, Wiley moved to Indianapolis and began teaching at Butler University while earning his Ph.D. from the Medical College of Indiana. It was in 1874 that Dr. Wiley began his work as a chemist at Purdue University, where he developed an interest in adulterated food. Wiley argued that mass-produced food, as opposed to food produced locally in small quantities, contained harmful additives and preservatives and misled consumers about what they were actually eating. In the coming decades, Wiley would prove that this theory was correct and serve as one of the public faces of the pure food movement. As a 1917 advertisement in The (New York) Sun put it:
“Dr. Wiley it was who, at Washington, first roused the country to an appreciation of purity and wholesomeness in foods. He has been the one conspicuous figure in food betterment and food conservation in the present generation.”
In 1883, Wiley was appointed Chief Chemist of the Bureau of Chemistry, a division of the United States Department of Agriculture. While serving in this capacity, Wiley made the establishment of federal standards of food, beverages, and medication his priority. To this end, governmental testing of food, beverages, and ingredients began in 1902. The most famous of these tests were the “hygienic table trials,” better known by the name given to them by the media: “The Poison Squad.”

During these trials, “twelve young clerks, vigorous and voracious” were fed and boarded in the basement of the Agricultural Department building in Washington D.C. Before each meal the men would strip and be weighed, any alteration in their condition being noted. At any one time, six of the group would be fed wholesome, unadulterated food. The other six were fed food laced with commonly used additives such as borax and formaldehyde. Every two weeks, the two groups would be switched. While the position of poison squad member may sound like it would be a hard one to fill, volunteers were lining up to participate in the tests, even writing letters such as the following to Dr. Wiley:

The experiments commenced in November of 1902 and by Christmas, spirits among the Squad members were low. According to a Washington Post article from December 26,
“The borax diet is beginning to show its effect on Dr. Wiley’s government-fed boarders at the Bureau of Chemistry, and last night when the official weights were taken just before the Christmas dinner the six guests who are taking the chemical course showed a slight decrease in avoirdupois . . . To have lost flesh on Christmas Day, when probably everybody else in Washington gained more or less from feasting, was regarded by the boarders themselves as doubly significant.”
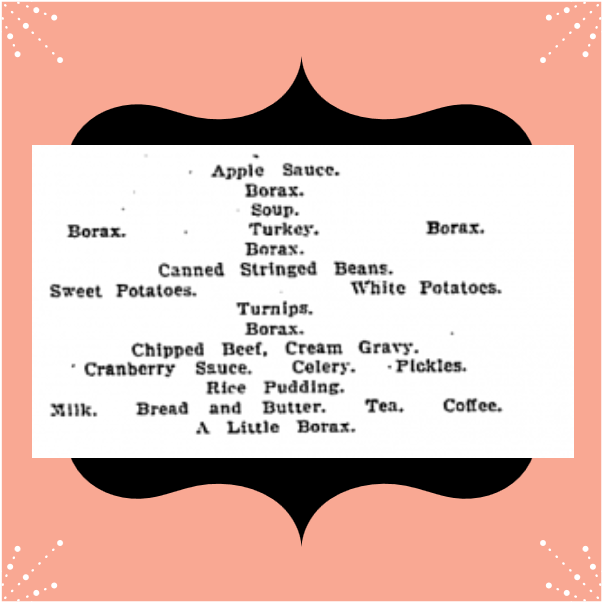
A look at the “unprinted and unofficial menu” from the Christmas meal, also printed in the Post, sheds some light on what may have given the boarders pause in their Christmas feasting.
Much of the information reported by the press during this time came from the members of the squad themselves, until “Old Borax” as Wiley came to be known, issued a gag-order in order to preserve the sanctity of the scientific studies happening. Despite the order, public interest had been peaked and tongues and pens wagged around the country. As one Columbia University scholar put it, “Supreme County justices could be heard jesting about the Squad in public, and even minstrel shows got in on the act.” There were even poems and songs written about the trials.
If ever you should visit the Smithsonian Institute,
Look out that Professor Wiley doesn’t make you a recruit.
He’s got a lot of fellows there that tell him how they feel,
They take a batch of poison every time they eat a meal.
For breakfast they get cyanide of liver, coffin shaped,
For dinner, undertaker’s pie, all trimmed with crepe;
For supper, arsenic fritters, fried in appetizing shade,
And late at night they get a prussic acid lemonade.
They may get over it, but they’ll never look the same.
That kind of a bill of fare would drive most men insane.
Next week he’ll give them moth balls,
a LA Newburgh, or else plain.
They may get over it, but they’ll never look the same.
-Lew Dockstade, “They’ll Never Look the Same”
At the close of the Borax trials in 1903, Wiley began cultivating relationships with some journalists, perhaps in hopes of turning the reports from jovial, and sometimes untrue, conjectures to something more closely resembling the serious work being done.
Along with borax and formaldehyde, the effects of salicylic acid, saccharin, sodium benzoate and copper salts were all studied during the Hygienic Table Trials. The reports generated during the Hygienic Table Trials and the media coverage that followed set the stage for the passage of the Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906, the same year in which the trials were concluded. According to the FDA, the Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906, also known as The Wiley Act, serves the purpose of “preventing the manufacture, sale, or transportation of adulterated or misbranded or poisonous or deleterious foods, drugs, medicines, and liquors, and for regulating traffic therein.”
By requiring companies to clearly indicate what their products contained and setting standards for the labeling and packaging of food and drugs, the Act helped consumers make informed decisions about products that could affect their health. While controversies over additives and government regulations continue to this day, Dr. Harvey Wiley and his Poison Squad played a major role in making the food on our tables safe to eat.
Check out our historical marker and corresponding review report to learn
more about Wiley.  Learn about the history of public health in Indiana and Wiley’s contributions with our publication The Indiana Historian.
Learn about the history of public health in Indiana and Wiley’s contributions with our publication The Indiana Historian.
