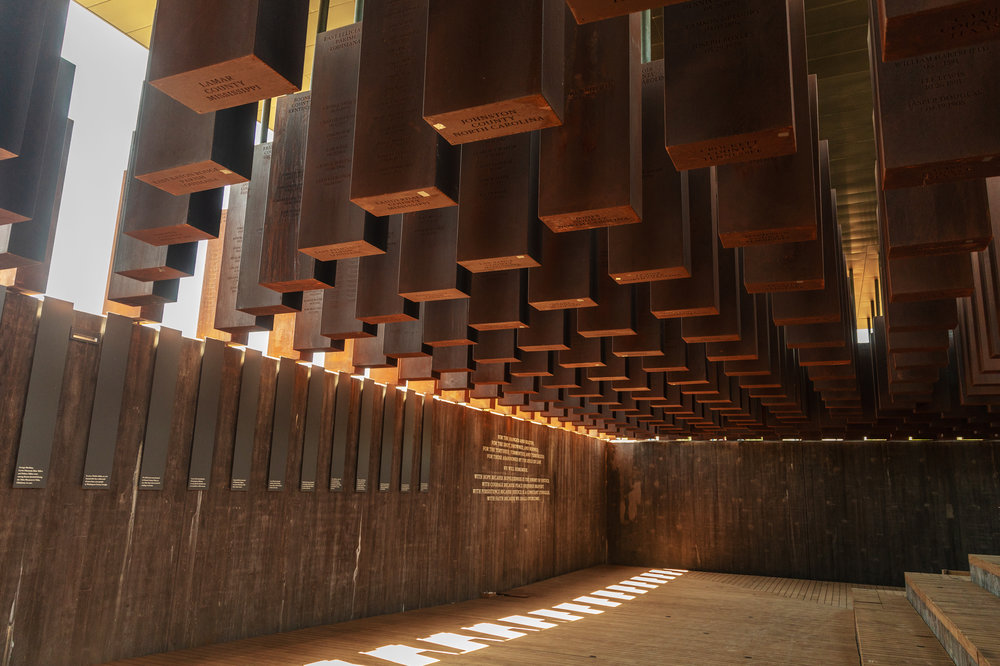
After investigating over 4,000 incidents of “racial terrorism” that took place in the United States between 1877 and 1950 in the form of lynchings, the Equal Justice Initiative realized the trauma left in their wake had never been properly confronted by the nation. The EJI sought to remedy this and opened the Memorial for Peace and Justice in Montgomery, Alabama on April 26, 2018. Memorial visitors first encounter sculptures of chained slaves before experiencing memorial square, an exhibition of 800 6-foot monuments that represent lynchings in each of the counties where they took place. The memorial concludes with a bronze sculpture that examines “contemporary issues of police violence and racially biased criminal justice.”
Woven into the fabric of racially-motivated violence in America is a summer night in Marion, Indiana in 1930. On August 7, black teenagers Tom Shipp, Abe Smith, and James Cameron were held in the Marion jail for the murder of Claude Deeter and rape of Mary Ball. Before they could stand trial, a mob comprised of white residents tore the young men from their cells and brutally beat them, mutilating and hanging Shipp and Smith from a tree on the courthouse lawn. They intended to send a message to other African American residents, one which Marion NAACP leader Katherine “Flossie” Bailey scrambled to prevent.

Local photographer Lawrence Beitler took a photograph of the swinging bodies, capturing a white crowd that looked on in a mixture of satisfaction, hostility, amusement, and bewilderment. This photo was reproduced on postcards and circulated by the thousands. NPR noted that in the late 1930s white poet, activist, and Bronx school teacher Abel Meeropol remained haunted by the image of “strange fruit hanging from the poplar trees” and penned a poem about the lynching, published by the teacher’s union. Inspired by Meeropol’s words, artists like Billie Holiday, Diana Ross, Sting, Kanye West, and Nina Simone have performed their own versions of “Strange Fruit.”
Historian Dr. James Madison contends that the Marion lynching continues to command attention because it took place outside of the Deep South and occurred after the Ku Klux Klan-prompted lynchings of the 1920s. The East Tennessee News noted weeks after the lynching that the “deplorable affair” confirmed the notion that “mob law” can break “forth in all its furry [sic] in North as readily as in the south.” The paper added that only the enactment of a federal law would “serve to discourage the tendency of irresponsible hoodlums who are inclined to take the law into their own hands.” Prior to August 7, 1930, it is believed that the last lynching in Indiana took place in 1902 in Sullivan County and the resurgence sent shockwaves through Indiana and around the nation.

As white residents gathered on the afternoon of the 7th, formidable NAACP state president Flossie Bailey mobilized. Born in Kokomo, Bailey was described as a “hotrod,” “born leader,” and “superb organizer” for her tireless work with the NAACP. She established the Marion branch in 1918 and built it up, despite encountering apathy created by Great Depression conditions. She became head of the Indiana NAACP and offered her house as headquarters when Marion’s Spencer Hotel refused to accommodate black guests.
As the restless crowd hoisted Claude Deeter’s blood-stained shirt from the window of the Marion City building, Bailey called Sheriff Jacob Campbell to alert him to the mob’s plan to lynch the prisoners. According to NAACP acting secretary Walter White, upon Bailey’s phone call, Sherriff Campbell checked the jail’s garage and found that gasoline had been removed from the cars and the tires flattened, preventing transportation of the endangered prisoners. He made no attempt to procure working cars, despite three hours passing until the lynching. Bailey also called on Governor Harry G. Leslie’s secretary, operating in his absence, to dispatch troops to the restless city. He abruptly hung up on her.

As Bailey tried to intervene, Mary Ball’s father, Hoot Ball, entered the jail to speak with Sheriff Campbell and, upon failing, the crowd broke into violence and stormed the jail. The Muncie Evening Press estimated that of the thousands gathered around the jail “only about 75 men actually took part in the rioting,” encouraged by the shouts of onlookers. The mob penetrated the front and side of the jail using crowbars and hammers. Officials inside tried to stop rioters with tear bombs, one of which was lobbed back into the jail and exploded among nearly fifty prisoners.

Walter White declared the lynching of Shipp and Smith to be the “most horrible and brutal in the whole history of lynching.” He stated that Smith was taken first and lynched from the jail bars and “When first pulled up he held on to the rope, preventing strangulation.” Shipp “fought furiously for his life, burying his teeth in the arm of one of the lynchers. In order to make him loosen his teeth his skull was crushed in with a crow-bar and a knife plunged into his heart.”
The rancorous mass took Smith’s life by dragging him to the courthouse square and hung him from a tree before a crowd that included children, an act witnessed and recounted by Muncie podiatrist Dr. E. Frank Turner. He saw the “ghastly spectacle” around 8 p.m. and, hearing that water would be used to disperse the crowd, “felt that everything would be alright, and went away.” When he returned around 10 o’clock, he saw the mob drag Shipp and Smith to the courthouse lawn. Lynchers utilized shadows created by tree branches to obscure their identities. Dr. Turner recalled that:
The body went up, dangling on the rope, and a demoniacal yell surged from the crowd. It was hideous! That mob sounded like wild wolves, the yells were more like vicious snarls. Some even clapped their hands.
Not all observers cheered, he recalled. Some wept and others condemned the crowd.
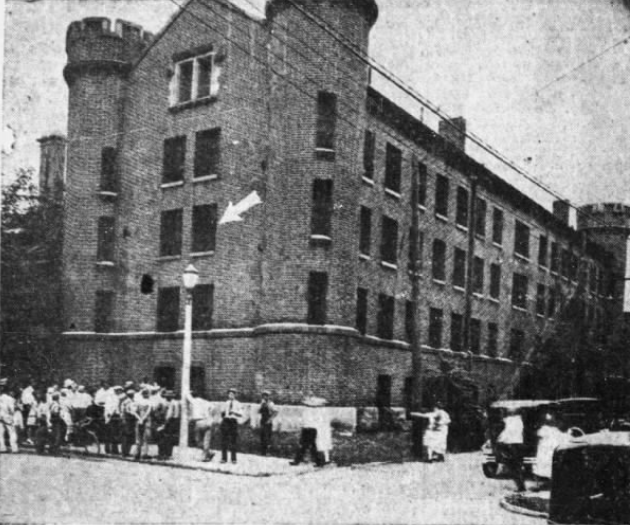

Cameron, the youngest of the three accused men, was ripped from his cell and nearly hanged before someone in the crowd shouted that he was not involved in the crime. Muncie policeman Earl Doolittle noted that when Indianapolis officers finally arrived in their “big touring car” they were “greeted with boos and catcalls” from the crowd, lingering to prevent the coroner from removing the bodies. This was the same crowd that had left the jail “ravaged,” with “gaping holes in the walls” and the “twisted remains of broken locks.” Reportedly by midnight, an “indignation meeting” formed in Johnstown, the Marion neighborhood where African Americans lived. Hundreds of black residents listened to speeches about the sheriff’s unwillingness to order officers to shoot at the mob. Officers broke up the meeting, which prevented further violence. An Illinois newspaper reported that about 200 black residents fled Marion for Weaver, a historic black community in Grant County, out of fear of escalating violence.
At the time of the lynching, the state militia was training in Kentucky and, therefore, the “lawless element” controlled the scene of the lynching for over half a day. After Sheriff Campbell removed the bodies the following day, the crowd used penknives to cut buttons and shreds of fabric from the victims’ clothes as “souvenirs.” Shipp’s and Smith’s bodies were then taken to Shaffer Chapel African Methodist Episcopal Church in Muncie because Marion lacked a black mortician.
Echoing editor George Dale‘s 1920s skewering of the Ku Klux Klan via the Muncie Post-Democrat, the Muncie Evening Press condemned the act, stating “Not alone Marion but the state of Indiana stands today disgraced in the eyes of the world as a result of the lynching of two Negroes in that city last night. As for Marion herself she will be regarded abroad as a city of barbarians.” The paper believed that Marion could be partially redeemed only by indicting rioters on murder charges. The article noted “This ought not to be difficult.”
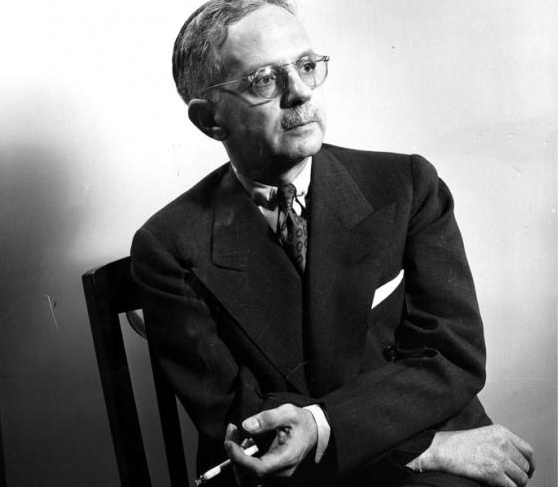

Flossie Bailey knew otherwise. According to James Madison, after the crime Bailey convinced Walter White to investigate the lynching. Fearing her phone calls were being monitored, she traveled back to Kokomo to communicate with NAACP leaders in Indianapolis and Marion. She received threatening phone calls, Madison noted, and drivers “deliberately backfired their cars as they cruised past her house.” Despite these threats, Bailey worked diligently to hold the perpetrators accountable. She joined a delegation of ten African American citizens from Marion and Indianapolis that met with Governor Leslie, including prominent pastors and Walker Manufacturing Company attorney Robert L. Brokenburr. In a formal resolution presented by Bailey, the group demanded that Governor Leslie ask for Sheriff Campbell’s resignation and promise protection for those who would testify about the identity of the lynchers. According to The Kokomo Tribune, Governor Leslie responded by claiming that “rumors had come to him that negroes in Marion were equipped with dynamite and were threatening to blow up the county jail.”
Bailey countered this rumor directly in a letter-to-the-editor for the Pittsburgh Courier, one of the leading African American newspapers in the country. The Courier previously printed a story about plans for retaliation by Marion’s black residents. Bailey noted that this was a “LIE,” one absolutely not perpetuated by the city’s black pastors, as the Courier had claimed. She stated that because of the rumors she and her husband “are daily receiving anonymous letters of a threatening nature” and alleged that “The Negroes who start rumors of this sort are the ones who will not help in anything constructive.” She concluded her letter “A few of us refused to be intimidated and do all we can in the name of the Association [NAACP] to bring law and justice again to Marion.”
The county grand jury began its investigation into the lynching in September. Bailey testified that she warned Sheriff Campbell of the formation of the mob just before 5 p.m., countering Campbell’s statement that it was made after 7 p.m. When questioned about his lack of action, he stated he feared hitting a woman or child with a stray bullet. Ultimately, the jury decided that Sheriff Campbell handled the mob in a “prudent manner” and exonerated him of any responsibility for the deaths of Shipp and Smith.

Unable to extricate Campbell from office, Bailey and her husband focused their efforts on prosecuting the lynchers. Historian Emma Lou Thornbrough noted that they led the effort to gather names from witnesses at “considerable personal risk.” White sent a list of twenty-seven alleged participants, along with evidence of their involvement, to Governor Leslie and Indiana Attorney General James M. Ogden. According to Thornbrough, only seven men were arrested, two tried, and both acquitted. She noted that at the trial of the second man, antagonism “against the blacks who attended it was described by a representative of the national NAACP as ‘appalling.’ Most of the whites who packed the courtroom were jubilant when the accused man was acquitted.” The New York Age noted of Bailey that “A high tribute is paid her courage and energy in working to restore order in Marion and to bring the lynchers to justice.” The NAACP awarded Bailey with the Madam C.J. Walker Medal for her refusal to be intimidated in her quest to bring the perpetrators to justice.
While Bailey’s efforts were ultimately unfruitful, she used the Marion lynchings as a springboard to enact anti-lynching legislation in Indiana. House Democrats introduced a bill in February 1931, for which Bailey organized statewide meetings, and convinced African Americans to contact their legislators. Her legwork paid off. Governor Leslie signed the bill into law in March, which allowed for the dismissal of sheriffs whose prisoners were lynched. The law also permitted the families of lynching victims to sue for damages. The Indianapolis Recorder, one of state’s preeminent African American newspapers, praised the law. The paper stated, “Indiana has automatically retrieved its high status as a safe place to live.” It added that without the law, Indiana “would be a hellish state of insecurity to our group, which is on record as the most susceptible victims of mob violence.” Although the newspaper praised Governor Leslie, it credited a “small group which stood by until the bill became a law.”
Using this momentum, Bailey and her NAACP colleagues worked to pass a similar bill on a federal level. Madison noted that she tried to change national lynching laws by publishing editorials, wiring President Franklin D. Roosevelt, and distributing educational materials to Kiwanis clubs. Although these efforts were unsuccessful, Bailey fought for the rights and safety of African American citizens until her death in 1952, challenging discrimination at IU’s Robert W. Long Hospital, speaking against school segregation, and suing a Marion theater for denying Bailey and her husband admittance based on their race.

The Memorial for Peace and Justice has made tangible the tragic events of August 7, 1930. Perhaps one day the American landscape will represent Flossie Bailey and other individuals who tried to prevent racial terrorism at considerable personal risk. Learn how to apply for a state historical marker via the Indiana Historical Bureau.
SOURCES USED:
“Marion and Indiana Are Disgraced,” “Negro Killers Hanged in Courthouse Yard After Big Mob Storms Jail; Trio Accused of Attacking White Girl,” “Muncie Man is Lynching Witness,” and “Police Tell of Scenes at Marion,” Muncie Evening Press, August 8, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“Negroes Leave City,” Journal Gazette (Mattoon, Illinois), August 9, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“Gross Failure of Officials Is Exposed by Investigators” and “Lynching, North and South,” Indianapolis Recorder, August 30, 1930, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles.
Mrs. F.R. Bailey, Letter to the Editor, The Pittsburgh Courier, August 30, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“Marion, Indianapolis Negroes Call upon Governor for Action,” The Kokomo Tribune, August 21, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“Five Heard in Lynching Quiz,” Muncie Evening Press, September 3, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“Sheriff Was Negligent,” The New York Age, September 6, 1930, accessed Newspapers.com.
“The Anti-Lynching Law” and “Cruising Around,” Indianapolis Recorder, March 14, 1931, accessed Hoosier State Chronicles.
James H. Madison, “A Lynching in the Heartland: Marion, Indiana, August 7, 1930,” Journal of American History (June 2011), accessed Organization of American Historians.
James H. Madison, “Flossie Bailey,” Traces of Indiana and Midwestern History (Winter 2000): 22-27.
Emma Lou Thornbrough, Indiana Blacks in the Twentieth Century (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2002), 67-69.