Today, we expect presidential candidates to come to us. They speak on the capitol steps, at memorials, and in high school gyms. They shake hands, meet local leaders, and in Indiana at least, make sure they’re seen eating a homemade pie or pork tenderloin of local renown. Beyond these appearances, however, campaign ads, emails, and social media posts bring candidates into our living rooms, our inboxes, and our daily lives.

This was not always the case, however. In fact, for much of U.S. history, such active campaigning was seen as power hungry, uncouth, and beneath the dignity of the office. While they didn’t hit the campaign trail, the candidates were still working hard to win over voters with events and promotional material. If we start our story in Indianapolis, Indiana, in 1888 and close it twenty years later in Brook, Indiana, we see a sea change in Republican Party campaign tactics. And believe it or not, our modern barrage of presidential politicking owes a lot to the 1908 presidential campaign of William Howard Taft.
Republican Politics from the Front Porch

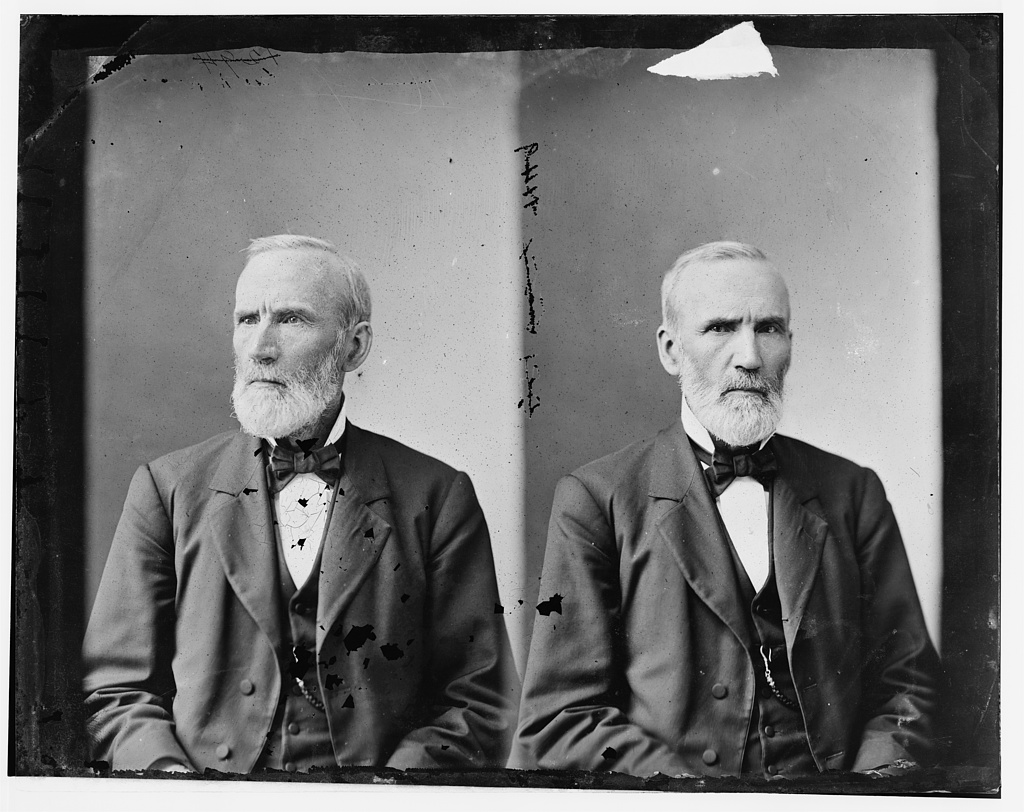
During the 1888 presidential campaign, Hoosier candidate Benjamin Harrison and incumbent President Grover Cleveland mostly stayed home. That’s not to say they weren’t politicking. Harrison ran a “front porch” campaign, speaking to crowds that gathered at his Indianapolis home and the reporters he invited to cover the event. Political organizations produced “posters, political cartoons, speeches, rallies, parades, brass bands, and torchlight demonstrations” in support of their candidates (Miller Center). And while Harrison stayed in Indianapolis, his supporters took the campaign on the road for him with a memorable publicity stunt. Inspired by a gimmick used for his grandfather William Henry Harrison‘s successful 1840 campaign, a Maryland supporter built a steel and canvas ball and rolled it 5,000 miles across the country to Benjamin Harrison’s home. In an attempt to draw comparisons between the two Harrisons, the campaign slogan became, inevitably, “Keep the Ball Rolling.” Harrison won the presidency, losing the popular vote, but carrying the electoral college. During the rematch in 1892, Cleveland declined to campaign out of respect for Harrison’s wife’s illness and Harrison made only a few public appearances. However, the Republican Party only tenuously backed Harrison because of “his failure to resolve three national issues,” and Cleveland won easily in 1892. (more here: Miller Center).
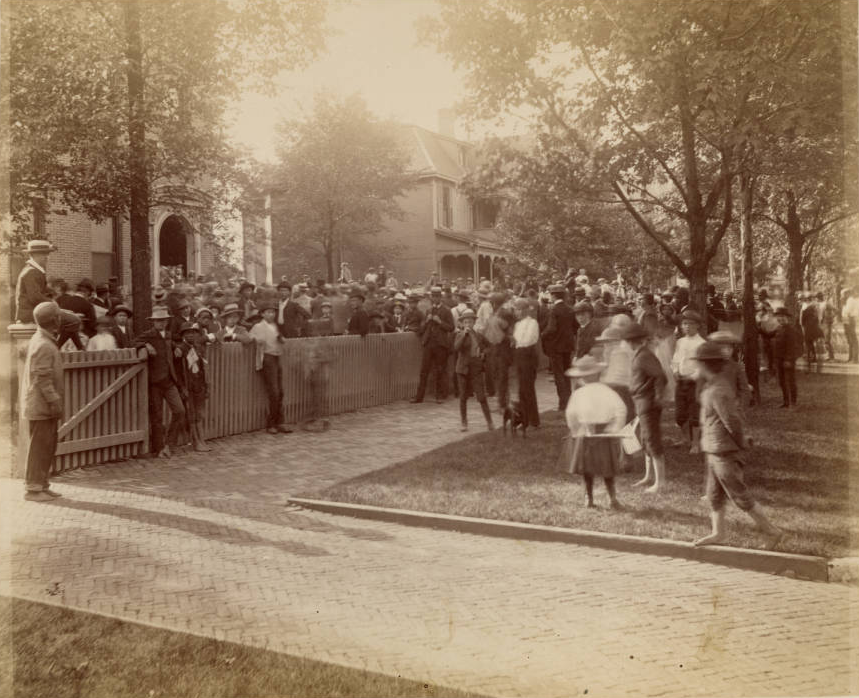

In 1896, the Democrats, with the support of the Populist Party, ran former U.S. Representative William Jennings Bryan for president. (Remember him; he’ll be back later). Bryan was a dynamic speaker and hit the campaign trail with enthusiasm, covering 18,000 miles in three months. Still, the Republican candidate and former Governor of Ohio William McKinley stayed home. Having raised four million dollars mainly from business and banking interests, the party organization dumped money into the printing and distribution of campaign pamphlets. Meanwhile, McKinley delivered 350 speeches to 750,000 people – all from his front porch- resulting in his election. McKinley won easily again in 1900, bringing New York Governor Theodore Roosevelt with him to the White House as his vice president. (Miller Center)

After McKinley was assassinated in 1901, Roosevelt served out McKinley’s presidential term and was the clear choice of the Republican Party to run in 1904. (Roosevelt picked Indiana Senator Charles W. Fairbanks as his running mate.) The Democrats selected New York Supreme Court Judge Alton B. Parker as a safe choice for presidential candidate, appealing to those who opposed TR’s progressive domestic politics and expanding foreign agenda. Parker refrained from campaigning as was the norm, but heavily criticized his opponent in the press. TR made a thirty day tour of Western states after his nomination was announced, but also refrained from actively campaigning for election. By the summer of 1904 he began speaking from his Sagamore Hill front porch at Oyster Bay, New York. Like McKinley, large campaign donations helped TR secure the presidential office. (Miller Center)
Taft V. Bryan: The Game Changer
William Howard Taft doesn’t get a lot of love as a president. He was indecisive, easily railroaded by Congress, and never wanted the office as badly as his wife or TR wanted it for him. However, the strategy crafted by Taft and his advisers to win the 1908 election was brilliant and the fierce showdown of the two major party candidates changed campaigning forever. And for the Republicans, it started just outside tiny Brook, Indiana.

Taft was TR’s handpicked successor to the presidency and thus had the backing of a beloved president and the powerful Republican political machine. He easily won the nomination at the June 1908 Republican National Convention in Chicago. However, Taft had an image problem – one that could lose him the essential votes of farmers, laborers, and African Americans. As an U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals judge, he made several anti-labor decisions. In 1894, Taft had ruled against the railroad workers of the Chicago Pullman Strike. Taft’s Democratic opponent William Jennings Bryan, (remember him?) on the other hand, was a Populist who appealed to laborers and farmers by promising to protect their interest from the Republicans, who were backed by exploitative big business.
During the 1908 campaign, Bryan, now on his third presidential run, again stormed the U.S. like an evangelist, talking directly to the people and criticizing Taft’s anti-labor record. This time, it seemed, the Republican candidate was not going to be able to stay home. Taft needed to defend his record, assure workers that the Republican Party backed their interests, and smile and shake as many hands as possible.

Mitchell, S.D. (1909) [i.e. 1908] Wm. Howard Taft shaking hands
Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division Washington, D.C.
The campaign was strikingly modern in other ways too. Speeches by presidential candidates were traditionally quite long – an hour of expounding on the party platform was not unusual. However, Taft kept it short, speaking for thirty minutes at major events, but sometimes spending only five minutes joking with crowds on train platforms. Bryan, known for lengthy rhetoric, was not to be outdone. He recorded a series of two minute speeches on a wax cylinder for Thomas Edison’s National Phonograph Company. Of course, Taft then had to do the same. Thus, we get the modern sound bite. [Listen here: NPR]
George Ade: Reluctant Republican Ringleader
Meanwhile, in Indiana, the Republican Party was in danger of being torn apart over temperance (prohibition versus local option). Leaders thought that a visit from a national candidate could unify the party at least for long enough to push through a Republican state ticket. Charles S. Hernly, Chairman of Indiana’s State Republican Committee, could see that the base needed a flamboyant event to generate enthusiasm for the Party. Recalling a promising conversation from the previous spring, he formed a plan. It involved George Ade, a native of Newton County, a beloved Indiana author, and a dabbler in local politics.
By this time, Ade had achieved financial success as the writer of clever and observant fictional stories for books and newspapers. He gained fame as the wit behind several popular comedic Broadway plays. Ade was known for using humor and rustic, slangy language and was often compared to Mark Twain. He had done well for himself and wisely trusted his brother William to invest his money in real estate.
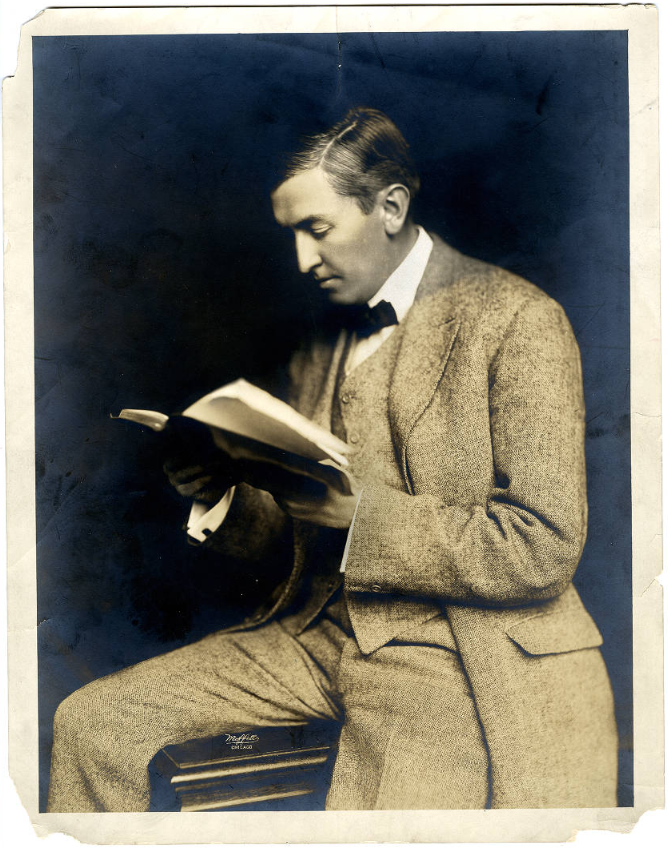

In 1902, William secured 417 acres near the small town of Brook for his brother to build a cottage as a writer’s retreat. George named the estate “Hazelden.” By 1904, when he began to stay at Hazelden more regularly, “it had grown into an Elizabethan manor house . . . complete with cow barn, greenhouse, caretaker’s cottage, dance pavilion, several smaller outbuildings, swimming pool, softball diamond, and forty foot water tower,” plus extravagant landscaped gardens. (Indiana Magazine of History)
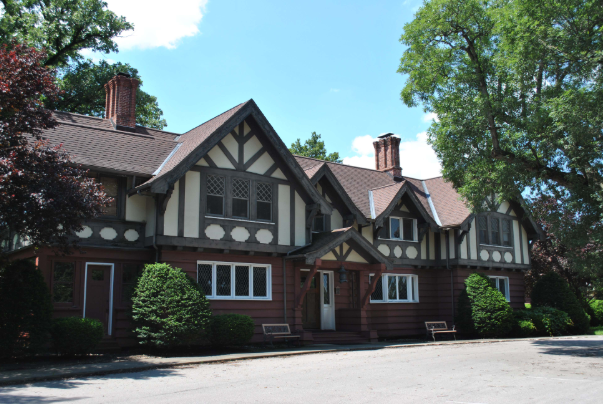

When Ade awoke at Hazelden the morning of August 20, 1908 and settled in to read the day’s Indianapolis Star, he received somewhat of a shock. The front page headline read, “Ade’s Farm Rally Will be Big Event.” Ade later wrote that he recalled a casual conversation with Chairman Charles Hernly about the possibility of a political picnic. However, they had not had formally planned any kind of function, let alone one that Hernly described to reporters as “the biggest Republican event Indiana will see this campaign.”
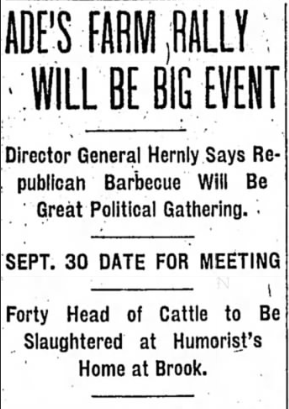
Hernly had colorfully expounded on the day’s details for reporters. He listed the names of prominent state and national politicians who would likely speak, “all the big guns,” and promised a meal of “roast beef, potatoes, bread and butter and coffee” for the Midwestern farmers who were invited to attend. Hernly emphasized that Ade was “enthusiastic in his support of the Republican ticket,” and the reader assumed, the event to take place at his estate. “The only thing that is bothering Mr. Ade is the fact that it is going to take forty of his best beef cattle to satisfy the hunger of the crowd,” Hernly claimed.
Ade was now in an impossible position. He would have liked to “have headed off the barbecue idea,” but was also an enthusiastic Republican who wanted to help his party. [Indiana Magazine of History] He had served as a visible delegate to the Republican National Convention where Taft was nominated – a fact that made headlines even in the New York Times – and as a member of the notification committee that formally told Taft of his nomination. Ade was a respected figurehead for the party. If he were to refuse to host this now public event, he risked further demoralizing the already troubled Indiana Republican Party. If Hernly meant to force Ade’s hand, it worked. The “biggest Republican rally of the coming campaign” would be held in George Ade’s backyard.
The Taft Special to Ade Station
Through the summer Taft was hanging back, assessing the political climate, trying to determine how best to campaign. By September 1908, however, it was clear that he was going to have to defend his labor record from Bryan’s attacks. Taft needed to align himself with the more progressive agenda of the Republican Party as announced at the June convention. He had also been briefed on the tenuous situation in Indiana and knew he needed to appeal directly to Hoosier farmers if he wanted to win the state. The rally planned at Ade’s farm was an opportunity the candidate could not pass up. Taft accepted the invitation sent to him by Chairman Hernly.

On September 16, the Taft campaign announced the tour itinerary. The candidate would leave Cincinnati the morning of September 23 to travel though Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin, Minnesota, the Dakotas, Iowa, Nebraska, Colorado, and Kansas over several weeks. The New York Times reported:
Judge Taft’s first address on his Western speaking tour will be made at Brook, Ind., on Sept. 23. It will be at a big Republican rally on the farm of George Ade, the Hoosier humorist and politician.
Notably, the newspaper reported that Taft would be following the route that William Jennings Bryan had undertaken in his campaign.
The morning of September 23, Taft and his staff boarded a five car train dubbed “The Taft Special” and headed for Indiana. The train stopped briefly in Indianapolis, where Taft shook hands with local politicians and waved to the approximately 200 people gathered to greet him. He joked with the crowd, forgoing a formal speech. The Taft Special stopped again briefly in Lafayette and switched tracks at Sheff before arriving at Ade station just west of Brook. Ade and a welcome committee arrived in a six car caravan to take Taft, staff, and guests to Hazelden.
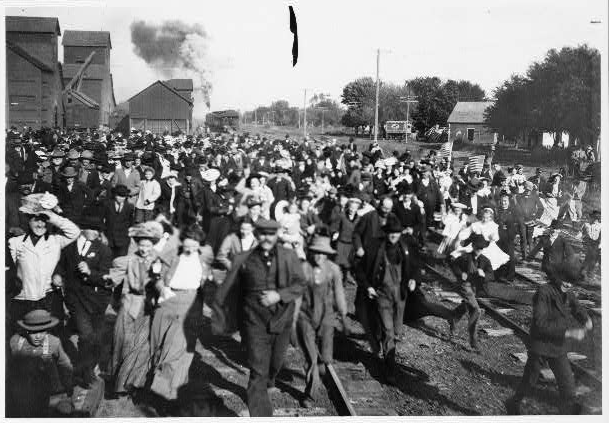

Prints & Photographs Online Catalog.
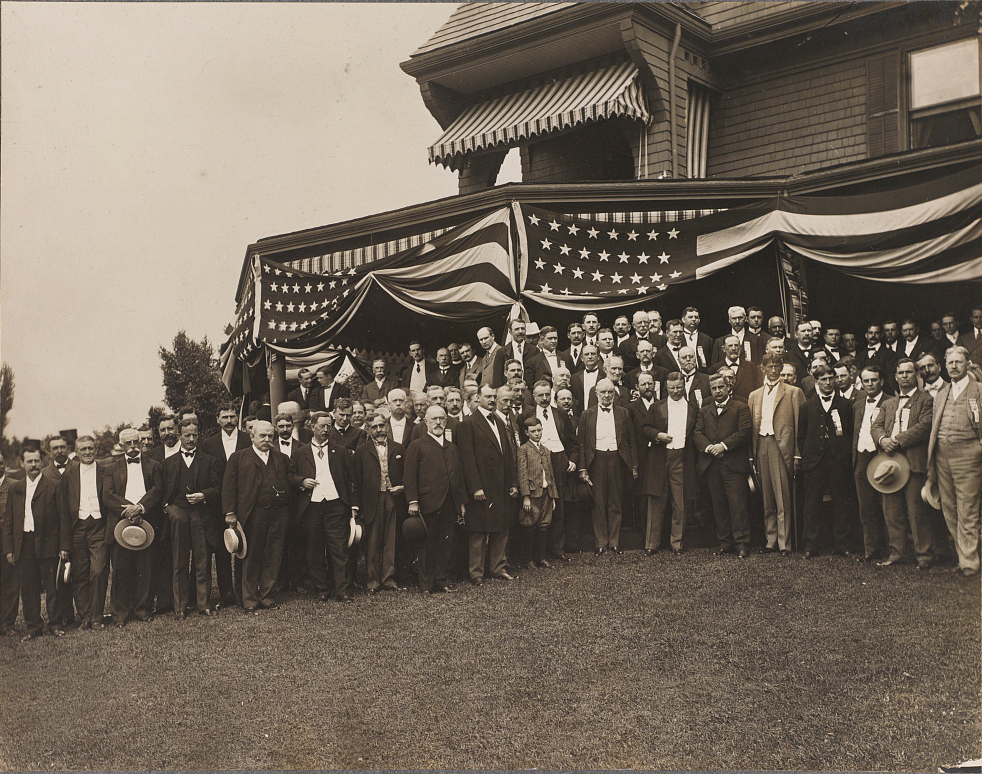
As the caravan drove through Brook, a large sign made of evergreen reading “Welcome” framed in marigolds and goldenrod greeted them. “Triumphal arches” also made of evergreen spanned the main street and supported large pictures of Taft and the other Republican candidates. Newspapers around the country described the scene in detail. The New York Times reported:
All forenoon, from miles around the countryside, buggies, family carryalls, hay racks, and farm vehicles of every description crowded the roads leading to Hazelden, the country home of George Ade. When the candidate, seated in the humorist’s automobile, reached the farm he was driven through a veritable gauntlet of vehicles hitched to telephone poles, fence posts, trees, or anything else calculated to restrain the horses.

The Indianapolis News described the scene that greeted Taft upon his arrival at Ade’s estate:
Before the arrival of the Taft party there was a concert by the Brook Band and later by the Purdue Military band, followed by short speeches from some of the local statesmen. At noon the Second Regiment Band, of Chicago, gave a great display of daylight Japanese fireworks. When the Taft party appeared in sight down the road, a dozen bombs were hurled in the air — the explosions resembled a salute by a gun squad and the air was filled with smoke as if from a battle.
The spectacle of this political theater was not lost on the Indianapolis News. The newspaper referred to the rally as a clever “stunt” and a “big play” put on by Ade. It continued to draw comparisons between the playwright’s craft and the political event:
The frameup of Ade’s latest act was all that could be desired. It was elaborately staged, and the scenery was all that nature could do for one of the prettiest places in northern Indiana, and the actors were of a pedigree out of the ordinary.
Upon arrival, the official party had lunch in the Ade home while the crowd purchased “full dinner pails,” a reference to the 1900 Republican slogan that appealed to the labor vote and helped William McKinley defeat William Jennings Bryan. At 1:15 p.m., Ade and Taft appeared on the decorated speaker’s platform. Ade introduced the candidate, and Taft officially kicked off his campaign.

Taft had not only remembered Ade from the notification committee, he was a fan of the writer’s work, “The Sultan of Sulu,” which was set in the Philippines. Taft had presided over the U.S. commission overseeing the new U.S. protectorate of Philippines under McKinley and spent a great deal of time there. National newspapers reported that Taft referred to Ade as “the Indiana Sultan of Sulu” and stated that “the Philippine original had no advantage over Ade.” Then, Taft got down to brass tacks.
He looked out at the faces of the farmers, the constituents that brought him to Indiana, and addressed them directly. He wanted this point to hit home, stating:
I was told if I came here I should have the privilege of meeting 10,000 farmers of the State of Harrison and [former Indiana Governor Oliver P.] Morton, and I seized the opportunity to break my journey to Chicago to look into your faces and to ask you the question whether your experience as farmers with Mr. Bryan and your recollection of his course since 1892 is such as to command him to you as the person into whose hands you wish to put the executive power over the destinies of this nation for four years.
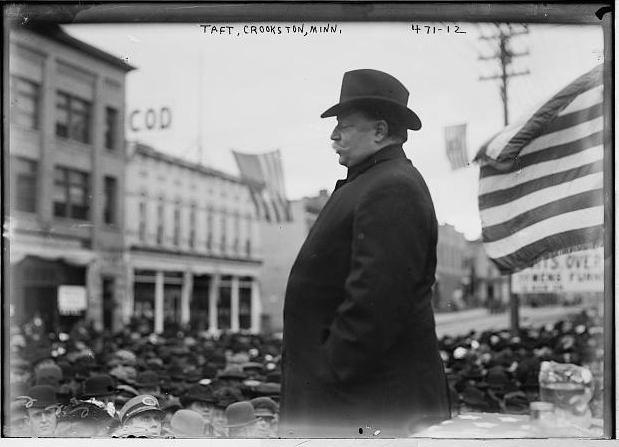

Taft then espoused the progressive policies of the Republican administration that had directly improved farmers’ lives. He especially focused on the administration’s introduction of free rural mail delivery, which helped to connect farmers to new ideas, keep them up-to-date on news, and reduce the feeling of isolation from which many rural people suffered.

Taft’s direct appeal to the farmers worked. The Brook Reporter could scarcely believe that “Mr. Taft would notice a small town like Brook.” The Indianapolis News ran the headline: “Brook Now On The Map, Thanks To George Ade.” In November, Hoosier farmers went to the polls. And while the split in the Indiana Republican Party proved fatal to the state ticket, Hoosiers chose Taft by over 10,000 votes. Taft was inaugurated March 4, 1909 as the twenty-seventh President of the United States.

Conclusion
Taft’s Indiana stop marked a sea change in campaign strategy. At Hazleden, Taft introduced the political tactics into his repertoire that he would hone through the rest of his tour and helped win him the election. He promoted the Republican platform as a progressive agenda that would benefit farmers and laborers. He crafted a likable, jovial, and personable image by speaking casually and humorously with crowds, while still seriously addressing their concerns. He went on the offense against his opponent in a manner the Baltimore Sun called “aggressive,” stopping in many places where Bryan had recently spoken in order to rebut his opponent’s statements. And perhaps, most importantly, he shook hands and flashed that unbeatable Taft smile at as many voters as his schedule would allow. Through sheer spectacle and tenacity, the man who had squashed labor strikes as a judge was now the candidate of the working man. A little support from Teddy didn’t hurt either, but Taft’s tour of the Midwest shaped him as a speaker and directly led to his election. And the 1908 election became the first where the Republican and Democratic candidates campaigned actively – an irreversible break with convention, as we see each election season through social media, a steady stream of ads, and even late night shows. It’s enough to make you nostalgic for the ol’ front porch.
Newspapers on the Rally
“George Ade’s Rally at Hazelden Farm,” Indianapolis News, September 23, 1908, 1; “George Ade As Sultan,” Buffalo Mourning Express and Illustrated Buffalo Express, September 24, 1908, 3; “Brook Now On The Map, Thanks To George Ade,” Indianapolis News, September 24, 1908, 4; “Taft Appeals To Labor,” Baltimore Sun, September 24, 1908, 2; “Taft Defends His Record On Labor,” New York Times, September 24, 1908, 3, accessed TimesMachine; “Taft at Brook,” Brook Reporter, September 25, 1908, 1, accessed Newspapers.com.
Secondary Sources
Peri E. Arnold, “William Taft,” Miller Center of Public Affairs, University of Virginia, https://millercenter.org/president/taft.
Jeffrey Bourdon, “‘Just Call Me Bill:’ William Taft Brings Spectacle Politics to the Midwest,” Studies in Midwestern History 2, no. 10 (October 2016): 113-138, accessed Grand Valley State University.
Howard F. McMains, “The Road to George Ade’s Farm: Origins of Taft’s First Campaign Rally, September, 1908,” Indiana Magazine of History 67, no. 4 (December 1971): 318-334, accessed Indiana University.




