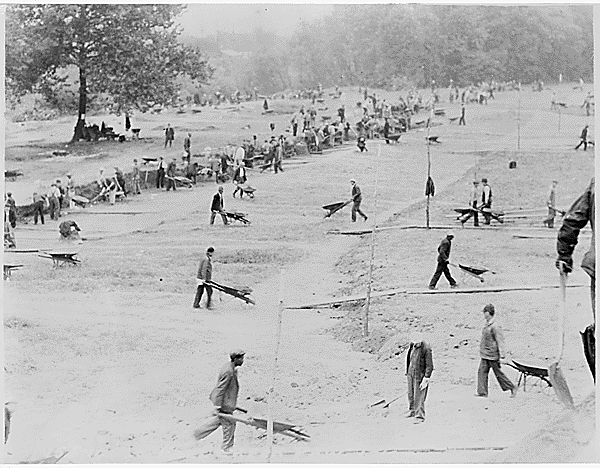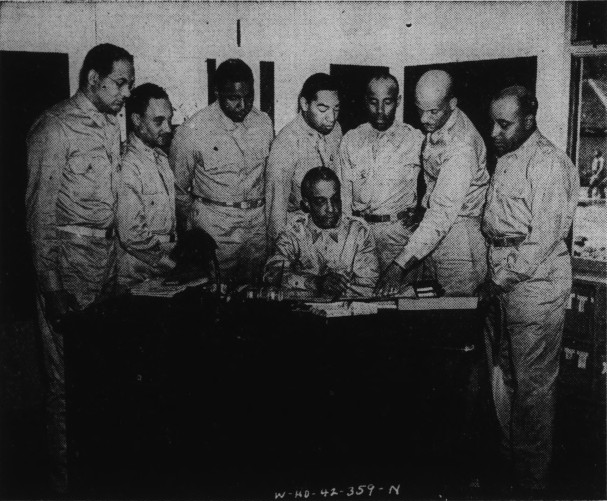
On May 21, 1950, a group of African American Studebaker workers and their wives formed a building cooperative in South Bend, Indiana called “Better Homes of South Bend.” Like other building cooperatives, the group appointed officers and a lawyer, drew up incorporation papers, and set times for regular meetings. Unlike other organizations, members decided their cooperative’s activities had to be kept secret to succeed. The cooperative’s first meeting minutes even stressed “no information is to be given out.”

Better Homes of South Bend members had good reason to be cautious. Discrimination in the local housing market had long limited African Americans to dwellings in the southwest part of South Bend, near the Studebaker Factory. Many members were part of the Great Migration of millions of African Americans from the South to the North for war industry jobs in the 1940s. Many had hoped to escape segregation and Jim Crow policies.
However, those with sufficient finances to make down payments found virtually no homes available to them and no banks willing to loan them money. Many of the city’s landlords would not rent to black residents. Real estate agents refused to show black home buyers houses in all-white neighborhoods and developments. White homeowners who tried to sell to black buyers risked physical threats and vandalism. Historian Emma Lou Thornbrough notes that the housing situation in South Bend was so dire for African Americans in the 1940s that many black families were forced to crowd into one or two bedroom units in substandard buildings.

Alan Pinado, one of the only black real estate agents in South Bend in the postwar era, noted in an oral history of the Civil Rights Heritage Center that:
There were no first quality homes being built for middle class, middle income blacks in South Bend . . . The federal government was part and parcel of the segregated housing pattern. It was legally mandated that new communities be kept segregated.
Federal housing and real estate policy strengthened prejudice in the housing market, not just in South Bend, but nationwide. The federal government first became heavily involved in the housing market in the 1930s. After the 1929 stock market crash and the ensuing Great Depression, the feds created several new agencies, like the Home Owners Loan Corporation (HOLC), the Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB), and the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), to try to stem the collapse of regional housing markets and bolster the failing economy.

Before the federal government stepped in, few became home owners. Banks spread mortgages only over three to five years. These mortgages required large payments that few could afford, especially during the Great Depression. In the 1930s, the government introduced the long-term, low-interest, self-amortizing mortgages most homeowners are familiar with today. Since these mortgages required smaller payments, home ownership became more economically feasible. Additionally, the federal government insured these loans through the FHA, making them an incredibly low risk for banks.
The government developed appraisal schemes to determine eligibility for these new loans. They adopted guidelines real estate associations had developed in the 1910s and 1920s to keep neighborhoods segregated. These associations erroneously decreed that the introduction of a non-white family into an all-white neighborhood would decrease surrounding property values. This policy kept many African Americans in poor neighborhoods, despite their income. For example, HOLC created survey maps of neighborhoods in 239 cities that color coded risk. Neighborhoods were coded into four groups, A-D. Only the best rated neighborhoods, marked A and B, would receive long-term loans. One criteria to receive an A or B rating included that the home in question sat in an all-white neighborhood.
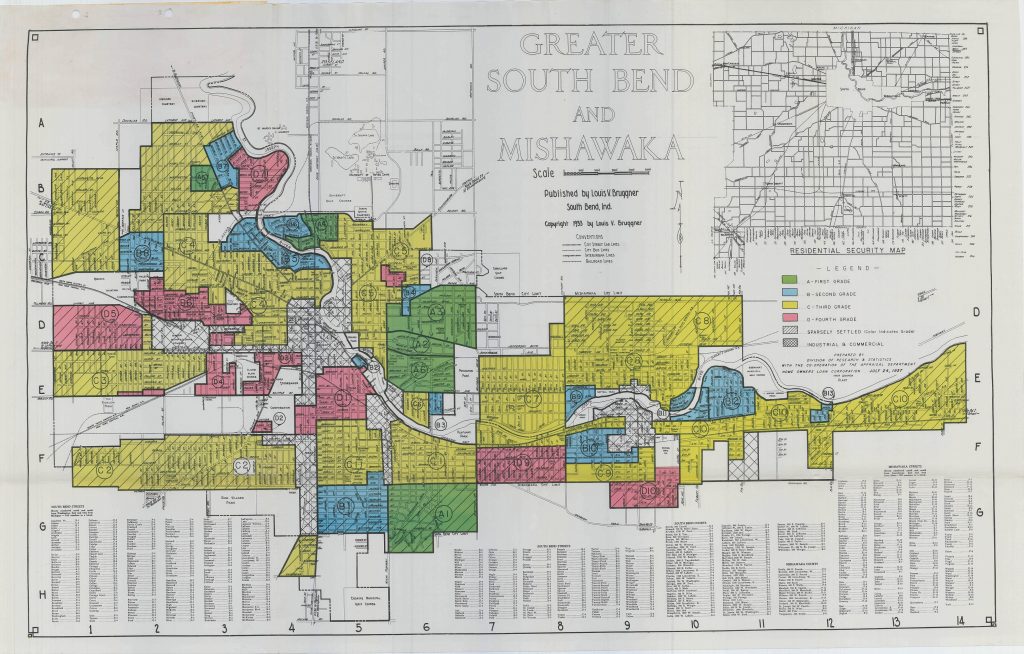
Similarly, the FHA Underwriting Manual, written in 1936, told appraisers to investigate areas surrounding a house for sale to “determine whether or not incompatible racial and social groups are present” because “if a neighborhood is to retain stability it is necessary that properties shall continue to be occupied by the same social and racial classes.” The manual further encouraged the use of local zoning and deed restrictions, like racially restrictive covenants that prevented potential black buyers from purchasing a home from a white homeowner.

By the time Better Homes of South Bend was established, the FHA insured 1 in 3 mortgages for new construction. However, the appraisal practices described above became standard practice and permeated the entire housing market. Though the Supreme Court ruled these practices unconstitutional in Shelly v. Kraemer in 1948, FHA did not stop publicly endorsing such actions until 1950 and prejudice in the housing market continued well after. Even in 1961, the United States Commission on Civil Rights admitted that housing still:
seems to be the one commodity in the American market that is not freely available on equal terms to everyone who can afford to pay.
Better Homes of South Bend members formed their building cooperative to combat this prejudiced housing market in 1950. According to scholar Jessica Gordon Nembhard, African Americans have established co-ops since the Civil War help fight economic racism. Cooperatives, or “companies owned by people who use their services,” work by pooling resources to satisfy an economic need created by a marketplace failure.

The first large African American housing co-operatives began in Harlem in the late 1920s. Many early African American co-ops in Indiana were markets or grocery stores, formed in the 1930s or 1940s. Better Homes of South Bend was likely one of the first successful African American building co-ops in the state. Only one other similar co-op, an apartment co-op in Indianapolis started by M.W. Jones in 1950, described in the Indianapolis Recorder as the “first Negro co-op Apartments in the city and the State,” is known to have existed.

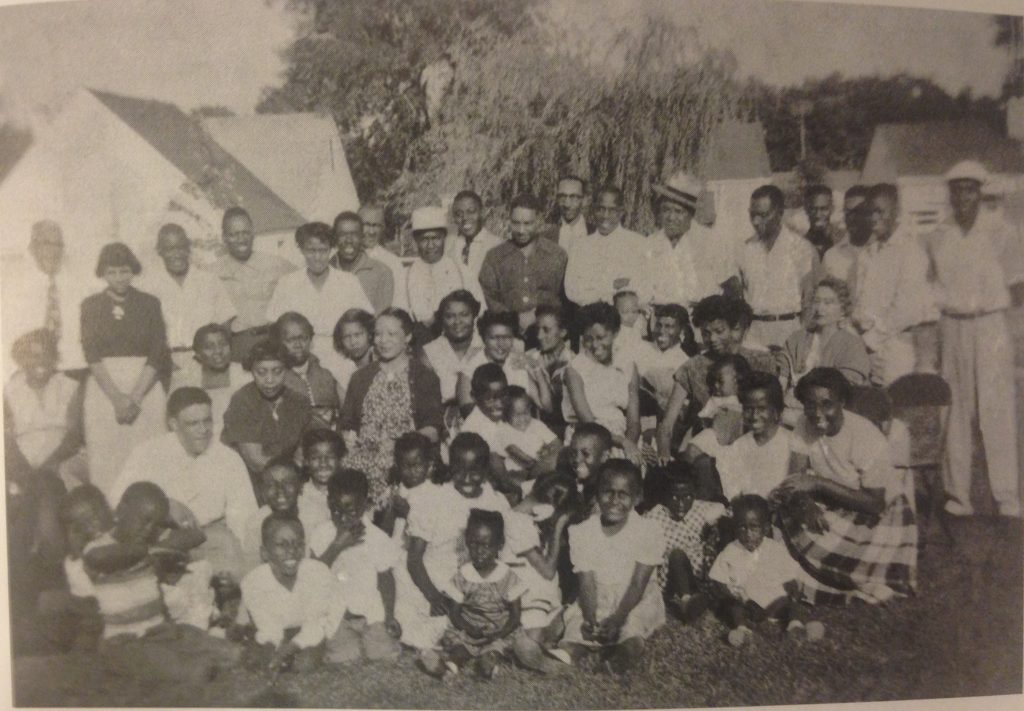
At the first meeting, Better Homes members elected officers to run the group: Lureatha Allen as President, Earl Thompson as Vice President, Louise Taylor as secretary, Ruby Paige as assistant secretary, and Bland Jackson as treasurer. Eventually, twenty-two couples joined the group. Many members were neighbors along Prairie Avenue or Western Avenue. Eighteen of the twenty-two male members worked at Studebaker. Most of the women stayed home to take care of children. Since many of the women had more flexible schedules than their husbands, they often took on leadership roles in the cooperative.

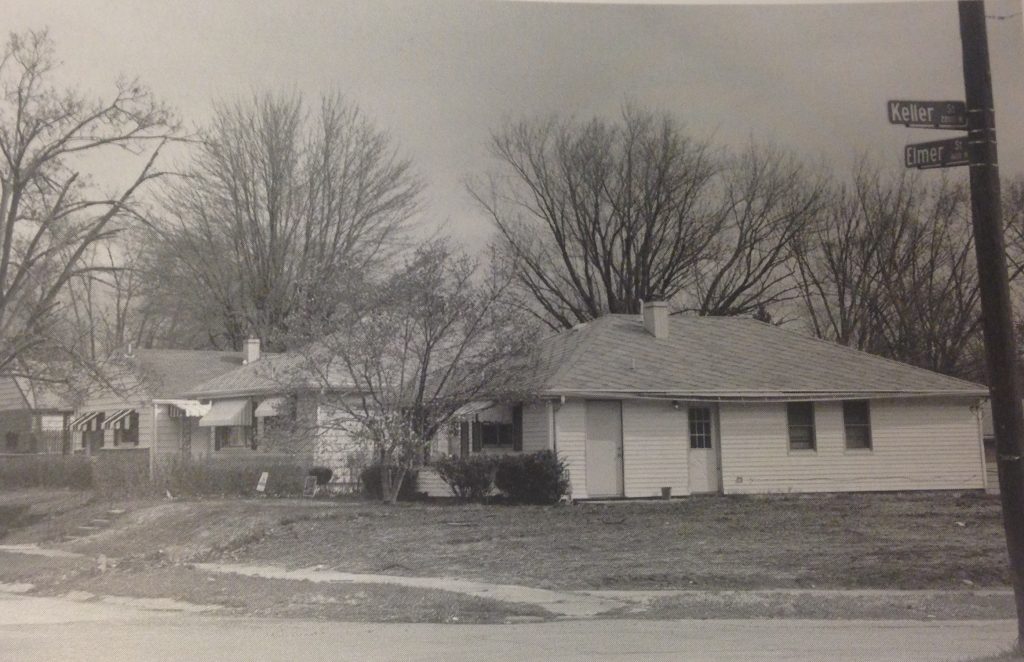
After incorporating, Better Homes members had to find land to build their homes. Their lawyer, J. Chester Allen, secured twenty-six lots on the northwest edge of the city on the 1700 and 1800 blocks of North Elmer Street from his acquaintance, George Sands, a prominent white lawyer in South Bend. Only a few families, all white, lived in this relatively undeveloped area. US Census and Housing Data, which divides South Bend into six wards containing roughly five to six thousand households. The data indicates that only seven “non-white” households lived in the ward containing 1700-1800 North Elmer Street in 1950. In contrast, all Better Homes of South Bend members lived in Ward 2 or Ward 6 at the time, both of which contained 530 and 835 non-white households, respectively.

At a general meeting in September 1950, members enjoyed divvying up the lots and receiving their house numbers. The next steps involved getting loans to finance construction and a contractor to build homes on the lots. Better Homes enlisted the help of DeHart Hubbard, who worked as a race relations advisor at the FHA office in Cleveland. The FHA had finally started cracking down on racially restrictive covenants in their mortgages, after years of pressure from civil rights groups.
Through Hubbard, Better Homes got the FHA to handle their permanent mortgages and found four local banks to handle financing. Many members worried about meeting with local bank executives because they had heard bankers often denied home loans to African Americans, especially those who wanted to build outside black neighborhoods. Hubbard accompanied members to meetings with banking executives to remind the bankers that the federal government was insuring Better Homes’ loans and that members had good credit, therefore there was no reason to deny financing. In Better Homes of South Bend, member Leroy Cobb told author Gabrielle Robinson:
What I was really proud of was that here was a black man standing up to white executives and telling them that Better Homes wants to have a fair shake. It inspired me.

Better Homes also had to find a competent contractor. Member Margaret Cobb noted in an oral history for the Civil Rights Heritage Center at Indiana University South Bend, that contractors they met with “wanted to give us substandard materials,” to build their homes because members were black. Construction companies at the time often employed a double standard in building, using higher quality materials on homes for white homeowners and cheaper stock for similar African American homes. Leroy Cobb remembered in Better Homes of South Bend that one prospective contractor refused to put doors on closets in their homes. After two years, Better Homes finally found two contractors that supplied good plans at reasonable prices. All the houses were to be one-story frame construction on a concrete slab. Most floor plans contained five rooms and one bathroom.
Before construction could start, the city had to install sewer and water lines. Though the postwar building boom strained the city’s resources, negotiations between the city and Better Homes attorney J. Chester Allen stretched over years. Members suspect that the process might have taken so long because of an unwillingness for the Better Homes families to move to North Elmer Street. After two years of letters and petitions, the group finally got sewers installed and construction began.
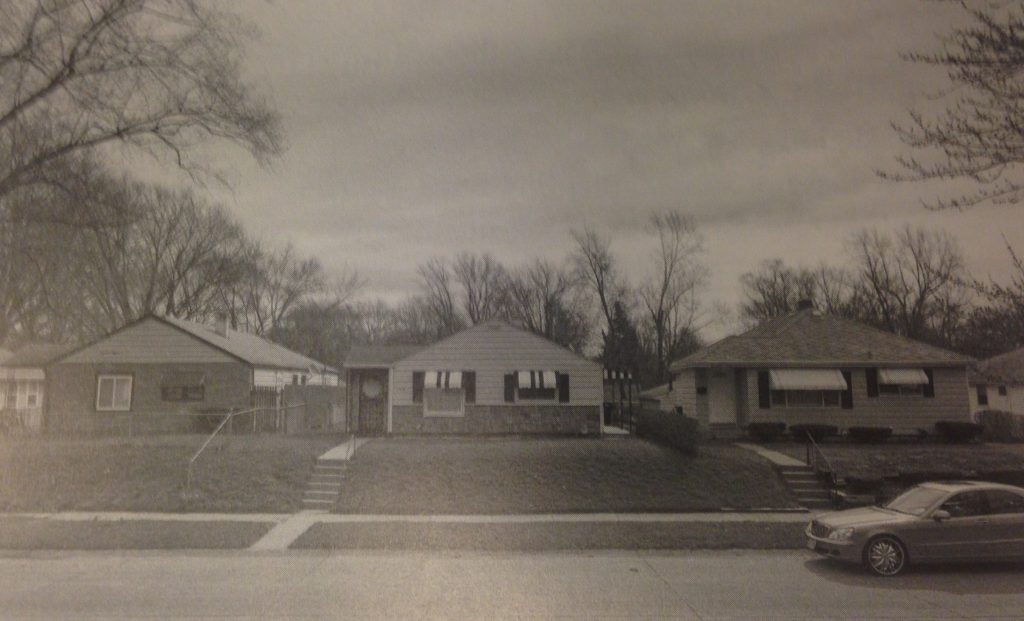

In the late fall of 1952, the first family, Bland and Rosa Jackson, moved into their home at 1706 North Elmer Street. By the mid-1950s, all twenty-two families had moved in between 1700 and 1841 North Elmer Street. Leroy and Margaret Cobb moved in on November 1, 1953 to 1702 North Elmer Street. Leroy Cobb told Gabrielle Robinson that on move-in day, “I was elated.” Finally, he and Margaret had enough space for their family.

In August 1954, the group celebrated their new neighborhood with a picnic featuring cakes, pies, potato salad and barbecued chicken and ribs. Over the years, Better Homes members grew a vibrant community, filled with family cookouts and outdoor activities like baseball, kickball, and building snowmen. There was even an annual Elmer Street Parade.
The Indiana Historical Bureau will honor Better Homes of South Bend with a new state historical marker. The marker will be revealed at a ceremony open to the public July 1, 2017 at 1702 North Elmer Street in South Bend. Check on our Facebook page and website for upcoming details.











