In 1971, the Indianapolis Public Schools (IPS) system was brought to court and found guilty of practicing de jure segregation or racial separation enforced by law. This lesser-known story of desegregation in Indianapolis’s schools reveals a community deeply divided over race and offers one local response to an important national conversation.
Indianapolis had been racially segregated long before the 1970s. In particular, residential segregation coupled with a practice called redlining reinforced boundaries between the city’s white and African American populations. Redlining is denying services to people based on race: in this case, financial services. In response to the Great Depression, between 1934 and 1968 the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) and the Home Owners’ Loan Corporation (HOLC) used the National Housing Act to make housing more affordable. In practice, the Act only made home ownership easily accessible to white people by guaranteeing their loans. It explicitly denied to back loans for black people or even residents of majority black neighborhoods.

Appraisers ranked residential areas on a grading scale from A (green) to D (red). These color-coded maps, created by lenders, developers, and real estate appraisers for the FHA and HOLC, dictated how easy or difficult mortgage companies would make it for residents to secure loans in different areas. The appraisal process proved damning to areas where African Americans lived. An A-grade area, as one appraiser said, would not include “a single foreigner or Negro.” The lowest D-grade, red areas included “detrimental influences in a pronounced degree” with “undesirable population or infiltration of it.” Since the appraisers purposefully graded areas where African Americans lived poorly, redlining made it impossible for African Americans to benefit from residential mobility and reinforced racial segregation in the city.
In Indianapolis, A-grade areas were mainly located in the suburbs while C- and D-grade neighborhoods were located in the inner-city – where 98 percent of the African American population lived. One Indianapolis neighborhood on the Old Northwest Central side of the city, where African Americans made up 90 percent of the population, was catalogued as D-25. The appraiser who surveyed the area in 1937 gave it a D-grade for being “blighted” and “almost solid negro.” Even areas described as having “better class” African Americans were still classified as D-grade. In contrast, desirable Grade-A locations, like A-1 near Butler University, boasted “[n]ative white; executive and other white-collar type” residents with “nominal” foreign-born and no black residents.
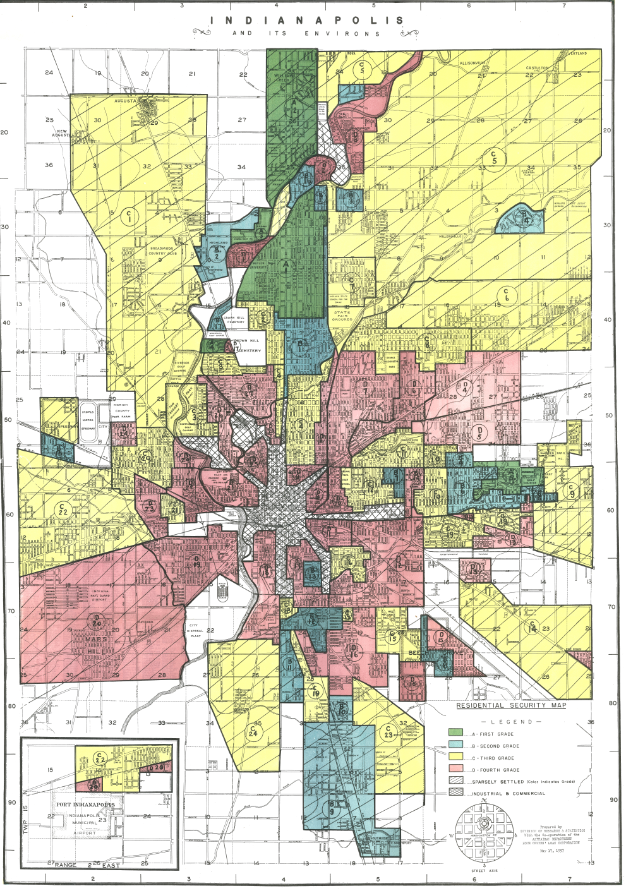
Explore the redlining map of Indianapolis.
These residential patterns made it easy for IPS to uphold segregation in the school system as the School Board would zone, or divide, different residential areas to feed into different schools. As such, racially segregated housing generated racially segregated schools. A deeply divided school system had been in place in the city since 1927 when the Ku Klux Klan pressured the Board of School Commissioners to build what became Crispus Attucks High School for African American students. IHB’s historical marker observes the school’s history.

Although school segregation was outlawed in Indiana in 1949, Indianapolis Public Schools (IPS) reestablished the elementary school boundaries in 1953 to ensure that the school system remained racially divided. The boundaries were so clearly racially-motivated that “[i]n some instances the lines drawn . . . ignored natural boundaries, requiring students to cross a canal, railroad track” or busy street “to get to their assigned school where no impediment stood between the student and an adjoining school.” An African American child tragically died after being struck by a train in 1952 because of these boundaries.

In 1968, a group of African American parents of children who attended IPS schools requested that the US Justice Department file a suit in the federal district court to charge IPS with unconstitutional segregation. The case, United States v. Board of School Commissioners, was tried in Indianapolis in July of 1971. The verdict, given on August 18, 1971, found “a purposeful pattern of racial discrimination based on the aggregate of many decisions of the Board and its agents.” IPS was guilty of de jure segregation, including racist “gerrymandering of school attendance zones, the segregation of faculty, the use of optional attendance zones among the schools, and the pattern of school construction and placement.” The court believed that “complete desegregation within IPS boundaries would encourage ‘white flight’ and lead to rapid resegregation” of IPS. To address this, the State of Indiana was added to the suit so that the township schools within Marion County would have to racially integrate with IPS.
In 1973, IPS having taken no significant steps towards desegregation, the district court asserted jurisdiction over the issue. Judge Dillin of the United States District Court for the Southern District of Indiana ordered a one-way busing system to force IPS and the township schools to integrate.

Many Indianapolis parents, both black and white, were nervous for this transition the preceding summer of the 1973 school year. Meridian-Kessler, located on the north side of the downtown, had only recently become multi-racial at the time, and the neighborhood’s August/September newsletter carried a somewhat anxious tone. The front page read:
Uppermost in the minds of most Indy residents this fall is the unsettled school situation . . . There are three grade schools within our boundaries, and our children attend two nearby high schools. All of these schools will be involved in the desegregation plan eventually due to the changing racial balance in this area.
The city had reason to be nervous. Forced busing schemes in other cities like Detroit and Boston made headlines for the violence they incited. Indianapolis residents associated with the Ku Klux Klan became a common presence at anti-busing protest events. On the morning of September 27, 1971, Sgt. J. Adamson of the Indianapolis Police Department (IPD), was assigned to cover an anti-busing demonstration at the Indiana Statehouse. He identified “[a] group of approximately twenty (20) mixed men, women and male teenagers…under the name of ‘Americans for America’,” noting, “[t]his organization has strong Klan affiliation.” Three days later, September 30, 1971, the IPD deployed their Special Investigation unit to cover another meeting: The Citizens Against Busing at the Indianapolis Baptist Temple. Again, many involved were members of the KKK-affiliated group “Americans for America.” Meetings like these were not uncommon.
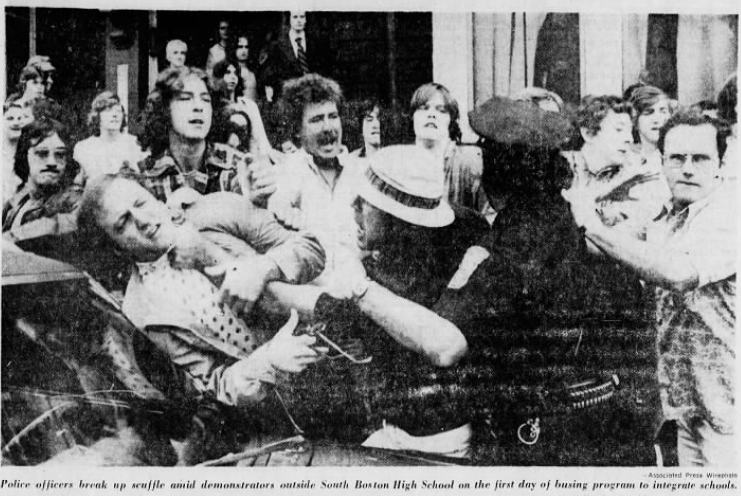
In Indianapolis, the first buses of black students began commuting to white schools in 1973. Not all schools responded to the desegregation order immediately. Some townships, including Perry, Decatur, Franklin, and Lawrence only began accepting IPS students bused to their schools in 1981. That year, when her bus, coming from Indianapolis’s east side, pulled into Perry Meridian High School, LaTonya Kirkland was terrified. She “remembers a dozen of her white classmates approaching the bus, their hands slapping against the yellow metal side panels . . . the bus started to rock as the white students slammed against the bus” before throwing an egg at the window. Police had to escort her and her fellow black classmates into the school.
Perry Meridian High School was the site for many violent racial altercations. The burden of reversing segregation, a problem instigated by the white population, fell heavily on the shoulders of black teenagers. The letters “KKK” were found painted on the school building, and there were rumors of black students coming to school with weapons to protect themselves. Only one African American girl was actually caught with such a weapon. She was concealing a meat cleaver. The situation at Perry Meridian High School had escalated so much that in 1981 the FBI came to investigate.
The interconnected stories of redlining and the desegregation of IPS reveal a city deeply divided, struggling with issues of race and equality. In the end, busing briefly achieved what it was meant to do. The court order created schools which appeared racially balanced and integrated on paper, but were often still segregated and hostile. Indianapolis began to phase out forced busing in 1998, ending the court-ordered desegregation era with LaTonya Kirkland’s daughter LaShawn’s graduating class in the 2015-2016 school year.






