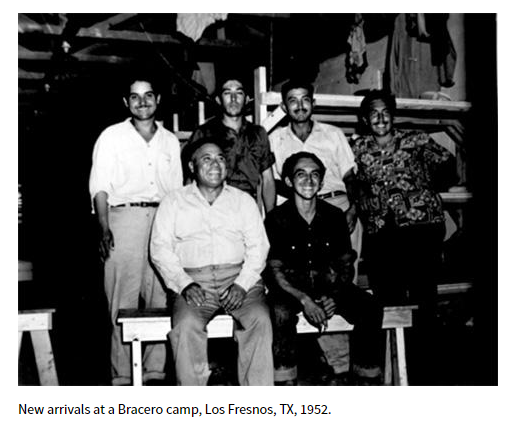
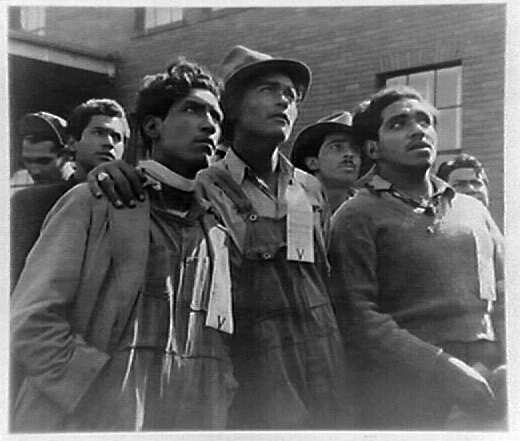
Immigrants have long helped to create a healthier U.S. economy. The work of respected historians and economists has repeatedly dispelled the xenophobic myth that immigrants “steal American jobs.” Instead, immigrants (both those who arrive through documented and undocumented venues) increase the earning potential for all Americans. Pia Orrenius, Vice President and Senior Economist at the Dallas Federal Reserve Bank and Fellow at the John Tower Center for Political Studies at Southern Methodist University, explains:
Immigration fuels the economy. When immigrants enter the labor force, they increase the productive capacity of the economy and raise GDP. Their incomes rise, but so do those of natives . . . In addition to the immigration surplus, immigrants grease the wheels of the labor market by flowing into industries and areas where there is a relative need for workers — where bottlenecks or shortages might otherwise damp growth. [1]
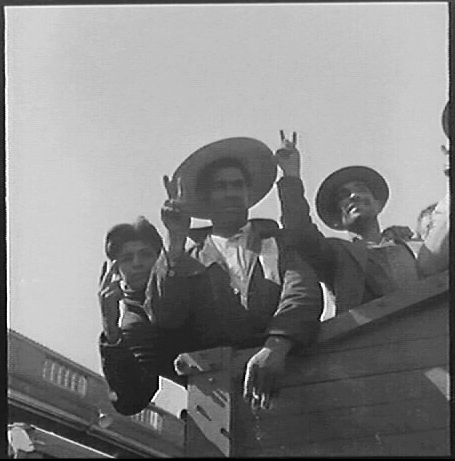
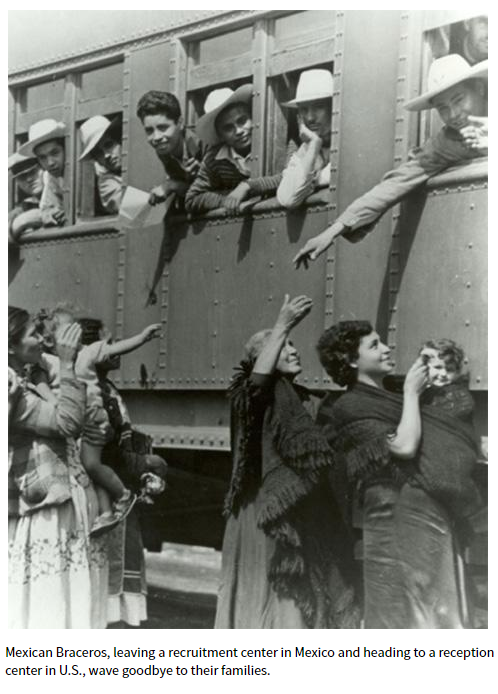
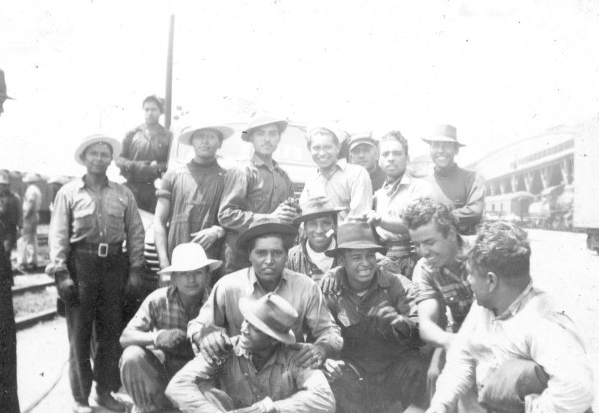
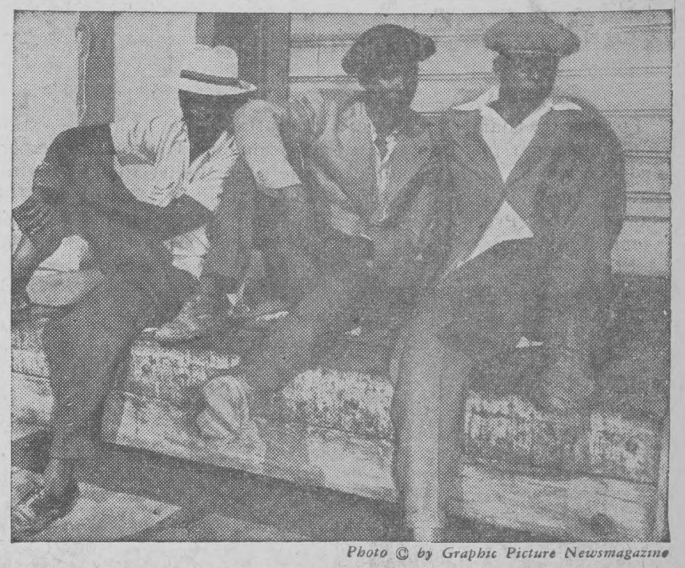
This was especially true of Mexican immigrants who came to the United States in the first half of the twentieth century. Not only did they help stimulate the United States economy, but they were willing to move into areas like rural Indiana where farmers needed extra help at harvest time. And several Indiana businesses can attribute their success during the lean years of the Great Depression and the labor shortages of the Second World War to the contributions of workers of Mexican origin. [2]
Sechler’s Pickles, Inc., just outside the town of St. Joe in DeKalb County has become a successful company and nationally recognized brand over their last century of operations. In addition to the hard work, vision, and savvy of its founders, Ralph and Anne Sechler, the company attributes much of its success to the workers who helped them meet increasing demand over the years. Since the 1940s, many of these laborers have come from Mexico or have had Mexican ancestry. But within that group, there is much more diversity than newspapers and other sources have recognized. As immigration continues to diversify today, this nuance is worth understanding better. [3]

Some of these workers were U.S. citizens whose parents were born in Mexico, such as Carmen (Morales) Ortiz, who was born in Kansas. Some were born in Mexico and became U.S. citizens through naturalization, including Carmen’s husband Floyd Ortiz, who was a U.S. citizen for decades before starting at Sechler’s. Others, including Aurelio Rivera, were Mexican citizens who came to Indiana at the behest of the U.S. government via the Bracero Program to help meet increased wartime food production demands. And still others, such as Rosalio and Paula Luna, were migrant workers, travelling with the harvests through the Midwest, sometimes returning to Mexico to help family there. Despite their varied backgrounds, contemporary sources, especially newspapers, often treated these individuals as a monolith. Thus, it can be difficult to record an accurate history of workers of Mexican origin and their experiences in Indiana. An exploration of this Hoosier pickle company, however, provides a glimpse into workers lives in a way that adds richness to the story of our state.
This post, the first of two, will look at the experiences of two U.S. citizens of Mexican origin at Sechler’s Pickles, Carmen and Floyd Ortiz. Notably, this study suffers from a lack of sources created by the Ortizes themselves. To address this hole in the record, I have juxtaposed newspapers, government records, contextual sources, and family and corporate histories. In doing so, this post also serves as a lesson in the importance of comparing sources created from different perspectives and how that creates more accurate history. This balance is especially important in telling the history of marginalized groups. Personal stories of the Ortizes and vital records, such as census and immigration papers, help to counter biased newspaper accounts given by Indiana newspapers. The rhetoric of these newspapers also provides insight into Hoosier opinions on immigration and how perspectives about Mexican immigrants changed depending on external forces such as the Great Depression and WWII. And finally, this concentrated study reinforces the fact that many immigrants arrived here because Hoosier farmers and the U.S. government asked them to, establishing the migration patterns that continue to shape the state and nation. The stories of the workers and their families at Sechler’s Pickles, Inc., are part of the story of Indiana and a diversifying United States. Additionally, this story of how Sechlers got started, how the Ortizes arrived at Sechler’s Pickeles, and how these families formed a relationship that would last for generations is in interesting look into the lesser-explored agricultural history of the state.
Sechler’s Pickles
Ralph E. Sechler was born in 1894 in St. Joe, DeKalb County. He attended St. Joe and then Butler High School, graduating circa 1912. He taught at a local high school for three years and worked summers at a “pickle receiving and salting station in St. Joe” ran by the D.M. Sears Company of Fort Wayne. In 1915, he entered Indiana State Normal School in Terre Haute where he thrived. He played basketball, managed the track team, and served as secretary of the Daedalian Literary Society through which he participated in debates and delivered speeches. [4]

When the U.S. entered WWI in 1917, Ralph registered with the U.S. Army. When his name came up for service, he was one of only eighteen (out of 781 names) who did not attempt to claim an exemption. Before he left home for the war, he married Anna Florence Martindale, a Greenfield native two years his senior. [3]

Anna was just as sharp as Ralph and worked as a teacher at Seymour High School during her new husband’s absence. In September 1917, Ralph left for Camp Taylor in Louisville. His superiors quickly noticed his intelligence and aptitude for teaching. In October, the Fort Wayne Sentinel reported that “Ralph Sechler, another St. Joe boy, is still at Camp Taylor, engaged four nights in the week teaching night school for the benefit of Uncle Sam’s boys who have not learned to read and write.” [4] He was commissioned Second Lieutenant but did not serve overseas because of the Army’s need for competent teachers at the officer’s training camp.

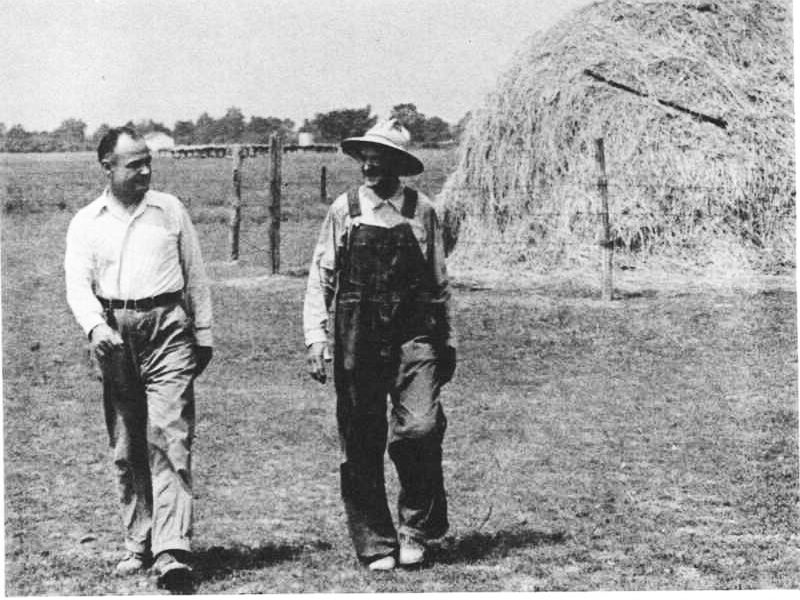
After his discharge from the Army in 1919, he went back to work for the D.M. Sears Company and was soon put in charge of approximately a dozen “receiving stations,” where farmers brought their produce to be processed. Between 1920 and 1923, he transitioned from managing these stations to leasing them and securing his own contracts with local cucumber growers. Soon Ralph and Anne Sechler had established their own pickle processing business at their home and farm just north of St. Joe. By 1925, local grocery stores carried “St. Joe Valley” pickles and by 1930, they were popular in local restaurants as well. [5]

The Sechlers employed creative strategies to stay afloat during the Great Depression. As one would expect, they worked with local cucumber growers, processing this produce into pickles. But they also worked with Chicago processors, purchasing goods to resell to Hoosier grocery stores and restaurants, and thus besting other businesses with the variety they could offer. They also brought barrels of pickles to homebound locals who would jar the goods. These neighbors worked for low wages, but also received income they would otherwise have not been able to access. [6]

Around 1933, Ralph and Anne turned their barn into a pickle processing factory and a driver began making deliveries to businesses in a new truck marked “St. Joe Valley Pickles.” In 1937, the Sechlers made major improvements to the processing facility, hooking up a steam engine to the threshing machines and pickling tanks and increasing production. Early on a late October morning in 1937, the Sechlers’ pickle processing center, which they had built in their barn, burned down. By the following Monday, workers were already building a new, larger facility. This larger facility helped the company grow; the following year, the company also purchased more delivery trucks. [7]

Over the following decade, Sechler’s added more varieties of products. One Indiana grocery store advertised in 1944: “St. Joe Valley sweet pickles, raisin crispies, sweet relish, sweet chips, sweet mixed dills, sweet orange marmalade, jellies, Apple butter, strained honey.” Thus, by the time the U.S. increased agricultural production for the war effort and the Bracero Program was in full swing, Sechler’s Pickles was a thriving Indiana business employing a number of local growers, packers, and delivery drivers and serving stores and restaurants across the state. [8]

The Ortiz Family
Floyd Ortiz was born circa 1903 to John and Isabelle Gutierez-Ortiz in Salamanca in the Mexican state of Guanajuato. [9] While today, Salamanca is a thriving manufacturing city with a renowned university, at the beginning of the twentieth century, the area was not economically or politically stable. President Porfirio Díaz made some economic improvements, increasing the mining output of the region, but it was mainly already wealthy people who benefited. His tax breaks for the rich and “unwillingness to recognize minority rights” of the indigenous people of the region led to a revolt against the administration in 1910. [10] In 1911, a coalition led by Francisco Villa, Emiliano Zapata, and Venustiano Carranza ousted President Díaz and replaced him with Francisco Madero. However, battles between federal and rebel factions continued for years, destabilizing the region and making it hard for average citizens to make a living. Floyd Ortiz, like many others from Guanajuato, likely came to the United States as “displaced refugees fleeing the political upheaval and violence” of the 1910 revolution.[11]

In 1919, Floyd Ortiz arrived in the United States at Laredo, Texas, where he received documentation for “lawful entry” into the country. He was just 16 years old. [12] Within four years, in 1923, Ortiz became a naturalized U.S. citizen. [13] Just one year later, the U.S. shut the door to refugees with the Immigration Act of 1924 (the Johnson-Reed Act), the result of xenophobic ideas and no small amount of lobbying by the Ku Klux Klan. And while Mexican immigration was exempted from this exclusionary immigration act – for reasons we’ll examine further in part two – Mexican immigrants were not exempt from prejudices of pseudoscientific thinking influenced by eugenics and general racism and bigotry. They often endured low wages, poor living conditions, and hard labor to make a life in the United States. [14]
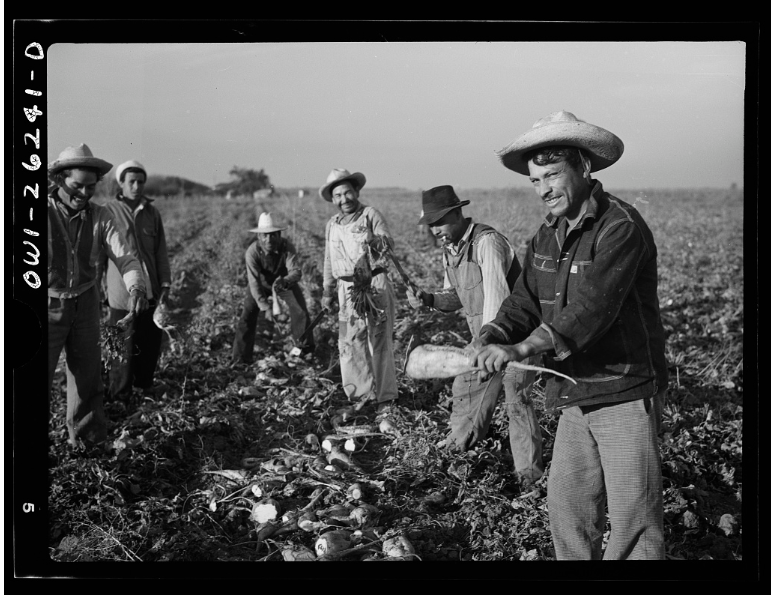

Carmen Morales was born circa 1908 in Kansas to parents of Mexican origin. Throughout her life, newspapers and even official government sources recorded her as “Mexican,” despite the fact that she was a native born U.S. citizen. We don’t know much about her family’s path to Indiana, but by the mid-1920s Carmen was “employed in beet work” in central Indiana and her mother and step father were living in northwest Indiana. [15] Perhaps she met Floyd Ortiz through work because he was also working the beet harvests in Tipton and Madison Counties. Or perhaps they met through family, friends, or church events, as later records show they were both devout Catholics.

In 1927, Floyd Ortiz and Carmen Morales, got married at the county clerk’s office in Tipton, Indiana. We’re lucky to have local newspaper coverage to supply some details of the day. However, the reporter for the Tipton Daily Tribune treated the event not as a wedding between two U.S. citizens living in Indiana but as an oddity, exaggerating the “foreignness” of the couple. The newspaper’s account of this “out of the ordinary” wedding focused on the Mexican heritage of the couple and their parents. [16]
The Tipton Daily Tribune called Floyd a “native born Mexican” and described Carmen as “full blooded Mexican, but who was born in the state of Kansas.” In other words, while Carmen was a United States citizen, the newspaper reporter still considered her Mexican. Despite Floyd’s almost ten years in the United States and his 1923 naturalization, and despite Carmen’s status as a native-born U.S. citizen, the 1927 newspaper article could only see their race and that construct made them Mexican and not American. The reporter further underscored the couple’s “foreignness” by detailing that their parents were both from Mexico. While both sets of parents were indeed born in Mexico, they were also Hoosiers by this point. The groom’s parents lived in Geneva, Indiana, and the bride’s mother and stepfather lived in Francisville, Indiana. Further research would be needed to determine if the parents were naturalized citizens, but it is likely they had also been in the United States for some time considering Carmen’s stepfather went by “John” as opposed to a “Juan” or another Spanish name. Without considering the citizenship information offered by the census and immigration agencies, one would come away from reading the newspaper article believing that two “Mexicans Married” as opposed to two U.S. citizens with families of Mexican origin. This theme of juxtaposing sources will continue to be important as we dig deeper into the story of workers of Mexican origin at Sechler’s Pickles, Inc. [17]
Why is it important to clarify that Floyd and Carmen are U.S. citizens? Because at the time, and even today, many treat all workers of Mexican origin as a monolith, usually assuming that they are Mexican citizens and migrant workers coming to the U.S. to make money at harvest time and then return to Mexico. This is, in fact, an assumption that allowed Mexico to avoid immigration restrictions that impacted other groups in the 1920s. However, Mexican immigrants and migrants of Mexican origin are not a monolithic group; there are a range of reasons people left Mexico and either returned home or stayed in the United States to brave the road to citizenship. Every Hoosier has their own family immigration story, creating a rich and diverse state history. Families of Mexican origin are not different. The array of migration experiences is as diverse as Hoosiers of Potawatomi, German, African, or Serbian heritage.
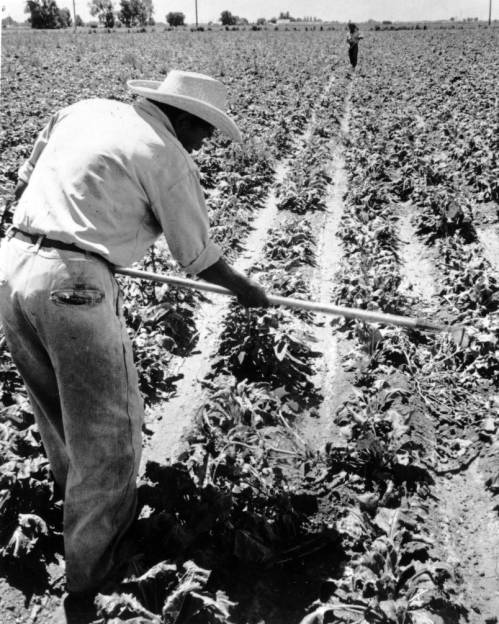

The Ortiz Family at Sechler’s Pickles
After Floyd and Carmen worked the beet harvests in Tipton and Madison Counties and got married in Adams County, Indiana, they moved to Paulding County, Ohio. The 1930 census listed Floyd as a “beet worker” here as well, while listing Carmen’s occupation as “none,” likely because she had recently given birth to their first daughter, Mary. Their family grew quickly and by 1940, the census reported that Floyd and Carmen were the parents of eight children. Times must have been very difficult; though the census reported that both Floyd and Carmen were beet workers, Floyd had been out of work for unknown reasons for thirty weeks. [18]
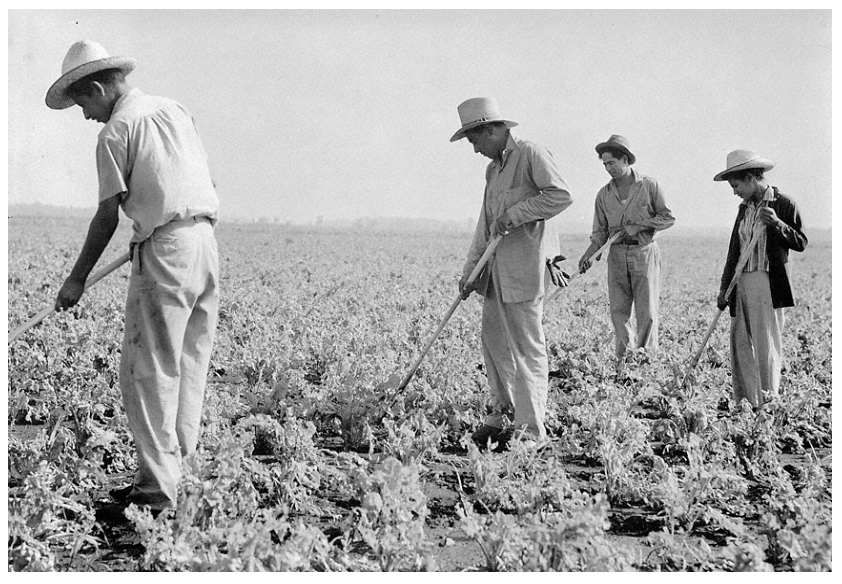

By 1944, however, Floyd was at work at the Paulding Sugar Beet Co. The company contacted Sechler’s Pickles about growing and processing beets for them and offered to send “a real good family,” as well as housing for them, in exchange for Sechler’s help with production. The Ortizes and the Sechlers accepted the arrangement. By this point, Floyd and Carmen had fourteen children and they moved the family to DeKalb County. Floyd and several of the children went to work for Sechler’s. The younger children worked in the field picking produce and then, after they turned sixteen, they worked in the processing factory. [19]
We don’t know too much about their life in DeKalb County except that they were able to take care of their family and save money, as eventually they purchased their own 80-acre farm just east of St. Joe on the Ohio border. Frank Sechler, son of Ralph and manager of the company by this point, speculated that the Ortizes picked the location because of it’s proximity to their church. Frank recalled Floyd’s devout faith:
I seldom walked up to Floyd in the field but what he didn’t reach in his pocket and pull out a stone he had just found, which would have a figure of Christ, a cross, or some other religious item on it. Sometimes I had a little trouble discerning it, but he would convince me!!! [20]
By the 1960s, Floyd and Carmen Ortiz were living in Hicksville, Ohio where Floyd died in 1973. Several family members, including daughter Dorothy Chew, daughter-in-law Betty Ortiz, and many grandchildren and great grandchildren continued the Ortiz family connection with Sechler’s, working in the fields and factory. [21] In fact, the Ortiz family helped to fund the state historical marker for Sechler’s Pickles that will be installed this fall 2022. The text will read:
Ralph and Anne Sechler established Sechler’s Pickles (first named St. Joe Valley) on their homestead here in the 1920s. Despite the Great Depression, they grew the business, selling many varieties of pickles to local restaurants and building a larger processing facility in 1937. By the early 1950s, grocery stores across Indiana and Ohio carried Sechler’s Pickles.
Workers of Mexican origin, including Braceros who arrived in the 1940s to aid the U.S. war effort, were essential to the Sechlers’ success. Several of these families remained with the company for decades. A network of salesmen, mail orders, church fundraisers, and partnerships with well-known companies made Sechler’s Pickles a respected and nationally recognized brand. [22]

In addition to the Ortizes, Sechler’s Pickles, Inc. also employed Mexican migrant workers and dozens of Braceros. The experiences of workers who were Mexican citizens in Indiana were much different than that of the Ortiz family’s experiences as U.S. citizens. In Part Two of this post, we’ll examine the work and lives of Mexican migrant and Bracero workers at Sechler’s Pickles, Inc., their reception by their Hoosier neighbors, and how they were portrayed in Indiana newspapers. Check back for:
“Rancho Allegre:” Experiences of Bracero, Migrant, and U.S. Workers of Mexican Origin at Sechler’s Pickles Inc. Part Two.
Notes
Newspaper articles accessed Newspapers.com unless otherwise noted.
[1] Pia Orrenius, “Benefits of Immigration Outweigh the Costs,” The Catalyst, Spring 2016, Issue 2, George W. Bush Institute, https://www.bushcenter.org/catalyst/north-american-century/benefits-of-immigration-outweigh-costs.html.
[2] Ibid.; Jorge Durand, Douglas S. Massey, and Emilio A. Parrado, “The New Era of Mexican Migration to the United States,” Rethinking History and the Nation State: Mexico and the United States, A Special Issue of the Journal of American History 86, No. 2 (September 1999): 518-536, accessed Organization of American Historians.
[3] Frank Sechler, History of Sechler Pickles, 1921-1996, Willennar Genealogy Center, Eckhart Public Library, copy in marker file. According to the corporate history written by founder Ralph Sechler’s son Frank Sechler, “Hispanics were very much a part of our operations, both in the field and in the plant.” This source is consulted throughout the post and compared with the other sources listed in the notes below.
[4] Ralph E. Sechler, Medical Certificate of Death, Indiana State Board of Health, December 12, 1962, Indiana Archives and Records Administration, Roll 19, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; Grave of Ralph E. Sechler [photograph], Riverside Cemetery, Saint Joe, DeKalb County, Indiana, accessed Find-A-Grave; Butler High School Yearbook, 1912, p. 16, U.S., School Yearbooks, 1900-1999, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; “Juniors and Sophs Wine in Normal Series,” Terre Haute Daily Tribune, November 13, 1915, 5, Hoosier State Chronicles; Edgar L. Morphet, “Freshies Finish Last,” Daily Tribune [Terre Haute], December 2, 1915, 11, Hoosier State Chronicles; Indiana State Normal School, Program of Commencement Week, Terre Haute, Indiana, 1916, U.S., School Yearbooks, 1900-1999, AncestryLibrary.com; “Literary Society Meets,” Daily Tribune [Terre Haute], October 4, 1916, 12, Hoosier State Chronicles; “State Normal Presents Baseball Players with Letters,” Daily Tribune [Terre Haute}, June 11, 1917, 9, Hoosier State Chronicles.
[5] “Ralph Sechler,” Registration Card, DeKalb County, Indiana, U.S., World War I Draft Registration Cards, 1917-1918, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; “DeKalb County Fails to Get Quota of Eighty-Eight,” Fort Wayne News, August 9, 1917, 1; “St. Joe News,” Fort Wayne Journal-Gazette, August 14, 1917, 11.
[6] “St. Joe News,” Fort Wayne Daily News, September 20, 1917, 11; “St. Joe News,” Fort Wayne Sentinel, October 29, 1917, 3; “Will Visit Camp Taylor,” Fort Wayne Sentinel, July 26, 1918, 11; “Newsy Paragraphs,” (Seymour) Tribune, September 12, 1918, 3; “Newsy Paragraphs,” (Seymour) Tribune, June 10, 1919, 8.
[7] “St. Joe News,” March 11, 1920, newspaper clipping, in Frank Sechler, History of Sechler Pickles, 1921-1996, 3, Willennar Genealogy Center, Eckhart Public Library, copy in marker file; Fort Wayne City and Allen County Directory, 1922 (Fort Wayne: R. L. Polk & Co. Publishers), 924, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; “Local and General,” Waterloo Press (DeKalb Co.), August 30, 1923, 5; Advertisement, South Bend Tribune, July 31, 1925, 30; Garrett Clipper, October 4, 1926, 7; Fifteenth Census of the United States, 1930, Concord, De Kalb, Indiana; Page: 2A; Enumeration District: 0003, FHL microfilm: 2340320, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; Advertisement, South Bend Tribune, May 23, 1930, 36; Sechler, 4.
[8] Sechler, 10-11.
[9] “Thousands See Great Parade at County Fair,” Garrett Clipper, October 8, 1934, 2; “Pickle Plant at St. Joe Consumed,” Waterloo Press, October 21, 1937, 1; “Personal,” Garrett Clipper, November 1, 1937, 2; Sechler, 11-12.
[10] Advertisement, Daily Reporter (Greenfield), May 12, 1944, 5.
[11] Non-statistical Manifests and Statistical Index Cards of Aliens Arriving at Laredo, Texas, May 1903-November 1929, NAI: 2843448, Record Group Title: Records of the Immigration and Naturalization Service, 1787-2004., Record Group Number: 85, Microfilm Roll Number: 072, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; Floyd Ortiz and Carmen Morales, Marriage Registration, August 27, 1903, Tipton, Indiana, 88, Indiana Marriages 1810-2001, accessed AncestryLibrary.com.
[12] Victor Garcia and Laura Gonzalez Martinez, “Guanajuatense and Other Mexican Immigrants in the United States: New Communities in Non-Metropolitan and Agricultural Regions,” JSRI Research Report #47, Julian Samora Research Institute, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, 1999, accessed https://jsri.msu.edu/upload/working-papers/wp47.pdf.
[13] Ibid.
[14] Non-statistical Manifests and Statistical Index Cards of Aliens Arriving at Laredo, Texas, May 1903-November 1929, NAI: 2843448, Record Group Title: Records of the Immigration and Naturalization Service, 1787-2004., Record Group Number: 85, Microfilm Roll Number: 072, National Archives and Records Administration, accessed AncestryLibrary.com.
[15] Fifteenth Census of the United States, 1930, Jackson Township, Paulding County, Ohio, Page: 6B, Enumeration District: 0018, FHL microfilm: 2341594, accessed AncestryLibrary.com.
[16] Jill Weiss Simins, “Braceros in the Corn Belt Part Two: Ambassadors of Goodwill,” Untold Indiana, March 13, 2019, https://blog.history.in.gov/braceros-in-the-corn-belt-part-two/.
[17] Floyd Ortiz and Carmen Morales, Marriage Registration, August 27, 1903, Tipton, Indiana, 88, Indiana Marriages 1810-2001, accessed AncestryLibrary.com; “Mexicans Married,” Tipton Daily Tribune, December 28, 1927, 6.
[18] Ibid.
[19] Fifteenth Census of the United States, 1930, Jackson Township, Paulding County, Ohio, Page: 6B, Enumeration District: 0018, FHL microfilm: 2341594, accessed AncestryLibrary.com.
[20] Ibid; Sixteenth Census of the United States, 1940, Blackcreek Township, Mercer County, Ohio, Page: 11A, Enumeration District: 54-1, accessed AncestryLibrary.com.
[21] Sechler, 26.
[22] Ibid.
[23] “Former Decatur Resident Dies,” Decatur Daily Democrat, October 8, 1973, 1.
[24] Learn more about the Indiana Historical Bureau and the state historical marker program: in.gov/history.