Learn about the origins of the Brown County Jamboree in Bean Blossom, Indiana in Part I.

William “Bill” Monroe’s Hoosier roots run deep. While Bill was born and raised in Kentucky, he moved to northwest Indiana in 1929 when was he was just eighteen years old. His brother Charlie had gotten a job at the Sinclair Oil refinery in Whiting, Indiana, and sent for Bill and their other brother Birch. It was the start of the Great Depression and the crowds outside the refinery of men hoping for a job grew large enough that the police had to move them so the street cars could get through. Luckily for Bill, Charlie Monroe was well liked at Sinclair and was able to help his brother to secure employment there as well. Birch was not as lucky and remained unemployed for some time. Charlie was afraid that Bill wouldn’t be able to do the heavy labor as a result of an appendectomy. Bill soon proved that he was up to the job, unloading empty oil barrels from the freight trains and cleaning them. However, Bill also had to do janitorial work at the company, something of which he was embarrassed and wouldn’t speak of publicly.

“Inferno
Bill was also sensitive about the problems with his eyes. Bill’s vision was poor, but he was also “hug-eyed,” a term for one eye that faces inward. Around 1930, the brothers were still working at Sinclair and settled in East Chicago, just a short train ride away from the Windy City. Somehow Bill, likely with his brothers’ help, was able to afford an expensive and delicate eye surgery. Luckily a Chicago surgeon was able to align the eye, “a major turning point” for the shy teenager, according to Richard D. Smith’s Can’t You Hear Me Callin’: The Life of Bill Monroe, Father of Bluegrass.

A lot of southerners were displaced by the Depression, but were able to bring their culture with them to northern industrial cities. The Monroe brothers were no exception. They went to square dances in nearby Hammond, Indiana, sometimes held in an old storefront. “Hillbilly music” had become nationally popular and there was demand for mountain ballads and energetic string bands for both live performances and on the radio. As they had back in Kentucky, the Monroe boys began playing at dances and gatherings around northwest Indiana. Along with their friend Larry Moore, they formed The Monroe Brothers.

Despite the death of their beloved Uncle Pen, who raised Bill and influenced his music greatly, 1931 looked like a better year for the brothers. All three now had refinery jobs and a little extra money to head to the square dances in Hammond. Here they were “discovered” by country music program director Tom Owens, who hired them for a “square dance team” which performed at a traveling variety show sponsored by a radio-station. Soon after, a Hammond radio station gave The Monroe Brothers airtime, a Gary station gave them a regular fifteen minute show, and the Palace Theater in Chicago booked them to perform. The Monroe Brothers’ next break took them away from the Hoosier state. Birch kept his refinery job, but Charlie and Bill headed to Shenandoah, Iowa to perform on a radio show. They were a hit and became full-time professional musicians.

During the time Bill Monroe was away from Indiana, his career took off. By 1936, The Monroe Brothers signed to RCA Victor and released a hit single, “What Would You Give in Exchange For Your Soul?” The Monroe Brothers disbanded in 1938, but Monroe quickly formed other groups, including an early version of the soon-to-be legendary Blue Grass Boys. In 1939 Bill successfully auditioned for the iconic Grand Ole Opry, which made him a star. By this time, the four-hour Opry radio broadcast reached country music fans in almost thirty states and its stars became household names. With the addition of Earl Scruggs on banjo and Lester Flatt on guitar to Bill Monroe’s mandolin and high tenor voice, the classic Blue Grass Boys line-up was born in 1945. Over the next two years, the band recorded several successful songs for Columbia Records, including “Blue Moon of Kentucky,” which again became a hit in 1954 when Elvis recorded it for the b-side of his first single.

Flatt and Scruggs left the band in the late 1940s, but Bill Monroe success continued. He signed with Decca records in 1949 and recorded several songs which became classics of bluegrass music, the genre named for the Bluegrass Boys. The New York Times referred to Monroe as “the universally recognized father of bluegrass” and reported that he “helped lay the foundation of country music.” The writer continued:
Mr. Monroe, who played mandolin and sang in a high, lonesome tenor, created one of the most durable idioms in American music. Bluegrass, named after his band, the Blue Grass Boys, was a fusion of American music: gospel harmonies and Celtic fiddling, blues and folk songs, Tin Pan Alley pop and jazz-tinged improvisations. The Blue Grass boys sang, in keening high harmony, about backwoods memories and stoic faith; they played brilliantly filigreed tunes as if they were jamming on a back porch, trading melodies among fiddle, banjo, and Mr. Monroe’s steeling mandolin. By bringing together rural nostalgia and modern virtuosity, Mr. Monroe evoked an American Eden, pristine yet cosmopolitan.
Link to NYT article: NYTimes.com

In the early 1950s, Monroe returned to Indiana and was impressed with what he saw at Bean Blossom in Brown County. The Brown County Jamboree was a country music variety show held in Bean Blossom that became hugely popular in the state by 1941. Thousands of people came to the small town to see local musicians and stars of the Opry. Bill Monroe began playing at the popular Brown County Jamboree by 1951. Likely it was that same year that Bill decided to purchase the Jamboree grounds from local owners Mae and Francis Rund. He took over management for the 1952 season. The Brown County Democrat reported:
The famous Brown County Jamboree at Bean Blossom has new owners. Mr. and Mrs. Francis Rund, founders and owners for 13 years, have sold the Jamboree Hall to the Grand Ole Opry entertainer, Bill Monroe, of Nashville, Tennessee.
Monroe himself confirmed the 1952 date in a later interview, stating:
This festival here in Bean Blossom Indiana . . . It means a lot to me. I bought this place here back in ‘52 and to set out to have a home base here where we could play to the folks and give them a chance enjoy and to learn about bluegrass music. And It’s really growing in this state and I’m glad that it has.
The Brown County Democrat reported that when Bill Monroe purchased the Brown County Jamboree, the show continued to operate “every Sunday night from the first Sunday in May until the first Sunday in November.” Advertisements throughout the 1950s and 60s for the Jamboree at the park and the Jamboree musicians (including Bill Monroe) at other venues and on the radio continued through the next few decades. However, in the Monroe years, there was much less advertising. The regular show was well-known and attended and so most of the advertising was done through posters. Bluegrass historian Thomas Adler also states in his book Bean Blossom: The Brown County Jamboree and Bill Monroe’s Bluegrass Festivals that the Jamboree under Monroe fell into a regular pattern: “Bill opened each season and played frequent shows in the barn and also used the park for other non-Jamboree events, especially those involving rural pursuits like fox hunting…”

With the rise of rock and roll in the first half of the nineteen fifties, people were much less interested in country music, according to Adler. This affected attendance at the Jamboree and less people visited Bean Blossom. However, with the revival of the folk movement in the late 50s and early 60s, Bill Monroe and his unique style of bluegrass attracted national attention once more. Long time New York Times music reporter Robert Shelton noted in 1959 that bluegrass “is enjoying a vogue in city folk music circles.” Shelton wrote that, through changing tastes, bluegrass was “earning the reconsideration of many serious listeners.” This reinvigorated interest in Bean Blossom as well, and the time was right for Monroe’s next move: a large annual bluegrass festival.

The first annual festival hosted by Bill Monroe in 1967 was called the “Big Blue Grass Celebration.” According to Adler, Bill Monroe didn’t want to put his name on the event and didn’t want the word “festival” because competing bluegrass and folk events used the term. It was officially a two day event, June 24 and 25, but according to Adler, there were a few performances and a dance the night before.
The next year the festival was extended to three days to accommodate the large crowds. This 1968 festival attracted ten thousand people. By 1969 the event was billed as “Bill Monroe’s Bluegrass Festival” and the location referred to as the “Brown County Jamboree Park.” This year the festival was extended to a four day event. According to the Indianapolis Star, highlights included “a banjo-pickin’ contest,” a bluegrass band contest, a “sunset jam session,” an “old-time square dance,” a workshop for learning bluegrass instruments, and church services. When the headlining musicians weren’t performing, they participated in “pick and sing” sessions, improvisational jams where the professionals and amateur players exchanged ideas.
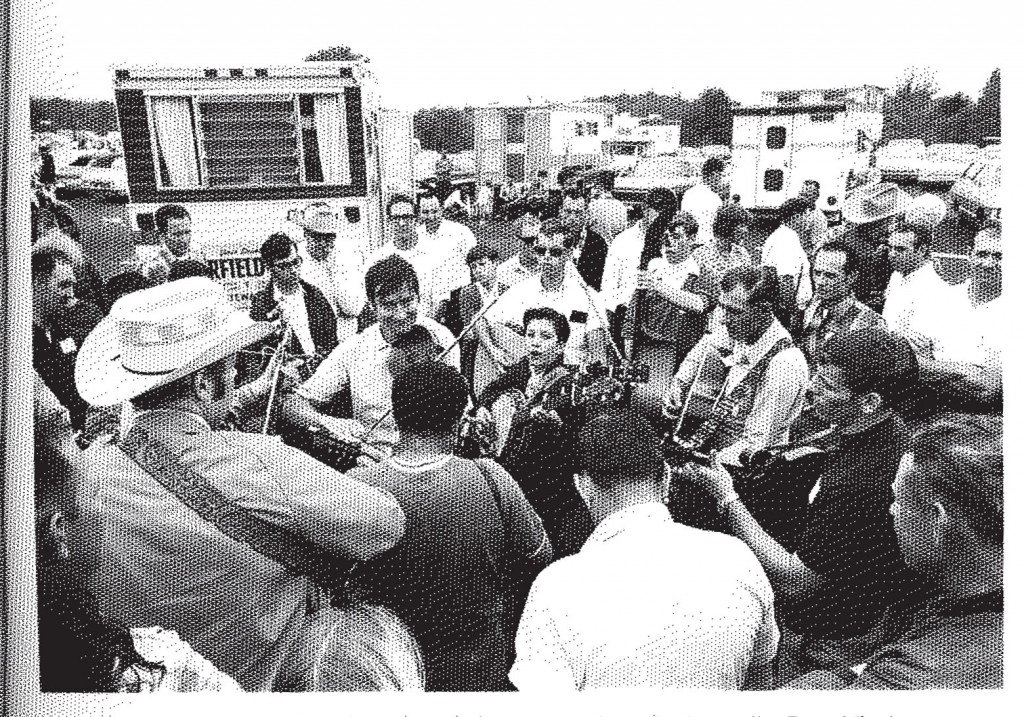

The Bill Monroe Bluegrass Festival soon attracted not just fans but also performers from around the world. The 1969 festival included “Pete Sayers, country singer from London, England,” and Adler writes that Sayers returned in 1970. However, Sayers appears to be the only foreign performer until 1971. Writing for Bluegrass Unlimited Magazine in 1971, Frank Overstreet, a musician and festival attendee, reported on the event being the first international festival at Bean Blossom. He wrote, “The international aspect of bluegrass was brought to light at the festival this year by the presence of a New Zealand group, the Hamilton County Bluegrass Band and a Japanese one, The Bluegrass 45.” The 1971 festival included concerts, jam sessions, dancing, a church service, a bluegrass music school, and bands which travelled from all over to perform, including from other countries. Nonetheless, the main attraction remained Bill Monroe and the Blue Grass Boys “who started it all,” according to the Indianapolis Star.

According to Adler, the “golden age of the festival” was 1972-1982, a period which saw steady growth in attendance. In June 1972, the Indianapolis News reported that the previous year’s festival drew 15,000 people and that organizers were expecting up to 35,000 people for the 1972 event. In June 1973, the Indianapolis News reported that 35,000 people attended the festival. In June 1976, just ahead of the festival, the Indianapolis Star reported that festival organizers again expected up to 35,000 people to attend. In the midst of the festival, Monroe confirmed in a locally televised interview that the numbers of attendees was above 30,000. Monroe also stated that attendees represented thirty-six different states and eight foreign counties. In 1977, the festival was extended to nine days (from seven days the previous year) to accommodate the growing crowd; organizers were expecting crowds of up to 50,000 people.

Bill Monroe made his festival an international success and repeated that success annually. He died September 9, 1996 in Tennessee days before his 85th birthday. According to the Indianapolis Star, even while he was sick in the hospital, he played his mandolin for the other patients. On September 10, 1996, New York Times reporter John Pareles wrote:
He perfected his music in the late 1940’s and stubbornly maintained it, and he lived to see his revolutionary fusion become the bedrock of a tradition that survives among enthusiasts around the world . . . Every musician now playing bluegrass has drawn on Mr. Monroe’s repertory, his vocal style and his ideas of how a string band should work together. And his influence echoes down not just through country music but from Elvis Presley (who recorded Mr. Monroe’s ‘Blue Moon of Kentucky’ on his first single disk) to bluegrass-rooted rock bands like the Grateful Dead and the Eagles.

Upon Monroe’s death in 1996, the deed for the Jamboree grounds was transferred to his son James. In 1998, Dwight Dillman purchased the park and named it “Bill Monroe’s Memorial Park & Campground.” This year the park is preparing for the “50th Annual Bill Monroe Memorial Bean Blossom Bluegrass Festival” to be held June 11 – June 18, 2016. Bill Monroe’s legacy continues in the larger world of bluegrass and will certainly never be forgotten in Indiana, where he got his humble start at a Hammond square dance. As President Bill Clinton stated the year before Monroe’s death, “Bill Monroe is truly an American legend.”





 The “free” aspect of the free show didn’t last long, as the organizers couldn’t help but see how the crowd was growing. The lunchroom business was booming and there was no reason the promoters and performers shouldn’t make a little money too. They built a small stage, fenced in the area, and started to charge twenty five cents per show. Soon, they put up a tent as can be seen in the only known photograph of the Jamboree from this period.
The “free” aspect of the free show didn’t last long, as the organizers couldn’t help but see how the crowd was growing. The lunchroom business was booming and there was no reason the promoters and performers shouldn’t make a little money too. They built a small stage, fenced in the area, and started to charge twenty five cents per show. Soon, they put up a tent as can be seen in the only known photograph of the Jamboree from this period.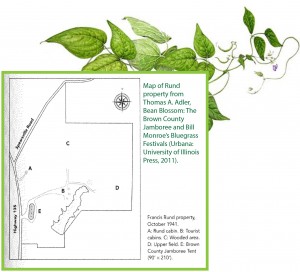 Just before the Jamboree launched, locals Francis and Mae Rund had been making improvements to their nearby property and building cabins with some sort of tourism-related business in mind as early as August 1940. By the summer of 1941, as the large crowds coming to the Jamboree were causing traffic and parking problems and more seating was needed at the outdoor venue, the Runds saw an opportunity to construct a permanent building (as opposed to a tent) so the programs could continue be held in the winter. Construction began in October. The barn-like building was funded by residents and was to seat 2,500 attendees. On October 23, 1941, the Brown County Democrat reported:
Just before the Jamboree launched, locals Francis and Mae Rund had been making improvements to their nearby property and building cabins with some sort of tourism-related business in mind as early as August 1940. By the summer of 1941, as the large crowds coming to the Jamboree were causing traffic and parking problems and more seating was needed at the outdoor venue, the Runds saw an opportunity to construct a permanent building (as opposed to a tent) so the programs could continue be held in the winter. Construction began in October. The barn-like building was funded by residents and was to seat 2,500 attendees. On October 23, 1941, the Brown County Democrat reported: The shows during the Rund decade (1941-51) generally featured a variety show format hosted by an emcee which included comedic performers as well as music. However, the country and “hillbilly” music was always the main draw. Adler writes, “Brown County Jamboree shows were professional, fast paced, and entertaining. From the beginning, the music, comedy, and ambience of the site combined to present a nostalgic and entertaining whole.” The Indianapolis Star on August 10, 1941 described the Jamboree as “a co-operative program providing real, homespun talent, rail-fence variety of music and frivolity . . . old fiddlers and rural crooners, who would sing and warble Brown county ballads brought over the mountains by their pioneer ancestors.” The Indianapolis Times noted October 10, 1941 that in addition to “singing and dancing” the Jamboree included “vaudeville skits.” The Runds ran large advertisements for the Jamboree in the local newspaper and partnered with nearby radio stations, notably WIRE and WFBM, Indianapolis. On October 23, 1941, the Brown County Democrat reported that the Indianapolis radio station WIRE referenced the Jamboree many times during its programs.
The shows during the Rund decade (1941-51) generally featured a variety show format hosted by an emcee which included comedic performers as well as music. However, the country and “hillbilly” music was always the main draw. Adler writes, “Brown County Jamboree shows were professional, fast paced, and entertaining. From the beginning, the music, comedy, and ambience of the site combined to present a nostalgic and entertaining whole.” The Indianapolis Star on August 10, 1941 described the Jamboree as “a co-operative program providing real, homespun talent, rail-fence variety of music and frivolity . . . old fiddlers and rural crooners, who would sing and warble Brown county ballads brought over the mountains by their pioneer ancestors.” The Indianapolis Times noted October 10, 1941 that in addition to “singing and dancing” the Jamboree included “vaudeville skits.” The Runds ran large advertisements for the Jamboree in the local newspaper and partnered with nearby radio stations, notably WIRE and WFBM, Indianapolis. On October 23, 1941, the Brown County Democrat reported that the Indianapolis radio station WIRE referenced the Jamboree many times during its programs.