There was an early route though Indiana that is mostly forgotten today. It was known as the Lafayette Trace in Hamilton County, but as the Strawtown Trace in other counties. Voss Hiatt, a historian in Hamilton County, spent several years researching it, but was unable to publish anything definitive. A statewide effort may be required to establish the significance of the route.
The trail ran from the Whitewater Valley, up to the White River and paralleling it until crossing at Strawtown, and then heading northwest to the Wea and Wildcat prairies on the Wabash River. It probably began as a prehistoric game trail, used by elk and other migratory animals headed for the prairie pastures. Early Native Americans eventually followed the game and established settlements along the trail. Traces of those settlements, in the form of mounds, can be found at New Castle, Anderson, and Strawtown. Europeans began using the trail possibly as early as 1717 to get to the fur trading post of Fort Ouiatenon.
At the site of Strawtown in Hamilton County, a trail going north-south crossed the Lafayette Trace. This went to the Miami Indian town of Kekionga (Fort Wayne). Although north-central Indiana was Miami territory, the Lenape (Delaware) tribe had negotiated a treaty with them and established a town at Strawtown by the 1790’s. Sometime around 1800, a member of the Brouillette family of Vincennes allegedly became the first fur trader to establish a post there. As settlement increased, the traffic increased. The trail would have been the route that Tecumseh used when he would travel from the Delaware village at Anderson to the Tippecanoe River, an area that would become Prophetstown and the site of the Battle of Tippecanoe.

In the 1820’s, the trail was used by settlers heading into the territory opened up by the 1818 Treaty of St. Mary’s. The Brookville land office was established at one end of it. Sandford Cox describes traveling on the trail as a young boy in 1824 in his book “Recollections of the Early Settlement of the Wabash Valley.”
The trail was eventually replaced by roads created by Internal Improvement Act of 1836. County seats had been established and new roads were designed to connect them. Since the Lafayette Trace was not an official road, it’s not on the earliest maps. It starts appearing in the 1840’s, but is gone in many places by the 1880’s. The land had been sold for farming and had been plowed under. By the 1930’s, part of the trail was erroneously called the “Conner Trail,” although it was long established by the time William Conner used it. This notion was put forth in the book “Sons of the Wilderness.”
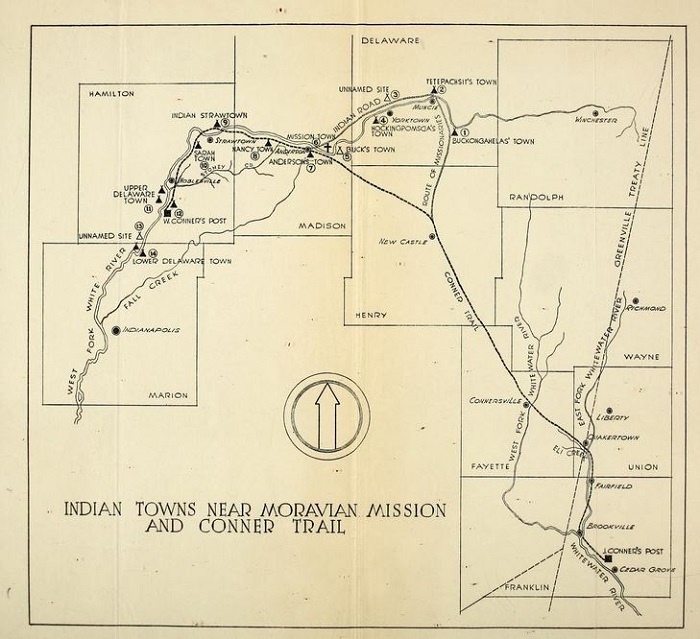
Not much is known about the trail after it left Hamilton County. Evidently, part of it split off to go to Thorntown. It would be a worthwhile project to identify and mark the old route.
Learn more about the area via Ball State University’s Archaeological Resources Management Service reconnaissance report.
