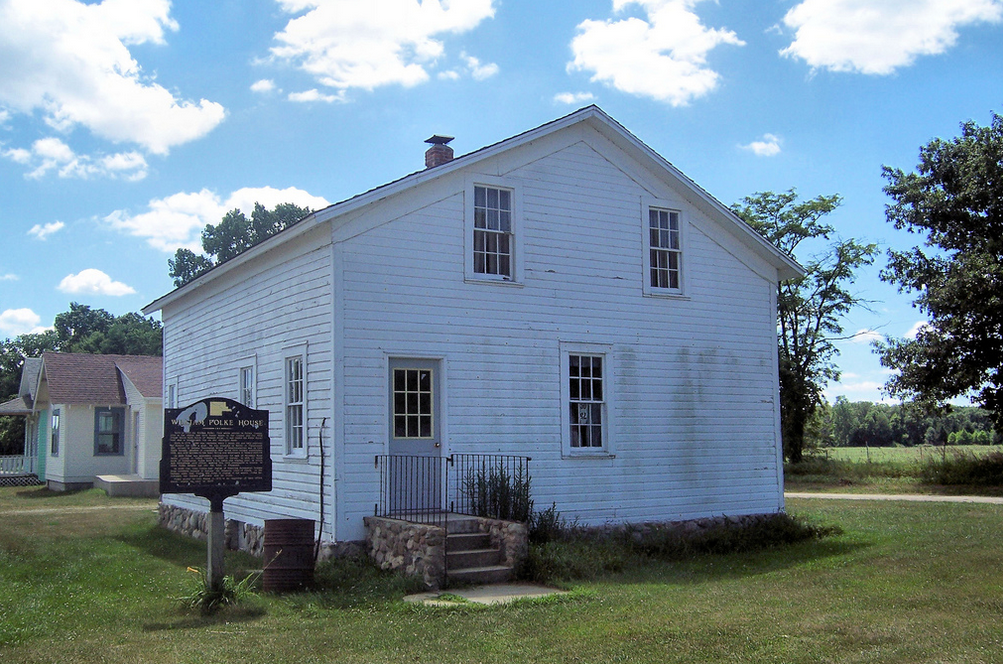
William Polke was born on September 19, 1775, in Brooke County, Virginia. As a boy in 1782, he was captured by raiding Native Americans, along with his mother and three sisters. Handed over to the British at Detroit, the family was held as prisoners for a year before being released in 1783 at the end of the American Revolutionary War.
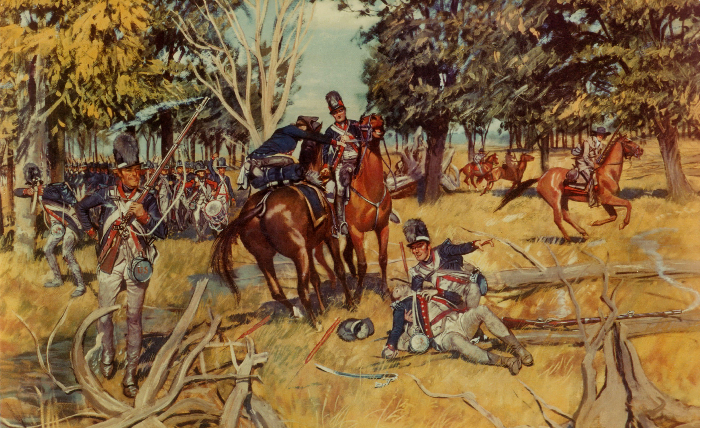
Later the Polke family moved to Knox County, Indiana, and as an adult, William established a military career. He was with Anthony Wayne at the Battle of Fallen Timbers, helped build the original stronghold at Fort Wayne, and was wounded during the Battle of Tippecanoe. In 1814 he served as a Knox County associate circuit court judge and won election to the Territorial Legislature. Polke became one of 43 delegates to the Constitutional Convention responsible for writing Indiana’s first state constitution in 1816.

He served two terms as the state senator of Knox County, but lost his bid for Lieutenant Governor in 1822, apparently ending his quest for elective office. From 1824 to 1825, Polke was a missionary teacher in Michigan among the Ottawa Indians. In 1830, he was appointed by an act of the Indiana General Assembly as one of the three commissioners for the construction of the Michigan Road. Polke served a critical role in the success of that project, which established a road extending from the Ohio River to Lake Michigan.

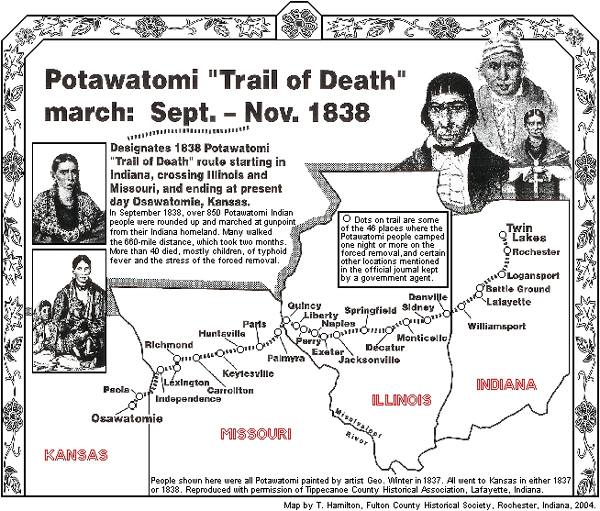
During 1838, Superintendent Emigration of Indians, Able C. Pepper, assigned Polke as a conductor of the Potawatomi peoples’ removal from their northern Indiana homeland on their grueling march to Kansas. Polke was instrumental in the removal of the Potawatmi in Indiana via a forced march of over 800, known as “The Trail of Death.” According to The History Museum, at Sandusky Point, Illinois command of the group of Native Americans was turned over to Polke. Along with “Father Petit, and an escort of fifteen men continued with the broken tribe to their destination on the Osage River in Kansas. The journey required about two months with the cost the lives at one-fifth of the tribe. A few Potawatomies remained in Indiana scattered on small reservations in various parts of the State.”
Paul Wallace Gates noted in The John Tipton Papers that Polke, “was convinced that his prompt action had prevented bloodshed between the two races. That he regretted the haste, the lack of preparation, and the suffering is equally clear. And once they reached Kansas he was certain the tribe would be protected . . . from the encroaching aggression.”
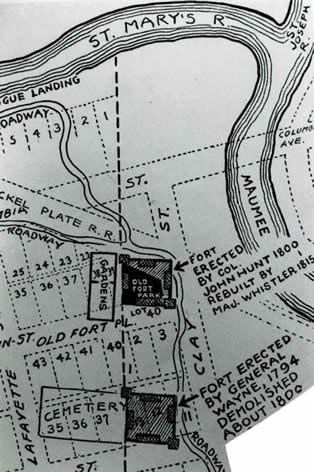
In 1841 President William Henry Harrison, in recognition of patriotic services, appointed Polke to serve at Fort Wayne as register of the land office. When Polke died, his April 29, 1843 the Fort Wayne Sentinel obituary ends with these lines: “He was buried with military honors; and a large concourse of citizens followed his remains to their last camping ground.” However, the cemetery name is not mentioned, creating questions about the location of his remains.
In 1860, the interred in Fort Wayne’s Broadway Cemetery (present-day McCulloch Park) were to be removed and re-interred in Fort Wayne’s Lindenwood Cemetery. Today, only one grave from its days as a cemetery is marked in McCulloch Park and that is Indiana’s seventh Governor Samuel Bigger. For years, questions persisted as to whether or not all the burials were found, and surviving family members located for approval to conduct the graves’ transferred. Since there is no record of Polke having been removed to Lindenwood, it was thought he was interred in McCulloch Park.
However, during a research project conducted to identify the burial site of each of the Constitutional Convention delegates, Indiana State Archivist, Jim Corridan led an effort and identified Polke’s long forgotten grave located, “in an early Fort Wayne cemetery.” Through a diligent search of records in Polke’s estate filed at the County Clerk’s office by SuzAnn Runge, Corridan has been able to confirm that William Polke, in fact, is interred in the Old Broadway Cemetery.
Learn how to attend the Indiana Archives and Records Administration’s June 27 event, commemorating William Polke.