Jonathan Jennings was born in 1784 in New Jersey, the sixth child of Jacob and Mary Jennings. His father was a physician and minister. The future first governor of the State of Indiana grew up in western Pennsylvania. He moved to the Indiana Territory at age 22, settling first in Jeffersonville, where he began a law practice. In 1807, Jennings moved to Vincennes, capital of the territory. There, he clerked for the land office, the General Assembly of the Indiana Territory, and for Vincennes University. An incident at the the university between Jennings and Territorial Governor William Henry Harrison and his supporters, prompted Jennings to leave Vincennes. In search of a more hospitable residence and career, he returned to Clark County and settled in Charlestown by 1809.
Jennings’ move would prove to be very timely for his political ambitions. Congress separated the Illinois Territory from the Indiana Territory, which lessened Governor Harrison’s political influence. Furthermore, Congress mandated that the Indiana Territory’s delegate to Congress be popularly elected, as opposed to elected by the territorial legislature.

While Jennings was an outsider to Harrison’s clique, he was extremely personable and a great campaigner. His outsider status was also relatable to the population in the eastern counties, who resented the patriarchal political power structures in Vincennes. Indiana historian William Wesley Woollen described Jennings’ appeal, noting he was “a man of polished manners . . . he was always gentle and kind to those about him. He was not an orator, but he could tell what he knew in a pleasing way.”
An oft-repeated story about Jennings illustrates his political populism in contrast to his patrician political opponents. Author John Bartlow Martin described the scene this way:
Jennings’s opponent, a Harrison man, arrived during a logrolling [at a Dearborn County farm], chatted at the farmhouse a short time, then rode away. But Jennings, arriving next day, pitched into the logrolling and when it was done, tossed quoits and threw the maul with the men, taking care to let them beat him. He was a natural politician, the kind the Hoosiers lived, almost the original model of the defender of the people against the interests.

In 1809, only white, property-holding men could vote in the Indiana Territory. At age 25, Jennings ran for Congress and defeated an older and better politically connected candidate. Jennings won re-election in 1811, 1812, and 1814. As a territorial delegate, and not a fully vested member of Congress, Jennings could not vote on legislation. However, his role was very important to Indiana’s road to statehood as he advocated for legislation from Indiana Territory constituents, including petitions for statehood. The first statehood petition was sent to Jennings in 1811, which Congress denied on account of the territory’s population not yet reaching 35,000. The United States had more pressing problems in subsequent years, most notably the War of 1812, which raged until 1814. The war disrupted the business of Congress when the British Army burned the U.S. Capitol and the White House.
A year after the Treaty of Ghent ended the war, Congress was back to lawmaking. On December 28, 1815, Jennings introduced another territorial petition for statehood. This time the U.S. House leadership referred the petition to a committee and named Jennings as chairman. A week later the committee reported a bill, which eventually passed. On April 19, 1816, President James Madison signed it into law. Known as the Enabling Act, the legislation authorized residents of the Indiana Territory to hold a Constitutional Convention. On June 10, 1816, convention delegates convened in Corydon to draft a constitution. Jennings was one of the delegates. He was so esteemed by his peers that he became president of the convention. The resulting document borrowed from previous state constitutions, but reinforced a lot of democratic ideals. Although there was a system of checks and balances, most of the power lay with the elected representatives, which many people viewed as being closer to the people than the governor. The constitution also allowed for universal white, adult male suffrage, gave voters the right to call for a new constitution, recommended a state-supported education system, prohibited establishment of private banks, and prohibited slavery.
Indiana held its first state elections in August 1816, and Jennings won the gubernatorial election over Territorial Governor Thomas Posey. Jennings was then only thirty-two years old. For the next six years he would serve as Indiana’s first executive. Keep in mind, under the 1816 Constitution, a governor’s powers were limited, and he could not set legislative agendas. He could make appointments, including judges, and could also sign or veto legislation.
According to Carl E. Kramer’s profile of Jennings in The Governors of Indiana, the state’s first governor faced the daunting challenge of “placing Indiana on a sound financial footing, implementing a court system, and developing rudimentary educational and internal improvements systems, while also attempting to prevent government from becoming so burdensome that it obstructed personal advancement and enterprise.” Kramer noted that as governor, Jennings concentrated on “organizing an educational system that reached from the common schools to a state university; creating a state banking system; preventing illegal efforts to capture and enslave blacks entitled to their freedom; organizing a state library; and developing a plan of internal improvements.” His limited success in accomplishing these, was “as much a reflection of the governor’s limited powers and the state’s impoverished financial condition as it is upon his political skills and knowledge of the issues.”

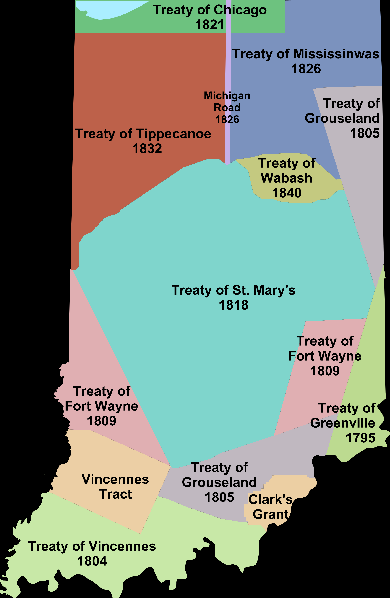
His most far-reaching action during the time he served as governor actually occurred when he was not acting in that capacity. In 1818, Jennings served as a treaty negotiator on the Treaty of St. Mary’s which obtained title to a large part of land from the Miami Indians. As an aside, while Jennings was absent from Corydon during these negotiations, Lieutenant Governor Christopher Harrison tried unsuccessfully to take power and remove Jennings from office.
The low-light of Jennings time as governor came in 1820 as the State Bank teetered and eventually collapsed. As historian Dorothy Riker noted, “Jennings was severely criticized for his failure to supervise the Bank and his refusal to instigate and investigation earlier.”
In 1822, with only months left to serve in his second term, Jennings resigned as governor so that he could return to Congress, where he served from 1822-1831. Internal improvements like roads and canals were hallmark pieces of legislation at this time in American history, especially under President John Quincy Adams (1825-1829) and his proto-Whig Party (Adams/Anti-Jackson) adherents like Jennings. For Jennings, internal improvements were a way for Indiana to advance, economically by allowing for Indiana’s agricultural goods to make it more easily to markets, and for finished goods to make their way into the state. Good roads and canals would also encourage immigration into the state, especially along the National Road, and would facilitate communication with other parts of the nation. Because of Jennings advocacy of better transportation networks, it is fitting that the Indiana Department of Transportation designated this section of I-65 as the “Governor Jonathan Jennings Memorial Highway.”

According to Woollen, Jennings lost his congressional seat in 1830 due, in part, to his drinking problem. He retired to his Charlestown farm, where he died on July 26, 1834. Historians have conflicting views on Jennings legacy. He was not an activist executive, which present-day observers have come to expect when rating their leaders. However, he was an incredibly popular politician. He played important leadership roles in Indiana reaching statehood, including at the Constitutional Convention. As for his role as governor, it is important to think about his service in the context of the time. Hoosiers at the time did not want an aristocratic leader like William Henry Harrison. Rather, Jennings set a precedence as the first governor which sought to honor the autonomy and democratic values of pioneer Hoosiers.