The turn of the twentieth century was marked by record rates of family desertion in the United States, especially among eastern European Jewish immigrant families. A family was considered deserted if the male head of household withheld his wages or if he were to leave and no longer offer monetary support.[i] Jewish women who were deserted by their husbands were left in a particularly vulnerable and liminal state; they were neither widowed nor wed, yet Jewish law dictated that they were bound to their spouse until a divorce could be obtained.[ii]
Rates of family desertion, or the act of a primary caregiver leaving their family without providing support, have been shown to significantly rise in times of mass migration, which made it a pressing issue as over two million eastern European Jews immigrated to the United States at the turn of the twentieth century.[iii] While it is not known how many women were victims of desertion during this migration period, data from Jewish philanthropic organizations suggest it affected a large number of women.[iv] Between 1900 and 1922, approximately 15% of aid distributed by Jewish charitable agencies in the United States was granted to deserted women and their families, most of which was granted to Jewish women and families due to their large migration numbers.[v]
The Struggles of Immigration
The pattern of Jewish migration was typically that of a family migration, though families were often disrupted throughout the process.[vi] The head of the household, who was generally the husband, would emigrate alone, later to be joined by their kin. The men would arrive in their new country, settle down, find a job, and build up the necessary funds to bring the remaining relatives to join them, typically in two to three years’ time.[vii] This separation placed great stress on families.
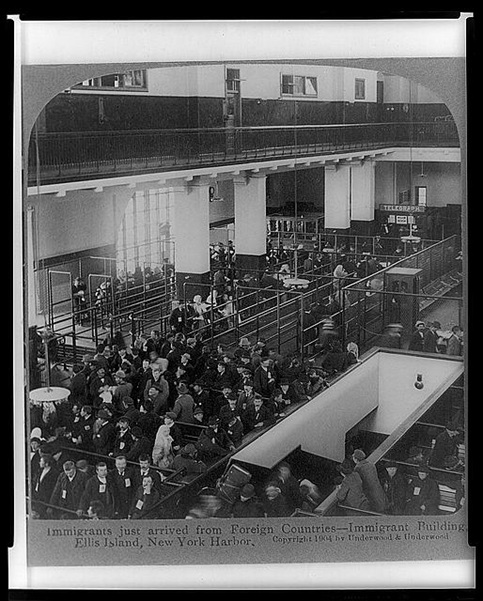

Upon arriving to the United States, the search for employment, long working hours, health issues, and poor living conditions took a heavy toll on immigrants. On top of these stressors, many Jewish immigrants did not know how to read or write, and therefore had to rely on the aid of others if they wished to write home. These limitations made contacting relatives difficult, if not impossible. Families were often left with silence for months or years at a time, waiting to hear that their loved one had made it to the United States, and that they were actively working towards a reunion in the New World.[viii]
Following immigration, many families experienced new tensions and challenges within the home, which threatened the stability of family units. Members of families, who were separated during the emigration process, often felt alienated from each other and their relationships became irreparable.[ix] American influences encouraged men to act more aggressively if they wished to thrive in their new capitalist country, while women were expected to behave in more submissive manners than the roles which they had previously assumed, drastically altering family dynamics.[x] Marriages established in eastern Europe were rarely the product of love and were more often based on tradition; after living in the United States for an extended period of time, it was not uncommon for married couples to simply drift apart to the point of incompatibility or to develop romantic relationships with new partners.[xi] Generational conflict, typically related to irreligiousness of children, placed stress on household relationships and generated feelings of shame, humiliation, and disconnectedness.[xii] As a result of the new tensions in their relationships, many men did not seek divorces and, instead, turned towards desertion as a solution. This became such an occurrence that National Desertion Bureau president Walter Liebman labeled the process a “poor man’s divorce.”[xiii]
For some men, however, desertion was an attempt to assist their families. They would leave their families behind to better their conditions and earn funds. By leaving without a word, though it caused much distress, many husbands felt confident that charities would offer assistance. Samuel Sorbel, a lawyer who worked on desertion cases in Indiana in 1908, reported in an August 29th, 1908 Evansville Courier and Press article that deserters often told him: “Well, as long as I was here the charities wouldn’t do anything for them, and I knew that if I went away they would feed the wife and children and keep a roof over their heads.” For these men, desertion felt like a mercy to their loved ones. By leaving their families and seeking employment in a different city, the men could save up money for their return home while local charities supported their families in the meantime. This outcome was preferable to making the difficult choice of whether to pay rent or to put food on the table with an inadequate income. Unfortunately, the aid given to deserted families during the man’s absence was not as grand as many men had hoped; Sorbel stated he had never met a case of desertion that was without destitution.
The Role of Philanthropic Organizations and the National Desertion Bureau

Jewish charitable organizations sought to assist deserted women in a number of ways. When working with a deserted family, most organizations hoped to locate missing husbands and reunite them with their families. This process, however, could take months, or even years, to complete. In the meantime, Jewish charitable organizations attempted to assist deserted families through financial and material charity, though the support was generally minimal.[xiv] The relationship between charitable organizations and immigrants—both the husbands and the wives— was tense and, at times, discriminatory and victim-blaming.
Anti-desertion campaigns were typically organized and managed by middle-class men who saw themselves as the protectors of women and children, many of whom were German Jewish Americans.[xv] These reformers had relative control over the public narrative surrounding desertion, spinning deserters as burdens to society. According to a May 12, 1920 Fort Wayne Sentinel article, deserters were “the arch villains of society, the primary cause of all social distress, the perpetrators rather than the victims of all social evils.” These reformers attempted to separate their own male identities from those of deserters by challenging the latter’s manhood, often painting working-class deserters as cowardly, unambitious, and incapable of becoming proper breadwinners for their families. Working-class families never fully adopted the ideal of having a male breadwinner due to their low wages, but this concept was of central importance to the middle-class’s understanding of manhood.[xvi]
Upon seeking external assistance, deserted women became subject to much public scrutiny and judgement. Philanthropic organizations consistently looked to categorize the people to whom they provide aid—a person’s marital status merited how much, if any, assistance should be granted to their case.[xvii] Immigrants who requested aid were studied for shortcomings or plausible blame for their being deserted. Nearly any characteristic or action of a woman could be twisted into rational for her circumstances; some women were criticized for their inability or unwillingness to forgo their traditions and customs to “Americanize” and assimilate to American customs, while others became too indulgent in material consumption and American trends.[xviii]

In Indianapolis, the Jewish Welfare Federation (JWF) of Indianapolis provided a great deal of support to deserted families. One such case of support was that for the Cohen family. On August 17, 1914, applied for aid from the JWF of Indianapolis after Morris Cohen deserted her and six of their seven children. Mr. Cohen had left for St. Louis, taking along one of their sons, Isidor. By the time the Federation had made contact with the United Jewish Charities in St. Louis, the two Cohens had relocated once again with no indication of their destination.[xix]
Just over a year later on November 15, 1915, the JWF discovered that Morris and Isidor had moved to in Birmingham, Alabama, where the latter was employed at a department store. Isidor encouraged the family to join the two in Birmingham, but Mrs. Cohen* was hesitant to do so; Morris had habitually moved from city to city the prior fourteen years, thus she questioned the finality of the move. Additionally, elder children were employed in positions they did not wish to lose, her three youngest children were well settled in school, and one was ill with pneumonia. The Federation contacted Isidor’s employers, Birmingham’s Federation of Jewish Charities, and a local Rabbi to gauge what would be the best action for the Cohen family. Following the correspondence, the JWF of Indianapolis agreed with Mrs. Cohen and believed it would be best for the family to stay in Indianapolis, and for her husband to send monetary support or to return to the city. Records suggest Morris obliged with the latter, and the family did not require further support from the JWF of Indianapolis.[xx]
Philanthropic organizations like the JWF quickly became inundated by the sheer number of women seeking assistance during the spike in immigration in the early 1900s. In 1909, the United Hebrew Charities reported that for every three relief applications received by widows, two were received from deserted women.[xxi] Desertion became such a strain on charitable organizations and state services that Jewish Americans feared, “Mah yomru hagoyim” (What will the gentiles say?”).[xxii] This concern contributed to the development of the United Hebrew Charities’ National Desertion Bureau (NDB) in 1905. The Bureau worked to locate deserters and return them home, or, if a deserter was unwilling to return, to negotiate support on behalf of his family.[xxiii] These negotiations would be finalized in front of a judge in the “Court of Tears,” aptly named due to the emotional distress associated with the hearings.

The NDB corresponded with local charities, organizations, religious institutions, and employers when attempting to locate missing husbands, much like the JWF had done in the case of the Cohen family. The NDB would gather the husband’s name, date of disappearance, physical description, photographs, and additional information that might be of assistance in locating him. Case descriptions and photos were frequently published in Yiddish newspapers in the cities of New York, Chicago, Cleveland, Montreal, and Toronto—cities to which deserters often fled. These postings became part of the newspapers’ “Gallery of Missing Husbands,” which pleaded for members of the public to inform the NDB if a deserter was found. These public tips were then used to apprehend the men so a solution could be found to satisfy both him and his family. It served a secondary purpose of attempting to prevent desertion; the gallery made it clear to men who read the paper that if they were to desert their families, they could be publicly humiliated.[xxiv]
Neglected Children

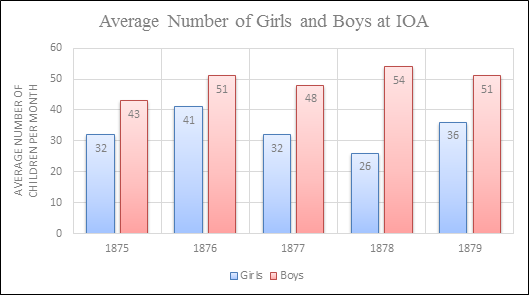
Desertion not only took a toll on immigrant wives, but it also deeply affected their children. For every ten families which applied for relief from charitable organizations, one came from a deserted family. Additionally, one of four children committed to orphanages at the time had been deserted by one, or both, of their parents; after desertion, some women felt that giving up their child was the only option as they struggled to provide adequate care and daily necessities.[xxv] Children who remained in the home felt the effects of desertion through parental neglect and the need to work to help the household. These stressors led deserted children to struggle with emotional instability and/or delinquency later in their lives.[xxvi]
This is precisely what happened to the Behrman family Louis Behrman deserted his wife and children in the summer of 1905, leaving them behind in Indianapolis while he took refuge in Chicago. found herself without support from her husband and responsible for ten children, the youngest of which was three years old and the eldest twenty years old. She and two of her children attempted to support the family, making a total of $12.50 a week. Trying to ease the burden on their family, Nathan and Robert Behrman, twelve and eight years old respectively, were caught stealing and begging and were committed to a day nursery for seven months as consequence, adding yet another stressor to the family’s circumstances. The JWF assisted the Behrman family until the husband could be found. Louis Behrman was arrested for contributing to their delinquency, received a fine, and was sentenced to a workhouse. He returned to his family after serving his sentence. Charitable organizations like the JWF of Indianapolis provided much needed services to the struggling families affected by desertion, providing resources, support, and a chance for justice against deserters.[xxvii]

A History of Hardship
Early-twentieth-century Jewish immigrants were not alone in their hardships. Desertion and family neglection were an issue for many immigrants, regardless of their origin and background. Catholics, for example, addressed issues of desertion through the Society of St. Vincent de Paul, but Catholic charities aided deserted families on a case-by-case basis. Jewish charities, on the other hand, identified desertion as a greater social problem in need of fixing and established national connections, including those with charities and businesses across the country, with which to address it. This unique approach stemmed from the fear of American Jews, who believed widespread discussion of family desertion in the Jewish community could encourage new waves of antisemitism.[xxviii]
Despite the fact that immigrants founded the United States, the country has rarely welcomed newcomers with open arms. There is a common misconception in the twenty-first century that European immigrants in the twentieth century became Americans with ease, persevering and prospering in a growing economy. Historically, however, adversities plagued every step of the immigration process, and fear of how these challenges were perceived by the greater public caused much stress in both existing and developing communities. The same can be said of immigrants today. By recognizing this historic trend, America has the opportunity to reduce this burden and provide better support to future immigrants. It is clear through the efforts of organizations like the National Desertion Bureau that creating specialized departments for societal problems can help those in need, and doing so would positively impact both native and foreign-born Americans.
* The author was unable to locate the first name of Mrs. Cohen or Mrs. Behrman.
For a bibliography, click here.
Notes:
[i] Reena Sigman Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband Who Is In New York City:’ Husband Desertion in the American Jewish Immigrant Community 1900-1926,” Jewish Social Studies 44, no. 1 (1982): 4.
[ii] Anna R. Igra, Wives Without Husbands: Marriage, Desertion, & Welfare in New York, 1900-1935 (Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2007), 2.; Gur Alroey, “‘And I Remained Alone in a Vast Land:’ Women in the Jewish Migration from Eastern Europe,” Jewish Social Studies 12, no. 3 (2006): 62; Bluma Goldstein, Enforced Marginality: Jewish Narratives on Abandoned Wives (Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2007), 2-6.
[iii] Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’” 60; Lindsey Mintz, “A Century of Jewish Education in Indianapolis: 1860 to 1960,” Indiana Jewish History 35, no. 1 (2003): 14-15.
[iv] Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’” 60.
[v] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 5.
[vi] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 10; Paula E. Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” in Jewish Women in America: An Historical Encyclopedia, ed. Paula E. Hyman (London: Routledge, 1998), 346-347.
[vii] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 10-11; Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’” 59-60; Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” 346-347.
[viii] Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’” 62; Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” 348-349.
[ix] Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’”59; Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” 349.
[x] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 3-4.
[xi] Alroey, “‘I Remained Alone,’” 286-287.
[xii] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 3-5.
[xiii] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 43; Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 4.
[xiv] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 7; Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” 346-347; Caroline Light, “‘A Predominant Cause of Distress:’ Gender, Benevolence, and the ‘Agunah’ in Regional Perspective,” American Jewish History 97, no. 2 (2013): 166-167.
[xv] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 3-4; Fridkis, “Desertion,” 289-291.
[xvi] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 3-5.
[xvii] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 2, 78-81; Light, “‘A Predominant Cause of Distress,’” 167.
[xviii] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 5-6; Light, “‘A Predominant Cause of Distress,’” 166-167.
[xix] Correspondence regarding Morris Cohen, 1913-1916, Jewish Federation of Indianapolis Records, 1880-() Collection (M0463, Box 264, Folder 40), Indiana Historical Society, Indianapolis, IN.
[xx] Correspondence regarding Morris Cohen, 1913-1916, Jewish Federation of Indianapolis Records, 1880-() Collection (M0463, Box 264, Folder 40).
[xxi] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 1.
[xxii] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 15.
[xxiii] Hyman, “Eastern European Immigration,” 349.
[xxiv] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 11; Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 23-26. Goldstein, Enforced Marginality, 92-100.
[xxv] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 8.; Goldstein, Enforced Marginality, 112-114.
[xxvi] Friedman, “‘Send Me My Husband,’” 8.
[xxvii] Correspondence regarding Louis Behrman, 1905-1912, Jewish Federation of Indianapolis Records, 1880-() Collection (M0463, Box 264, Folder 26), Indiana Historical Society, Indianapolis, IN.
[xxviii] Igra, “Wives Without Husbands,” 9.